Abstract
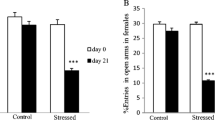
The prenatal stress during pregnancy has a wide variety of negative effects on the offspring behaviors. As such, in the present study the effect of prenatal immobilization stress was investigated on the brain BDNF level, spatial memory, anxiety and depression-like behavior in the F1 generation female NMRI mice. Twenty female pregnant mice were randomly allocated to stress and control groups (n = 10/group). The stress group was placed in PVC cylinders (2.5 cm in diameter and 20 cm in length) for one hour/day until the 15th day of pregnancy. The female F1 offspring was nursed by their mothers until reaching 25–30 g (9–10 weeks) which was tested for spatial memory, anxiety and depressive-like behavior using Barnes Maze, elevated plus-maze and forced swimming test, respectively. Also, the brain BDNF level was assessed by the ELISA method. Mice that underwent prenatal restraint stress exhibited impaired spatial memory in the Barnes Maze, which the time and distance to achieve the target hole and the number of errors in the female adult offspring increased than the control group. In the elevated plus-maze, the animals that underwent prenatal restraint stress spent less time in the open arms of the maze and reduced entering the open arms, compared to the control group. In addition, stress caused a significant decrease in swim time and a significant increase in float time for the female adult offspring compared to the control group. The brain BDNF concentration also decreased significantly in the stress group compared to the control group. This data suggests that prenatal stress may impair spatial memory and induce anxiety and depressive-like behavior in the adult offspring female mice via reducing brain BDNF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McEwen, B.S., Dialogues Clin. Neurosci., 2006, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 367.
McEwen, B.S., Bowles, N.P., Gray, J.D., Hill, M.N., Hunter, R.G., Karatsoreos, I.N., and Nasca, C., Nat. Neurosci., 2015, vol. 18, no. 10, pp.1353.
Glover, V., Adv. Neurobiol. 2015, vol. 10, pp. 269–283.
Abe, H., Hidaka, N., Kawagoe, C., Odagiri, K., Watanabe, Y., Ikeda, T., Ishizuka, Y., Hashiguchi, H., Takeda, R., Nishimori, T., and Ishida, Y., Neurosci. Res. 2007, vol. 59, pp. 145–151.
Benoit, J.D., Rakic, P., and Frick, K.M., Behav. Brain Res., 2015, vol. 281, pp. 1–8.
Boersma, G.J. and Tamashiro, K.L., Neurobiol. Stress, 2015, vol. 1, pp. 100–108.
Markham, J.A., Taylor, A.R., Taylor, S.B., Bell, D.B., and Koenig, J.I., Front. Behav. Neurosci., 2010, vol. 4, pp. 173–176.
Popoli, M., Yan, Z., McEwen, B.S., and Sanacora, G., Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2012, vol. 13, no. 1, pp. 22–37.
Maccari, S., Krugers, H.J., Morley-Fletcher, S., Szyf, M., and Brunton, P.J., J. Neuroendocrinol., 2014, vol. 26, pp. 707–723.
Wingenfeld, K. and Wolf, O.T., CNS Neurosci. Ther., 2011, vol. 17, pp. 714–722.
Brunton, P.J. and Russell, J.A., J. Neuroendocrinol., 2010, vol. 22, pp. 258–271.
Koehl, M., Darnaudery, M., Dulluc, J., Van Reeth, O., Le Moal, M., and Maccari, S., J. Neurobiol. 1999, vol. 40, pp. 302–315.
Miranda, A. and Sousa, N., Brain Behav., 2018, vol. 8, p. e00920.
Buss, C., Davis, E.P., Shahbaba, B., Pruessner, J.C., Head, K., and Sandman, C.A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2012, vol. 109, no. 20, pp. E1312–E1319.
Pryce, C.R., Brain Res. Rev. 2008, vol. 57, no. 2, pp. 596–605.
Rogalska, J., Vita Horm. 2010, vol. 82, pp. 391–419.
Ratajczak, P., Kus, K., Murawiecka, P., Słodzińska, I., Giermaziak, W., and Nowakowska, E., Acta Neurobiol. Exp., 2015, vol. 75, no. 3, pp. 314–325.
Zohar, I., Shoham, S., and Weinstock, M., Europ. J. Neurosci., 2016, vol. 43, p. 590e600.
Taliaz, D., Loya, A., Gersner, R., Haramati, S., Chen, A., and Zangen, A., J. Neurosci., 2011, vol. 31, no. 12, pp. 4475–4483.
Autry, A.E. and Monteggia, L.M., Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, vol. 64, p. 238e258.
Podsevatkin, V.G., Kiriukhina, S.V., Podsevatkin, D.V., Podsevatkina, S.V., and Blinov, D.S., Eksp. Klin. Farmakol., 2008, vol. 71, pp. 22–25.
Zhang, S.Y., Wang, J.Z., Li, J.J., Wei, D.L., Sui, H.S., Zhang, Z.H., Zhou, P., and Tan, J.H., Biol. Reprod., 2011, vol. 84, pp. 672–681.
Ehteram, B.Z., Sahraei, H., Meftahi, G.H., and Khosravi, M., Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol., 2017, vol. 60, p. e17160607.
Lucassen, P.J., Pruessner, J., Sousa, N., Almeida, O.F., Van Dam, A.M., Rajkowska, G., Swaab, D.F, and Czéh, B., Acta Neuropathologica. 2014, vol. 127, no. 1, pp. 109–135.
Markham, J.A., Taylor, A.R., Taylor, S.B., Bell, D.B., and Koenig, J.I., Front. Behav. Neurosci., 2010, vol. 25, pp. 173–176.
Yang, J., Han, H., Cao, J., Lingjiang, L., and Xu, L., Hippocampus, 2006, vol. 16, pp. 431–436.
Salomon, S., Bejarm C., Schorer-Apelbaum, D., and Weinstock, M., J. Neuroendocrinol. 2011, vol. 23, pp. 118–128.
Wu, J., Song, T.B., Li, Y.J., He, K.S., Ge, L., and Wang, L.R., Brain Res. 2007, vol. 1141, pp. 205–213.
Sierksma, A.S., Prickaerts, J., Chouliaras, L., Rostamian, S., Delbroek, L., Rutten, B.P., Steinbusch, H.W., and van den Hove, D.L., Neurobiol. Aging. 2013, vol. 34, pp. 319–337.
Matthews, S., Trends Endocrinol. Metab., 2002, vol. 13, pp. 373–380.
Wellberg, L., Seckl, J., and Holmes, M., Neurosci., 2001, vol. 104, pp. 71–79.
Benoit, J.D., Rakic, P., and Frick, K.M., Behav. Brain Res., 2015, vol. 281, pp. 1–8.
Shrager, Y., Bayley, P.J., Bontempi, B., Hopkins, R.O., and Squire, L.R., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, vol. 104, no. 8, pp. 2961–2966.
Krugers, H.J., Hoogenraad, C.C., and Groc, L. Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2010, vol. 11, pp. 675–681.
Kim, J.J. and Diamond, D.M. Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2002, vol. 3, pp. 453–462.
Cottrell, E.C. and Seckl, J.R., Front. Behav. Neurosci., 2009, vol. 3, pp. 19.
Levitt, N.S., Lindsay, R.S., Holmes, M.C., and Seckl, J.R., Neuroendocrinol., 1996, vol. 64, no. 6, pp. 412–418.
Van Lieshout, R.J. and Boylan, K., J. Psychiatry, 2010, vol. 55, pp. 422–430.
Walf, A.A. and Frye, C.A., Nature Protocols, 2007, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 322–328.
Glombik, K., Stachowicz A., Slusarczyk J., Trojan E., and Budziszewska B., Psychoneuroendocrinol., 2015, vol. 60, pp. 151–162.
Guan L., Jia N., Zhao X., Zhang X., and Tang G., Brain Res. Bull. 2013, vol. 99, pp. 1–8.
Akatsu, S., Ishikawa, C., Takemura, K., Ohtani, A., and Shiga, T., Neurosci. Res. 2015, vol. 101, pp. 15e23.
Palacios-García I., Lara-Vásquez, A., Montiel, J.F., Díaz-Véliz, G.F., Sepúlveda, H., Utreras E., Montecino M., González-Billault, C., and Aboitiz, F., PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10, p. e0117680.
Zhang, W. and Rosenkranzm, J.A., Neurosci. 2012, vol. 226, pp. 459–474.
Etkin, A., Functional Neuroanatomy of Anxiety: A Neural Circuit Perspective. In: Behavioral Neurobiology of Anxiety and Its Treatment, Stein, M.B. and Steckler, T., Eds., vol. 2, Springer-Verlag Berlin: Heidelberg, Germany, 2009, pp. 251–277.
Nuss, P., Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, vol. 11, pp. 165–175.
Licinio, J. and Wong, M.L., Molecular Psychiatry, 2002, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 519–519.
Dong, E., Dzitoyeva, S.G., Matrisciano, F., Tueting, P., Grayson, D.R., and Guidotti, A., Biol. Psychiatry, 2015, vol. 77, p. 589e596.
Yeh, C.M., Huang, C.C., and Hsu, K.S., J. Physiol., 2012, vol. 590, p. 991e1010.
Jia, N., Li, Q., Sun, H., Song, Q., Tang, G., Sun, Q., Wang, W., Chen, R., Li, H., and Zhu, Z., Neurochem-ical Res., 2015, vol. 40, no. 5, pp. 1074–1082.
Boersma, G.J., Lee, R.S., Cordner, Z.A., Ewald, E.R., Purcell, R.H., Moghadam, A.A., and Tamashiro, K.L., Epigenetics, 2014, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 437–447.
St-Cyr, S. and McGowan, P.O., Front. Behav. Neurosci., 2015, vol. 1, no. 9, pp. 1–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoudi, E., Sahraei, H., Bahari, Z. et al. Prenatal Immobilization Stress-Induced Spatial Memory, Depression and Anxiety-Like Behavior Deficit on the F1 Generation in the Female Mice: Possible Involvement of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Neurochem. J. 13, 201–209 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712419020065
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712419020065