Abstract
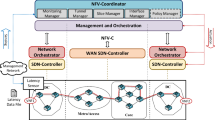
The current deployment of 5G networks in a way to support the highly demanding service types defined for 5G, has brought the need for using new techniques to accommodate legacy networks to such requirements. Network Slicing in turn, enables sharing the same underlying physical infrastructure among services with different requirements, thus providing a level of isolation between them to guarantee their proper functionality. In this work, we analyse from an architectural point of view, the required coordination for the provisioning of 5G services over multiple network segments/domains by means of network slicing, considering as well the use of sensors and actuators to maintain slices performance during its lifetime. We set up an experimental multi-segment testbed to demonstrate end-to-end service provisioning and its guarantee in terms of specific QoS parameters, such as latency, throughput and Virtual Network Function (VNF) CPU/RAM consumption. The results provided, demonstrate the workflow between different network components to coordinate the deployment of slices, besides providing a set of examples for slice maintenance through service monitoring and the use of policy-based actuations.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
NGMN Alliance 5G White Paper, Version 1.0, (2015)
G-PPP 5G Architecture White Paper, Version 2.0, (2017)
ETSI GS NFV-MAN 001 V1.1.1, (2014)
ONF TR-526, Applying SDN Architecture to Network Slicing, Issue 1, (2016)
Samdanis, K., Costa-Perez, X., Sciancalepore, V.: From network sharing to multi-tenancy: the 5G network slice broker. IEEE Commun. Mag. 54(7), 32–39 (2016)
Costa-Perez, X., Garcia-Saavedra, A., Li, X., Deiss, T., de la Oliva, A., di Giglio, A., Iovanna, P., Moored, A.: 5G-Crosshaul: an SDN/NFV Integrated Fronthaul/Backhaul transport network architecture. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 24(1), 38–45 (2017)
Ravindran, R., Chakraborti, A., Amin, S.O., Azgin, A., Wang, G.: 5G-ICN: delivering ICN Services over 5G Using Network Slicing. IEEE Commun. Mag. 55(5), 101–107 (2017)
Ye, Q., Li, J., Qu, K., Zhuang, W., Shen, X.S., Li, X.: End-to-end quality of service in 5G networks: examining the effectiveness of a network slicing framework. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 13(2), 65–74 (2018)
Munoz, R., Vilalta, R., Casellas, R., Martinez, R., Szyrkowiec, T., Autenrieth, A., López, V., López, D.: Integrated SDN/NFV management and orchestration architecture for dynamic deployment of virtual SDN control instances for virtual tenant networks. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 7, 62–70 (2015)
CogNet deliverable D2.2, “CogNet final requirements, scenarios and architecture”, (2017)
Neves, P., Cale, R., Costa, M.R., Parada, C., Parreira, B., Alcaraz-Calero, J., Wang, Q., Nightingale, J., Chirivella-Perez, E., Jiang, W., Schotten, H.D., Koutsopoulos, K., Gavras, A., Barros, M.J.: The SELFNET approach for autonomic management in an NFV/SDN networking paradigm. Int. J. Distrib. Sensor Netw. 12, 2897479 (2016)
G-PPP 5G Architecture White Paper, Version 3.0, (2019)
GPP TR 28.801, Study on management and orchestration of network slicing for next generation network, Version 15.1.0, (2018)
GPP TS 28.541: “Management and orchestration of networks and network slicing; NR and NG-RAN Network Resource Model (NRM); Stage 2 and stage 3”
ETSI GR NFV-IFA 015: “Network Functions Virtualisation (NFV) Release 3; Management and Orchestration; Report on NFV Information Model”
ETSI GR NFV-IFA 024: “Network Functions Virtualisation (NFV) Release 3; Information Modeling; Report on External Touchpoints related to NFV Information Model”
Montero, R., Pagès, A., Agraz, F., Spadaro, S.: Supporting QoE/QoS-aware end-to-end network slicing in future 5G-enabled optical networks, PW 2019, San Francisco (United States), 2–7 February 2019
ETSI Open Source MANO, “OSM VNF Onboarding Guidelines”, http://osm-download.etsi.org/ftp/Documentation/vnf-onboarding-guidelines/. Accessed 29 July 2019
ETSI Open Source MANO, OSM Release FIVE Technical Overview, 1st Edition, (2019)
ETSI TS 128 533 V15.0.0 (2018–2010), 3GPP TS 28.533 version 15.0.0 Release 15, “5G; Management and orchestration; Architecture framework”
ETSI GS NFV-SOL 005 V2.4.1 (2018–2002), “Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) Release 2; Protocols and Data Models; RESTful protocols specification for the Os-Ma-nfvo Reference Point”
Montero, R., Agraz, F., Pagès, A., Spadaro, S.: End-to-end Network Slicing in Support of Latency-sensitive 5G Services. In: 23rd Conference on Optical Network Design and Modeling, ONDM 2019, Athens (Greece), 13–16 May 2019
Gnocchi - Metric as a Service, Gnocchi 4.2.1.dev96 documentation. https://gnocchi.xyz/. Accessed 29 July 2019
Montero, R., Agraz, F., Pagès, A., Spadaro, S.,: Actuation Framework for 5G-enabled Network Slices with QoE/QoS Guarantees. In: 2019 21st International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Angers (France), pp. 1–4 (2019)
Mininet, https://mininet.org. Accessed 29 July 2019
Open Virtual Switch, Linux Foundation, https://www.openvswitch.org/. Accessed 29 July 2019
McKeown, N., et al.: OpenFlow: enabling innovation in campus networks. ACM Commun. Rev. 38(2), 69–74 (2008)
OpenDaylight, https://www.opendaylight.org. Accessed 29 July 2019
OpenStack, https://www.openstack.org. Accessed 29 July 2019
Open Source MANO, https://osm.etsi.org. Accessed 29 July 2019
Grafana Monitoring & Data Visualization Platform, https://grafana.com/. Accessed 29 July 2019
iPerf Measurement Tool, https://iperf.fr/. Accessed 29 July 2019
Pages, A., Agraz, F., Montero, R., Landi, G., Monno, R., Aznar, J.I., Viñez, A., Jackson, C., Simeonidou, D., Spadaro, S.,: Experimental Assessment of VDC Provisioning in SDN/OpenStack-based DC Infrastructures with Optical DCN. In: ECOC 2016; 42nd European Conference on Optical Communication, Dusseldorf, Germany, pp. 1–3, (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the H2020 5GPPP SLICENET Project (H2020-ICT-2016-2/761913) and the Spanish Government through Project ALLIANCE-B (TEC2017-90034-C2-2-R) with FEDER contribution.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montero, R., Agraz, F., Pagès, A. et al. Enabling Multi-segment 5G Service Provisioning and Maintenance through Network Slicing. J Netw Syst Manage 28, 340–366 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-019-09509-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-019-09509-9