Abstract
Isolated carbonate build-ups of Miocene age are important hydrocarbon reservoirs in SE Asia and globally. The architecture of the build-up rim and fore-reef talus is poorly understood. The Subis build-up is one of the cycle I–II carbonate outcrops exposed along the coastal Sarawak in an area of 5 × 6 km2, with an exposed thickness of 390 m. This provides an opportunity to document the composition and architecture of rim and talus deposits in an isolated build-up as an analogue for similar gas-bearing structures located offshore Central Luconia, in Malaysia, which were neither drilled nor cored so far. This paper documents sedimentological characteristics, lateral and vertical facies relationships, of the marginal sections of a build-up in a large quarry exposing the Subis Limestone. The Subis Limestone is composed of massive and branching corals, coralline red algae, benthic foraminifera, bivalves, gastropods, echinoids, and occasionally bryozoans and sponges. Eight microfacies types and four environments were defined to describe the Subis Limestone: outer talus, inner talus, reef rim, and lagoon. Nine genera of benthic foraminifera were interpreted, confirming an early Miocene age (cycle II) of the succession. Three major backstepping events were observed at the build-up, where they developed inward towards the center of the build-up.

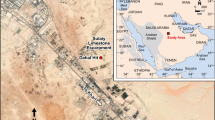
(adapted and modified from Google Terrain Map, 2016)

(modified from Dedeche 2012)






(adapted from Ali and Abolins 1999). These benthic foraminifera indicate shallow-marine reefoid, from fore-reef to protected back-reef environments (red rectangle)

The environment chart is adapted from Ali and Abolins (1999)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams CG (1965) The foraminifera and stratigraphy of the Melinau Limestone, Sarawak, and its importance in tertiary correlation. Q J Geol Soc Lond 121:283–338
Agostinelli E, Raisuddin M, Antoneilli E, Mohamad M (1990) Miocene–Pliocene paleogeographic evolution of a tract of Sarawak offshore between Bintulu and Miri. Geol Soc Malays Bull 27:117–135
Ali MY (2013) An integrated analysis of the depositional control, sedimentology and diagenesis of Cenozoic carbonates from the Sarawak basin, east Malaysia. PhD thesis, Imperial College London
Ali MY, Abolins P (1999) Central Luconia province. In: Leong KM (ed) The Petroleum geology and resources of Malaysia. PETRONAS, pp 453–474
Barbeito P (2005) The Niah complex fieldtrip notes for PETRONAS. Techno-Rada, pp 1–10
BouDagher-Fadel MK (2008) Evolution and geological significance of larger benthic foraminifera. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Braithwaite CJR (2014) Reef talus: a popular misconception. Earth-Sci Rev 128:169–180
Braithwaite CJR, Heath RA (1992) Deposition and diagenesis of debris flows in Upper Ordovician limestone, Hadeland, Norway. Sedimentology 29:753–767
Brondijk JF (1962) A reclassification of a part of the Setap Shale Formation as the Temburong Formation. British Borneo Geol Survey Ann Rept, pp 56–60
Bucur II, Granier B, Săsăran E (2008) Upper Aptian calcareous algae from Pădurea Craiului (northern Apuseni Mountains, Romania). Geol Croat 61(2–3):297–309
Burr IL, Crews WE (1950) Report on the Subis-Bintulu area, GR526
Cheong YL, Hilman A, Kupecz J (2017) A fault seal case study from the northern Luconia province, offshore Sarawak. In: Proceedings of Asia petroleum geoscience conference and exhibition (APGCE). Kuala Lumpur Convention Centre, Kuala Lumpur, pp 123–127
Dana JD (1853) On coral reefs and islands. GP Putnam, New York, p 143
Darwin C (1842) The structure and distribution of coral reefs. Being the first part of the geology of the voyage of the Beagle, under the command of Capt Fitzroy, RN during the years 1832 to 1836. Smith, Elder, London, p 214
Dedeche A (2012) Growth history and facies evolution of the Miocene carbonate limestone of Gunung Subis, onshore Sarawak. MSc thesis, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS
Doust H (1981) Geology and exploration history of offshore central Sarawak. In: Halbouty MT (ed) Energy resources of Pacific region. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Studies in Geology Series 12. AAPG, pp 117–132
Google Terrain Map, 2016. Taman Negara Niah. Retrieved from https://www.google.co.uk/maps/place/Niah+National+Park/@3.800341,113.7701914,15z/data=!4m5!3m4!1s0x321ee9d8b6c3a611:0xf08d64021c616958!8m2!3d3.8014209!4d113.7841189!5m1!1e4. Accessed 24 June 2016
Granier B, Dias-Brito D, Bucur II (2008) Calcareous algae from Upper Albian–Cenomanian strata of the Potiguar basin (NE Brazil). Geol Croat 61(2-3):311–320
Greenlee SM, Lehmann PJ (1993) Stratigraphic framework of productive carbonate buildups. In: Loucks RG, Sarg JF (eds) Carbonate sequence stratigraphy, vol 57. AAPG Memoir, USA, pp 43–62
Haak R (1955) Study of the Miocene Gunung Subis Limestone complex, Sarawak. Econ Pet Rep 25948:1–30
Haile NS (1962) The geology and mineral resources of the Suai-Baram area, north Sarawak. Geological Survey Department British Territories in Borneo, Memoir 13
Hall R (1996) Reconstructing Cenozoic SE Asia. In: Hall R, Blundell DJ (eds) Tectonic evolution of Southeast Asia, vol 106. Geological Society of London Special Publication, London, pp 153–184
Hall R (2002) Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: computer-based reconstructions, model and animation. J Asian Earth Sci 20:353–431
Hall R (2009a) Hydrocarbon basins in SE Asia: understanding why they are there. Pet Geosci 15:131–146
Hall R (2009b) Southeast Asia’s changing paleogeography. Blumea 54:148–161
Hall R, Cottam MA, Wilson MEJ (2011) The SE Asian gateway: history and tectonics of the Australia—Asia collision. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 355:1–6
Hazebroek HP, Abang Moshidi AK, Wong KM, Chung RCK (2000) National parks of Sarawak. Natural History Publications (Borneo), Malaysia, pp 199–210
Ho KF (1978) Stratigraphic framework for oil exploration in Sarawak. Bull Geol Soc Malays 10:1–13
Hutchison CS (1989) Geological evolution of South-East Asia. Oxford University Press, England, p 368
Hutchison CS (2005) Geology of north west Borneo, Sarawak, Brunei and Sabah. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 131–158
Ineson JR, Surlyk F (2000) Carbonate megabreccias in a sequence stratigraphic context; evidence from the Cambrian of north Greenland. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 172:47–68
Kosa E (2015) Sea-level changes, shoreline journeys, and the seismic stratigraphy of Central Luconia, Miocene–present, offshore Sarawak, NW Borneo. Mar Pet Geol 59:35–55
Li X, Yu M, Lehrmann DJ, Payne JL, Kelly BM, Minzoni M (2012) Factors controlling carbonate platform asymmetry: preliminary results from the Great Bank of Guizhou, and isolated Permian–Triassic platform in the Nanpanjiang Basin, south China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 315:158–171
Liechti P, Roe FW, Haile NS (1960) The geology of Sarawak, Brunei and the western part of North Borneo. Geological Survey Department, British Territories in Borneo, Bulletin, vol 3, Kuching
Longley AJ (1999) Differential compaction and its effects on the outer shelf of the Permian Capitan Reef complex, Guadalupe Mountains, New Mexico. In: Saller AH, Harris PM, Kirkland BL, Mazullo SJ (eds) Geologic framework of the Capitan Reef, vol 65. Special Publication SEPM, London, pp 85–105
Lunt P, Madon M (2017) A review of the Sarawak cycles: history and modern application. Bull Geol Soc Malays 63:77–101
Mathew MJ, Menier D, Rahman AHA, Siddiqui NA, Pubellier M, Hassaan M (2014a) Tertiary Sarawak basin origin: a small step in demystifying the ambiguity. AAPG Search and Discovery Article, Istanbul, Turkey
Mathew MJ, Siddiqui NA, Menier D (2014b) An evolutionary model of the nearshore Tinjar and Balingian provinces, Sarawak, Malaysia. Int J Pet Geosci Eng 2(1):81–91
Mihaljevic M, Renema W, Welsh K, Pandolfi JM (2014) Eocene–Miocene shallow-water carbonate limestones and increased habitat diversity in Sarawak, Malaysia. Palaios 29:378–391
Playton TE, Hocking R, Montgomery P, Tohver E, Hillbun K, Katz D, Haines P, Trinajstic K, Yan M, Hansma J, Pisarevsky S, Kirschvink J, Cawood P, Grice K, Tulipani S, Ratcliffe K, Wray D, Caulfield-Kerney S, Ward P, Playford P (2013) Development of a regional stratigraphic framework for Upper Devonian reef complexes using integrated chronostratigraphy: Lennard Shelf, Canning Basin, Western Australia. West Australia Basins symposium, Perth
Roohi G (1994) Biostratigraphy of the Subis Limestone, Sarawak. MSc thesis, University of Malaya
Sleumer BHG (1977) Paleoecology and internal architecture of the Subis Limestone complex (Sarawak). Shell Sarawak Bhd Exp R 50108 (unpublished Shell report)
Sorkhabi R (2012) Borneo’s petroleum plays. In exploration petroleum plays of Borneo. Geo Expro 9(4):20–22
Van de Weerd AA, Armin RA (1992) Origin and evolution of the tertiary hydrocarbon-bearing basins in Kalimantan (Borneo), Indonesia. Am Asso Pet Geol Bull 76:1778–1803
Wentworth CK (1922) A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. J Geol 30(5):377–392 (Research-article: full publication date: Jul–Aug, 1922)
Wilson MEJ (2002) Cenozoic carbonates in Southeast Asia: implications for equatorial carbonate development. Sed Geol 147:295–428
Wilson MEJ, Chang EEW, Dorobek S, Lunt P (2013) Onshore to offshore trends in carbonate sequence development, diagenesis and reservoir quality across a land-attached shelf in SE Asia. Mar Pet Geol 45:349–376
Wood Mackenzie (2015) Malaysia upstream summary country report, Wood Mackenzie Limited
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editor Dr. Axel Munnecke for a thorough editorial work and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions. We also gratefully acknowledge Dr. Manoj Mathew for help with the revision of the manuscript. The authors gratefully thank the generous support of the Debbestone Quarry management and staff (Mr. Albert Wong, Mr. Liabo, Mr. Lihan) and Ting King King from Shell Miri Malaysia. Lastly, we would like to thank all SEACaRL staff for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saw, B.B., Schlaich, M., Pöppelreiter, M.C. et al. Facies, depositional environments, and anatomy of the Subis build-up in Sarawak, Malaysia: implications on other Miocene isolated carbonate build-ups. Facies 65, 28 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-019-0571-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-019-0571-6