Abstract
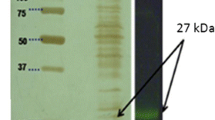
Gene CA_C0816 codes for a serine hydrolase protein from Clostridium acetobutylicum (ATCC 824) a member of hormone-sensitive lipase of lipolytic family IV. This gene was overexpressed in E. coli strain BL21and purified using Ni2+–NTA affinity chromatography. Size exclusion chromatography revealed that the protein is a dimer in solution. Optimum pH and temperature for recombinant Clostridium acetobutylicum esterase (Ca-Est) were found to be 7.0 and 60 °C, respectively. This enzyme exhibited high preference for p-nitrophenyl butyrate. KM and kcat/KM of the enzyme were 24.90 µM and 25.13 s−1 µM−1, respectively. Sequence analysis of Ca-Est predicts the presence of catalytic amino acids Ser 89, His 224, and Glu 196, presence of novel GYSMG conserved sequence (instead of GDSAG and GTSAG motif), and undescribed variation of HGSG motif. Site-directed mutagenesis confirmed that Ser 89 and His 224 play a major role in catalysis. This study reports that Ca-Est is hormone-sensitive lipase with novel GYSMG pentapeptide motif at a catalytic domain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tao W, Shengxue F, Duobin M et al (2013) Characterization of a new thermophilic and acid tolerant esterase from Thermotoga maritima capable of hydrolytic resolution of racemic ketoprofen ethyl ester. J Mol Catal B Enzym 85–86:23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2012.08.006
Javed S, Azeem F, Hussain S et al (2018) Bacterial lipases: a review on purification and characterization. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 132:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.07.014
Chen C-C, Chi Z, Liu G-L et al (2017) Production, purification, characterization and gene cloning of an esterase produced by Aureobasidium melanogenum HN6.2. Process Biochem 53:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.12.006
Arpigny JL, Jaeger KE (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343(Pt 1):177–183
Casas-Godoy L, Duquesne S, Bordes F et al (2012) Lipases: an overview. In: Sandoval G (ed) Lipases and phospholipases. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 3–30
Jayanath G, Mohandas SP, Kachiprath B et al (2018) A novel solvent tolerant esterase of GDSGG motif subfamily from solar saltern through metagenomic approach: recombinant expression and characterization. Int J Biol Macromol 119:393–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.057
Ramnath L, Sithole B, Govinden R (2017) Classification of lipolytic enzymes and their biotechnological applications in the pulping industry. Can J Microbiol 63:179–192. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjm-2016-0447
Singh R, Kumar M, Mittal A, Mehta PK (2016) Microbial enzymes: industrial progress in 21st century. 3 Biotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0485-8
Sarmah N, Revathi D, Sheelu G et al (2018) Recent advances on sources and industrial applications of lipases: biotechnol. Prog., 2017, Vol. 00, No. 00. Biotechnol Prog 34:5–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.2581
Ferrer M, Bargiela R, Martínez-Martínez M et al (2015) Biodiversity for biocatalysis: a review of the α/β-hydrolase fold superfamily of esterases-lipases discovered in metagenomes. Biocatal Biotransform 33:235–249. https://doi.org/10.3109/10242422.2016.1151416
Navvabi A, Razzaghi M, Fernandes P et al (2018) Novel lipases discovery specifically from marine organisms for industrial production and practical applications. Process Biochem 70:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.04.018
Kovacic F, Babic N, Krauss U, Jaeger K-E (2019) Classification of lipolytic enzymes from bacteria. In: Rojo F (ed) Aerobic utilization of hydrocarbons, oils and lipids. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 1–35
Lenfant N, Hotelier T, Velluet E et al (2013) ESTHER, the database of the α/β-hydrolase fold superfamily of proteins: tools to explore diversity of functions. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D423–D429. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1154
Hotelier T (2004) ESTHER, the database of the/-hydrolase fold superfamily of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 32:145D–147D. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh141
Lampidonis AD, Rogdakis E, Voutsinas GE, Stravopodis DJ (2011) The resurgence of Hormone-Sensitive Lipase (HSL) in mammalian lipolysis. Gene 477:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2011.01.007
Lass A, Zimmermann R, Oberer M, Zechner R (2011) Lipolysis—a highly regulated multi-enzyme complex mediates the catabolism of cellular fat stores. Prog Lipid Res 50:14–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2010.10.004
Langin D, Laurell H, Holst LS et al (1993) Gene organization and primary structure of human hormone-sensitive lipase: possible significance of a sequence homology with a lipase of Moraxella TA144, an antarctic bacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:4897–4901
Kim TD (2017) Bacterial hormone-sensitive lipases (bHSLs): emerging enzymes for biotechnological applications. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:1907–1915. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1708.08004
Osterlund T (2001) Structure-function relationships of hormone-sensitive lipase. Eur J Biochem 268:1899–1907
Østerlund T, Contreras JA, Holm C (1997) Identification of essential aspartic acid and histidine residues of hormone-sensitive lipase: apparent residues of the catalytic triad. FEBS Lett 403:259–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(97)00063-X
De Simone G, Galdiero S, Manco G et al (2000) A snapshot of a transition state analogue of a novel thermophilic esterase belonging to the subfamily of mammalian hormone-sensitive lipase 1 1Edited by D. Rees. J Mol Biol 303:761–771. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4195
Hemilä H, Koivula TT, Palva I (1994) Hormone-sensitive lipase is closely related to several bacterial proteins, and distantly related to acetylcholinesterase and lipoprotein lipase: identification of a superfamily of esterases and lipases. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Lipids and Lipid Metabolism 1210:249–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2760(94)90129-5
Noby N, Saeed H, Embaby AM et al (2018) Cloning, expression and characterization of cold active esterase (EstN7) from Bacillus cohnii strain N1: a novel member of family IV. Int J Biol Macromol 120:1247–1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.07.169
Li P-Y, Ji P, Li C-Y et al (2014) Structural basis for dimerization and catalysis of a novel esterase from the GTSAG motif subfamily of the bacterial hormone-sensitive lipase family. J Biol Chem 289:19031–19041. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.574913
Jeon JH, Lee HS, Kim JT et al (2012) Identification of a new subfamily of salt-tolerant esterases from a metagenomic library of tidal flat sediment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:623–631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3433-x
Kim B, Yoo W, Le Huong Luu LT et al (2019) Characterization and mutation anaylsis of a cold-active bacterial hormone-sensitive lipase from Salinisphaera sp. P7-4. Arch Biochem Biophys 663:132–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.01.010
Liu Y, Xu H, Yan Q et al (2013) Biochemical characterization of a first fungal esterase from rhizomucor miehei showing high efficiency of ester synthesis. PLoS One 8:e77856. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077856
Manco G, Giosuè E, D’Auria S et al (2000) Cloning, overexpression, and properties of a new thermophilic and thermostable esterase with sequence similarity to hormone-Sensitive Lipase subfamily from the Archaeon Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Arch Biochem Biophys 373:182–192. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1999.1497
Li C, Li Q, Zhang Y et al (2017) Characterization and function of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv Lipase Rv1076 (LipU). Microbiol Res 196:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2016.12.005
Zarafeta D, Moschidi D, Ladoukakis E et al (2016) Metagenomic mining for thermostable esterolytic enzymes uncovers a new family of bacterial esterases. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38886
Virk AP (2011) A new esterase, belonging to hormone-sensitive lipase family, cloned from Rheinheimera sp. isolated from industrial effluent. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:667–674. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1103.03008
Sánchez-Carbente MDR, Batista-García RA, Sánchez-Reyes A et al (2017) The first description of a hormone-sensitive lipase from a basidiomycete: structural insights and biochemical characterization revealed Bjerkandera adusta Ba EstB as a novel esterase. MicrobiologyOpen 6:e00463. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.463
Alvarez Y, Esteban-Torres M, Cortés-Cabrera Á et al (2014) Esterase LpEst1 from Lactobacillus plantarum: a novel and atypical member of the αβ hydrolase superfamily of enzymes. PLoS One 9:e92257. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092257
Emtenani S, Asoodeh A, Emtenani S (2013) Molecular cloning of a thermo-alkaliphilic lipase from Bacillus subtilis DR8806: expression and biochemical characterization. Process Biochem 48:1679–1685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.08.016
Choi Y-H, Lee Y-N, Park Y-J et al (2016) Identification of amino acids related to catalytic function of Sulfolobus solfataricus P1 carboxylesterase by site-directed mutagenesis and molecular modeling. BMB Rep 49:349–354. https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2016.49.6.077
Lee J, Jang Y-S, Choi SJ et al (2012) Metabolic engineering of clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 for isopropanol-butanol-ethanol fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1416–1423. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06382-11
Schwarz KM, Kuit W, Grimmler C et al (2012) A transcriptional study of acidogenic chemostat cells of Clostridium acetobutylicum—cellular behavior in adaptation to n-butanol. J Biotechnol 161:366–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.03.018
Rehdorf J, Behrens GA, Nguyen G-S et al (2012) Pseudomonas putida esterase contains a GGG(A)X-motif confering activity for the kinetic resolution of tertiary alcohols. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1119–1126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3464-3
Palm GJ, Fernández-Álvaro E, Bogdanović X et al (2011) The crystal structure of an esterase from the hyperthermophilic microorganism Pyrobaculum calidifontis VA1 explains its enantioselectivity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:1061–1072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3337-9
Mandrich L, Merone L, Pezzullo M et al (2005) Role of the N terminus in enzyme activity, stability and specificity in thermophilic esterases belonging to the HSL family. J Mol Biol 345:501–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.10.035
Bassegoda A, Fillat A, Pastor FIJ, Diaz P (2013) Special Rhodococcus sp. CR-53 esterase Est4 contains a GGG(A)X-oxyanion hole conferring activity for the kinetic resolution of tertiary alcohols. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:8559–8568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4676-x
Byun J-S, Rhee J-K, Kim N et al (2007) Crystal structure of hyperthermophilic esterase EstE1 and the relationship between its dimerization and thermostability properties. BMC Struct Biol 7:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6807-7-47
De Simone G, Menchise V, Manco G et al (2001) The crystal structure of a hyper-thermophilic carboxylesterase from the archaeon Archaeoglobus fulgidus 1 1Edited by R. Huber. J Mol Biol 314:507–518. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.5152
Huo Y-Y, Jian S-L, Cheng H et al (2018) Two novel deep-sea sediment metagenome-derived esterases: residue 199 is the determinant of substrate specificity and preference. Microb Cell Fact. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0864-4
Petrovskaya LE, Novototskaya-Vlasova KA, Spirina EV et al (2016) Expression and characterization of a new esterase with GCSAG motif from a permafrost metagenomic library. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 92:fiw046. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiw046
Benavente R, Esteban-Torres M, Acebrón I et al (2013) Structure, biochemical characterization and analysis of the pleomorphism of carboxylesterase Cest-2923 from Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. FEBS J 280:6658–6671. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12569
Neves Petersen MT, Fojan P, Petersen SB (2001) How do lipases and esterases work: the electrostatic contribution. J Biotechnol 85:115–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1656(00)00360-6
Declerck N, Machius M, Wiegand G et al (2000) Probing structural determinants specifying high thermostability in Bacillus licheniformis alpha-amylase. J Mol Biol 301:1041–1057. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4025
Bornscheuer UT (2002) Microbial carboxyl esterases: classification, properties and application in biocatalysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2002.tb00599.x
Ghati A, Paul G (2015) Purification and characterization of a thermo-halophilic, alkali-stable and extremely benzene tolerant esterase from a thermo-halo tolerant Bacillus cereus strain AGP-03, isolated from ‘Bakreshwar’ hot spring, India. Process Biochem 50:771–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.01.026
Yang S, Qin Z, Duan X et al (2015) Structural insights into the substrate specificity of two esterases from the thermophilic Rhizomucor miehei. J Lipid Res 56:1616–1624. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M060673
Sayer C, Finnigan W, Isupov MN et al (2016) Structural and biochemical characterisation of Archaeoglobus fulgidus esterase reveals a bound CoA molecule in the vicinity of the active site. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25542
Holm C, Davis RC, Osterlund T et al (1994) Identification of the active site serine of hormone-sensitive lipase by site-directed mutagenesis. FEBS Lett 344:234–238
Lee CW, Kwon S, Park S-H et al (2017) Crystal structure and functional characterization of an esterase (EaEST) from Exiguobacterium antarcticum. PLoS One 12:e0169540. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169540
Park HJ, Joo JC, Park K, Yoo YJ (2012) Stabilization of Candida antarctica lipase B in hydrophilic organic solvent by rational design of hydrogen bond. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 17:722–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0092-4
Alex D, Shainu A, Pandey A, Sukumaran RK (2014) Esterase Active in Polar Organic Solvents from the Yeast Pseudozyma sp. NII 08165. Enzyme Res 2014:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/494682
Fan X, Niehus X, Sandoval G (2012) Lipases as biocatalyst for biodiesel production. In: Sandoval G (ed) Lipases and phospholipases. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 471–483
Sivaramakrishnan R, Muthukumar K (2012) Isolation of thermo-stable and solvent-tolerant bacillus sp. lipase for the production of biodiesel. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166:1095–1111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9497-3
Delorme V, Dhouib R, Canaan S et al (2011) Effects of surfactants on lipase structure, activity, and inhibition. Pharm Res 28:1831–1842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0362-9
Neugebauer JM (1990) Detergents: an overview. Meth Enzymol 182:239–253
Legler PM, Leary DH, Hervey WJ, Millard CB (2012) A role for His-160 in peroxide inhibition of S. cerevisiae S-formylglutathione hydrolase: evidence for an oxidation sensitive motif. Arch Biochem Biophys 528:7–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2012.08.001
Jeon JH, Kim J-T, Kang SG et al (2009) Characterization and its potential application of two esterases derived from the arctic sediment metagenome. Mar Biotechnol 11:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-008-9145-2
Asoodeh A, Ghorani Azam A, Zardini H (2014) Biochemical characterization of a novel thermophilic esterase isolated from Shewanella sp F88. J Sci Repub Iran 25(1):5–12
Acknowledgements
Authors acknowledge IIT Madras for the facilities. Author N. Vijaya Lakshmi acknowledges AICTE-QIP and JNTUA College of Engineering Pulivendula.
Funding
The researcher did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not for profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any one of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagaroor, V., Gummadi, S.N. Biochemical characterization of an esterase from Clostridium acetobutylicum with novel GYSMG pentapeptide motif at the catalytic domain. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 47, 169–181 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02253-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02253-8