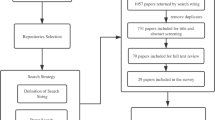
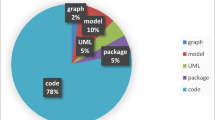
Abstract
Software systems are often released without formal specifications. To deal with the problem of lack of and outdated specifications, rule-based specification mining approaches have been proposed. These approaches analyze execution traces of a system to infer the rules that characterize the protocols, typically of a library, that its clients must obey. Rule-based specification mining approaches work by exploring the search space of all possible rules and use interestingness measures to differentiate specifications from false positives. Previous rule-based specification mining approaches often rely on one or two interestingness measures, while the potential benefit of combining multiple available interestingness measures is not yet investigated. In this work, we propose a learning to rank based approach that automatically learns a good combination of 38 interestingness measures. Our experiments show that the learning to rank based approach outperforms the best performing approach leveraging single interestingness measure by up to 66%.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Ensemble learners combine multiple learning algorithms to achieve higher classification accuracy.
References
Arcuri, A., Briand, L.: A hitchhiker’s guide to statistical tests for assessing randomized algorithms in software engineering. Softw. Test. Verif. Reliab. 24(3), 219–250 (2014)
Beschastnikh, I., Brun, Y., Schneider, S., Sloan, M., Ernst, M.D.: Leveraging existing instrumentation to automatically infer invariant-constrained models. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGSOFT Symposium and the 13th European Conference on Foundations of Software Engineering, pp. 267–277. ACM (2011)
Biermann, A.W., Feldman, J.A.: On the synthesis of finite-state machines from samples of their behavior. IEEE Trans. Comput. 100(6), 592–597 (1972)
Binkley, D., Lawrie, D.: Learning to rank improves IR in SE. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution, pp. 441–445. IEEE Computer Society (2014)
Blackburn, S.M., Garner, R., Hoffmann, C., Khan, A.M., McKinley, K.S., Bentzur, R., Diwan, A., Feinberg, D., Frampton, D., Guyer, S.Z., Hirzel, M., Hosking, A.L., Jump, M., Lee, H.B., Moss, J.E.B., Phansalkar, A., Stefanovic, D., VanDrunen, T., von Dincklage, D., Wiedermann, B.: The dacapo benchmarks: java benchmarking development and analysis. In: Proceedings of the 21th Annual ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Object-Oriented Programming, Systems, Languages, and Applications, OOPSLA 2006, October 22–26, 2006, Portland, Oregon, USA, pp. 169–190 (2006)
Breiman, L.: Random forests. Mach. Learn. 45(1), 5–32 (2001)
Burges, C., Shaked, T., Renshaw, E., Lazier, A., Deeds, M., Hamilton, N., Hullender, G.: Learning to rank using gradient descent. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 89–96. ACM (2005)
Cao, Z., Qin, T., Liu, T.Y., Tsai, M.F., Li, H.: Learning to rank: from pairwise approach to listwise approach. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 129–136. ACM (2007)
da Costa, D.A., Abebe, S.L., McIntosh, S., Kulesza, U., Hassan, A.E.: An empirical study of delays in the integration of addressed issues. In: ICSME, pp. 281–290 (2014)
Dang, V.: Ranklib. https://sourceforge.net/p/lemur/wiki/RankLib/ (2016). Accessed 17 Sept 2016
Demsky, B., Ernst, M.D., Guo, P.J., McCamant, S., Perkins, J.H., Rinard, M.: Inference and enforcement of data structure consistency specifications. In: Proceedings of the 2006 International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis, pp. 233–244. ACM (2006)
Dwyer, M.B., Avrunin, G.S., Corbett, J.C.: Patterns in property specifications for finite-state verification. In: Proceedings of the 1999 International Conference on Software Engineering, ICSE’ 99, Los Angeles, CA, USA, May 16–22, 1999, pp. 411–420 (1999)
Ernst, M.D., Perkins, J.H., Guo, P.J., McCamant, S., Pacheco, C., Tschantz, M.S., Xiao, C.: The Daikon system for dynamic detection of likely invariants. Sci. Comput. Program. 69(1–3), 35–45 (2007)
Fahland, D., Lo, D., Maoz, S.: Mining branching-time scenarios. In: ASE (2013)
Fox, E.A., Koushik, M.P., Shaw, J., Modlin, R., Rao, D., et al.: Combining evidence from multiple searches. In: The First Text Retrieval Conference (TREC-1), US Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology, vol. 500 (1993)
Freund, Y., Iyer, R., Schapire, R.E., Singer, Y.: An efficient boosting algorithm for combining preferences. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 4(Nov), 933–969 (2003)
Friedman, J.H.: Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 29, 1189–1232 (2001)
Gabel, M., Su, Z.: Online inference and enforcement of temporal properties. In: Proceedings of the 32nd ACM/IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering, Vol. 1, pp. 15–24. ACM (2010)
Geng, L., Hamilton, H.J.: Interestingness measures for data mining: a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 38(3), 9 (2006)
Ghotra, B., Mcintosh, S., Hassan, A.E.: A large-scale study of the impact of feature selection techniques on defect classification models. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Mining Software Repositories, pp. 146–157. IEEE Press (2017)
Gruska, N., Wasylkowski, A., Zeller, A.: Learning from 6, 000 projects: lightweight cross-project anomaly detection. In: Proceedings of the Nineteenth International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis, ISSTA 2010, pp. 119–130 (2010)
Henning, J., Pfeiffer, D.U., et al.: Risk factors and characteristics of H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) post-vaccination outbreaks. Vet. Res. 40(3) (2009). https://www.vetres.org/articles/vetres/abs/2009/03/v09120/v09120.html
Knight, J.C., DeJong, C.L., Gibble, M.S., Nakano, L.G.: Why are formal methods not used more widely? In: Fourth NASA Formal Methods Workshop, pp. 1–12 (1997)
Krka, I., Brun, Y., Medvidovic, N.: Automatic mining of specifications from invocation traces and method invariants. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Foundations of Software Engineering, pp. 178–189. ACM (2014)
Le, T.D.B., Lo, D.: Beyond support and confidence: exploring interestingness measures for rule-based specification mining. In: 2015 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Software Analysis, Evolution, and Reengineering (SANER), pp. 331–340. IEEE (2015)
Le, T.D.B., Le, X.B.D., Lo, D., Beschastnikh, I.: Synergizing specification miners through model fissions and fusions (t). In: 2015 30th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE), pp. 115–125. IEEE (2015)
Le, T.D., Lo, D., Le Goues, C., Grunske, L.: A learning-to-rank based fault localization approach using likely invariants. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis, pp. 177–188. ACM (2016)
Lee, C.P., Lin, C.J.: Large-scale linear ranksvm. Neural Comput. 26(4), 781–817 (2014)
Lemieux, C., Park, D., Beschastnikh, I.: General LTL specification mining (t). In: 2015 30th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE), pp. 81–92. IEEE (2015)
Li, Z., Zhou, Y.: Pr-miner: automatically extracting implicit programming rules and detecting violations in large software code. In: ESEC/SIGSOFT FSE (2005)
Li, W., Forin, A., Seshia, S.A.: Scalable specification mining for verification and diagnosis. In: Proceedings of the 47th Design Automation Conference, pp. 755–760. ACM (2010)
Liu, T.Y.: Learning to rank for information retrieval. Found. Trends Inf. Retr. 3(3), 225–331 (2009)
Liu, T.Y.: Learning to Rank for Information Retrieval. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Lo, D., Khoo, S.C.: Smartic: towards building an accurate, robust and scalable specification miner. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Foundations of Software Engineering, pp. 265–275. ACM (2006)
Lo, D., Maoz, S.: Scenario-based and value-based specification mining: better together. Autom. Softw. Eng. 19(4), 423–458 (2012)
Lo, D., Khoo, S.C., Liu, C.: Mining temporal rules for software maintenance. J. Softw. Maint. 20(4), 227–247 (2008)
Lo, D., Ramalingam, G., Ranganath, V.P., Vaswani, K.: Mining quantified temporal rules: formalism, algorithms, and evaluation. Sci. Comput. Program. 77, 743–759 (2012)
Lo, D., Xia, X., et al.: Fusion fault localizers. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, pp. 127–138. ACM (2014)
Louppe, G., Wehenkel, L., Sutera, A., Geurts, P.: Understanding variable importances in forests of randomized trees. In: Burges, C. J. C., Bottou, L., Welling, M., Ghahramani, Z., Weinberger, K. Q. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 431–439. Curran Associates, Inc. (2013). http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4928-understanding-variable-importances-in-forests-of-randomized-trees.pdf
Metzler, D., Croft, W.B.: Linear feature-based models for information retrieval. Inf. Retr. 10(3), 257–274 (2007)
Microsoft.: Rules for WDM drivers. http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ windows/hardware/ff551714(v=vs.85).aspx. Accessed 18 Oct 2016 (2016)
Mutegi, C., Ngugi, H., Hendriks, S., Jones, R.: Prevalence and factors associated with aflatoxin contamination of peanuts from Western Kenya. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 130(1), 27–34 (2009)
Niu, H., Keivanloo, I., Zou, Y.: Learning to rank code examples for code search engines. Empir. Softw. Eng. 22(1), 259–291 (2016)
Quoc, C., Le, V.: Learning to rank with nonsmooth cost functions. Proc. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 19, 193–200 (2007)
Rothman, K.J.: Epidemiology: An Introduction. Oxford university press, Oxford (2012)
Safyallah, H., Sartipi, K.: Dynamic analysis of software systems using execution pattern mining. In: 14th International Conference on Program Comprehension (ICPC 2006), 14–16 June 2006, pp. 84–88. Greece, Athens (2006)
Stampfer, M.J.: Welding occupations and mortality from Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases among united states men, 1985–1999. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 6, 267–272 (2009)
Svore, K.M., Volkovs, M.N., Burges, C.J.: Learning to rank with multiple objective functions. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on World Wide Web, pp. 367–376. ACM (2011)
Tamrawi, A., Nguyen, T.T., Al-Kofahi, J.M., Nguyen, T.N.: Fuzzy set and cache-based approach for bug triaging. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM SIGSOFT Symposium and the 13th European Conference on Foundations of Software Engineering, pp. 365–375. ACM (2011)
Tian, Y., Nagappan, M., Lo, D., Hassan, A.E.: What are the characteristics of high-rated apps? A case study on free android applications. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution (ICSME), pp. 301–310. IEEE (2015)
Tian, Y., Wijedasa, D., Lo, D., Le Gouesy, C.: Learning to rank for bug report assignee recommendation. In: 2016 IEEE 24th International Conference on Program Comprehension (ICPC), pp 1–10. IEEE (2016)
Walkinshaw, N., Bogdanov, K.: Inferring finite-state models with temporal constraints. In: Proceedings of the 2008 23rd IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, pp. 248–257. IEEE Computer Society (2008)
Walkinshaw, N., Taylor, R., Derrick, J.: Inferring extended finite state machine models from software executions. Empir. Softw. Eng. 21(3), 811–853 (2016)
Wang, S., Lo, D.: Version history, similar report, and structure: putting them together for improved bug localization. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Program Comprehension, pp. 53–63. ACM (2014)
Wilcoxon, F.: Individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biom. Bull. 1(6), 80–83 (1945)
Wu, S.: Data Fusion in Information Retrieval, vol. 13. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Wu, Q., Burges, C.J., Svore, K.M., Gao, J.: Adapting boosting for information retrieval measures. Inf. Retr. 13(3), 254–270 (2010)
Xu, J., Li, H.: Adarank: a boosting algorithm for information retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 30th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, pp. 391–398. ACM (2007)
Xuan, J., Monperrus, M.: Learning to combine multiple ranking metrics for fault localization. In: ICSME-30th International Conference on Software Maintenance and Evolution (2014)
Yang, J., Evans, D., Bhardwaj, D., Bhat, T., Das, M.: Perracotta: mining temporal API rules from imperfect traces. In: Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Software Engineering, pp. 282–291. ACM (2006)
Yang, C., Xu, Z., Gu, G., Yegneswaran, V., Porras, P.: Droidminer: Automated mining and characterization of fine-grained malicious behaviors in android applications. In: European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, pp. 163–182. Springer (2014)
Yang, X., Tang, K., Yao, X.: A learning-to-rank approach to software defect prediction. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 64(1), 234–246 (2015)
Ye, X., Bunescu, R., Liu, C.: Learning to rank relevant files for bug reports using domain knowledge. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Foundations of Software Engineering, pp. 689–699. ACM (2014)
Zhang, F., Zheng, Q., Zou, Y., Hassan, A.E.: Cross-project defect prediction using a connectivity-based unsupervised classifier. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Software Engineering, pp. 309–320. ACM (2016)
Zhong, H., Su, Z.: Detecting API documentation errors. In: Proceedings of the 2013 ACM SIGPLAN International Conference on Object Oriented Programming Systems Languages and Applications, OOPSLA 2013, Part of SPLASH 2013, Indianapolis, IN, USA, October 26–31, 2013, pp. 803–816 (2013)
Zhou, J., Zhang, H.: Learning to rank duplicate bug reports. In: Proceedings of the 21st ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp. 852–861. ACM (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was done while the author was visiting Singapore Management University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Z., Tian, Y., Le, TD.B. et al. Rule-based specification mining leveraging learning to rank. Autom Softw Eng 25, 501–530 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10515-018-0231-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10515-018-0231-z