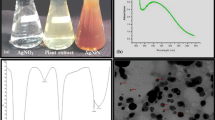
Abstract
The present study deals with the eco-synthesis and effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on pea (Pisum sativum L.). AgNPs were synthesized by using gelatine/glucose mixture as a reducing/stabilizing agent for silver nitrate. The AgNPs were characterized and their effects on early growth and cytotoxicity on cell division and chromosomes have been studied. Seeds of Pisum sativum cv. Master B were soaked in AgNPs solutions at concentrations of 20, 40, 80 and 160 mg/L for two hours, control seeds were simultaneously soaked in distilled water. Seeds were then germinated on filter papers moistened with the above concentrations. Seed germination was gradually enhanced at lower concentrations of AgNPs (20 and 40 mg/L) and decreased at higher concentrations (80 and 160 mg/L) compared to control. Seedling growth parameters except root length were all reduced. Deformation of root shape (twisted, folded and hocked roots) was induced upon exposure to AgNPs. Cytologically, mitotic index declined, and chromosomal abnormalities raised as the concentration of AgNPs increased. Observed abnormalities comprised disturbed mitotic phases and cladistic aberrations such as chromosome bridges, rings, breaks, and micronuclei indicating a genotoxic potential for the AgNPs at high concentrations.
Zusammenfassung
Die vorliegende Studie beschäftigt sich mit der Ökosynthese und den Auswirkungen von Silber-Nanopartikeln (AgNPs) auf Erbsen (Pisum sativum L.). AgNPs wurden unter der Verwendung einer Gelatine‑/Glukosemischung als Reduktions‑/Stabilisierungsmittel für Silbernitrat synthetisiert. Die AgNPs wurden charakterisiert und ihre Auswirkungen auf das frühe Wachstum und die Zytotoxizität bzgl. der Zellteilung und Chromosomen untersucht. Samen von Pisum sativum cv. Master B wurden zwei Stunden lang in AgNPs-Lösungen in Konzentrationen von 20, 40, 80 und 160 mg/L eingeweicht, Kontrollsaatgut wurde gleichzeitig in destilliertem Wasser eingeweicht. Die Samen wurden dann auf Filterpapieren, die mit den oben genannten Konzentrationen befeuchtet wurden, zum Keimen gebracht. Die Samenkeimung wurde im Vergleich zur Kontrolle bei niedrigeren Konzentrationen von AgNPs (20 und 40 mg/L) schrittweise gesteigert und bei höheren Konzentrationen (80 und 160 mg/L) verringert. Die Wachstumsparameter für Setzlinge mit Ausnahme der Wurzellänge wurden alle reduziert. Die Veränderung der Wurzelform (verdrehte, gefaltete und verknotete Wurzeln) wurde bei Exposition gegenüber AgNPs induziert. Zytologisch nahm der Mitoseindex ab und die Chromosomenanomalien nahmen mit zunehmender Konzentration der AgNPs zu. Beobachtete Anomalien umfassten gestörte mitotische Phasen und kladistische Aberrationen wie Chromosomenbrücken, -ringe, -brüche und Mikronuklei, die auf ein genotoxisches Potenzial für die AgNPs bei hohen Konzentrationen hinweisen.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Zeid HM, Moustafa Y (2014) Physiological and cytogenetic responses of wheat and barley to silver nano-priming treatment. Int J Appl Biol Pharm Technol 5(4):150–163
Albrecht MA, Evans CW, Raston CL (2006) Green chemistry and the health implications of nanoparticles. Green Chem 8 (5):417
Amooaghaie R, Saeri MR, Azizi M (2015) Synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility of silver nanoparticles synthesized from. Nigella sativa leaf extract in comparison with chemical silver nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 120:400–408X
Asare N, Instanes C, Sandberg WJ, Refsnes M, Schwarze P, Kruszewski M, Brunborg G (2012) Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles in testicular cells. Toxicology 291(1–3):65–72
Aubert T, Burel A, Esnault MA, Cordier S, Grasset F, Cabello-Hurtado F (2012) Root uptake and phytotoxicity of nanosized molybdenum octahedral clusters. J Hazard Mater 219–220:111–118
Auffan M, Rose J, Bottero JY, Lowry GV, Jolivet JP, Wiesner MR (2009) Towards a definition of inorganic nanoparticles from an environmental. health and safety perspective. Nat Nanotechnol 4:634–641
El Badawy AM, Silva RG, Morris B, Schekel KG, Suidan MT, Tolaymat TM (2011) Surface charge-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Environ Sci Tech 45:283–287
Badr A (1983) Cytogenetic activities of a triazine herbicide in root tips of Allium cepa and Vicia faba. Mutat Res 117:173–182
Badr A (1987) Effect of the S‑triazine herbicide turbutryn on mitosis, chromosomes and nucleic acids in root tips of Vicia faba. CYTOLOGIA 51:571–577
Badr A, El-Shazly HH, Halawa M (2014) Cytological effects of gamma radiation and its impact on growth and yield of M1 and M2 Plants of Cowpea Cultivars. Cytologia 79(2):195–206
Becaro AA, Siqueira MC, Puti FC, de Moura MR, Correa DS, Marconcini JM, MattosoLuiz HC, Ferreira MD (2017) Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticle/carboxymethyl cellulose on Allium cepa. Environ Monit Assess 189(7):352
Bonigala B, Kasukurthi B, Konduri VV, Mangamuri UK, Gorrepat R, Poda S (2018) Green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Stemona Tuberosa lour and screening for their catalytic activity in the degradation of toxic chemicals. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(32):32540–32548
Choudhury PR, Tanveer H, Dixit GP (2006) Identification and detection of genetic relatedness among important varieties of pea (Pisum sativum L.) grown in India. Genetica 130:183–191
Cieslarová J, Smýkal P, Dočkalová Z, Hanáček P, Procházka S, Hýbl M, Griga M (2011) Molecular evidence of genetic diversity changes in pea (Pisum sativum L.) germplasm after long-term maintenance. Genet Resour Crop Evol 58:439–451
Cvjetko P, Milošic A, Domijan AM, VinkovićVrček I, Tolić S, PeharecŠtefanić P, Letofsky-Papst I, Tkalec M, Balen B (2017) Toxicity of silver ions and differently coated silver nanoparticles in Allium cepa roots. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 137:18–28
Darlington , LaCour (1976) The handling of chromosomes, 6th edn. LF.La Cour. Allen And Unwin, London
Darroudi M, Ahmad MB, Abdullah AH, Ibrahim NA (2011) Green synthesis and characterization of gelatin-based and sugar-reduced silver nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed 6:569–574
Dash S, Panda KK, Pand BB (1988) Biomonitoring of low levels of mercurial derivatives in water and soil by Allium micronucleus assay. Mutat Res 203:11–21
Debnath P, Mondal A, Hajra A, Das C, Mondal NK (2018) Cytogenetic effects of silver and gold nanoparticles on Allium ceparoots. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 16(2):519–526
El-Azab EM, Soliman MA, Soliman E, Badr A (2018) Cytogenetic impact of gamma irradiation and its effects on growth and yield of three soybean cultivars. Egypt J Bot 58(3):411–422
Elavazhagan T, Arunachalam KD (2011) Memecylonedule leaf extract mediated green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed 6:1265–1278
Elghamery AA, Elnahas AI, Mansour MM (2000) The action of atrazine herbicide as an inhibitor of cell division on chromosomes and nucleic acids content in root meristems of Allium cepa and Vicia faba. Cytologia 55:209–215
Fahmy HM, Mosleh AM, Elghany AA, Shams-Eldin E, Abu Serea ES, Ali SA, et al (2019) Coated silver nanoparticles: synthesis, cytotoxicity, and optical properties. RSC Adv 9 (35):20118–20136
Fehér A, Ötvös K, Pasternak TP, Szandtner AP (2008) The involvement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the cell cycle activation (G0-to-G1) transition of plant cells. Plant Signal Behav 3(10):823–826
Gaulden ME (1987) Hypothesis: some mutagens directly alter specific chromosomal proteins to produce chromosome stickiness. Mutagenesis 2(5):357–365
Ghormade V, Deshpande MV, Paknikar KM (2011) Perspectives for nano-biotechnology enabled protection and nutrition of plants. Biotechnol Adv 29(6):792–803
Grant WF (1999) Higher plant assays for the detection of chromosomal aberrations and gene mutations—A brief historical background on their use for screening and monitoring environmental chemicals. Mutat Res 426:107–112
Grover IS, Kaur S (1999) Genotoxicity of wastewater samples from sewage and industrial effluent detected by the Allium root anaphase aberration and micronucleus assays. Mutat Res 426(2):183–188
Gudikandula K, Vadapally P, Singara Charya MA, (2017) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles from white rot fungi: Their characterization and antibacterial studies. OpenNano 2:64–78
Hackenberg S, Scherzed A, Kessler M, Humme S, Technau A, Froelich K, Ginzkey C, Koehler C, Hagen R, Kleinsasser N (2011) Silver nanoparticles: Evaluation of DNA damage, toxicity and functional impairment in human mesenchymal stem cells. Toxicol Lett 201(1):27–33
Jyoti K, Baunthiyal M, Singh A (2016) Characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Urtica dioica Linn leaves and their synergistic effects with antibiotics. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 9(3):217–227
Kettler K, Veltman K, van de Meent D, van Wezel A, Hendriks AJ (2014) Cellular uptake of nanoparticles as determined by particle properties, experimental conditions, and cell type. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:481–492
Kowshik M, Ashtaputre S, Kharrazi S, Vogel W, Urban J, Kulkarni SK, Paknikar KM (2003) Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by a silver-tolerant yeast strain MKY3. Nanotechnology 14:95–100
Kumar G, Rai P (2006) Partial genome elimination through micronuclei in soybean (Glycine max). Natl Acad Sci Lett 29:417–421
Lamsal K, Kim SW, Jung JH, Kim YS, Kim KS, Lee YS (2011) Inhibition effects of silver nanoparticles against powdery mildews on cucumber and pumpkin. Mycobiology 39:26–32
Lee J, Brooks M, Gerfen JR, Wang Q, Fotis C, Sparer A, Ma X, Berg RH, Geisler M (2014) Reproductive toxicity and life history study of silver nanoparticle effect, uptake and transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nanomaterials 4:301–318
Lee S, Chung H, Kim S, Lee I (2013) The Genotoxic effect of znO and CuO nanoparticles on early growth of buckwheat, Fagopyrum esculentum. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1668–1678
Liman R, Akyıl D, Eren Y, Konuk M (2010) Testing of the mutagenicity and genotoxicity of metolcarb by using both Ames/Salmonella and Allium test. Chemosphere 80(9):1056–1061
López-Millán A, Zavala-Rivera P, Esquivel R, Carrillo R, Alvarez-Ramos E, Moreno-Corral R, Guzmán-Zamudio R, Lucero-Acuña A (2017) Aqueous-organic phase transfer of gold and silver nanoparticles using thiol-modified oleic acid. Appl Sci 7(3):273
Maestre-López MI, Payà-Nohales JF, Cuesta-Garrote N, Arán-Ais F, Martínez-Sánchez MA, Orgilés-Barceló C, Bertazz M (2015) Antimicrobial effect of coated leather based on silver nanoparticles and nanocomposites: synthesis, characterisation and microbiological evaluation. J Biotechnol Biomater 5(1):1–10
Magudapathy P, Gangopadhyay P, Panigrahi BK, Nair KGM, Dhara S (2001) Electrical transport studies of Ag nanoclusters embedded in glass matrix. Physica B 299(1–2):142–146
Mamta K, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2009) Genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in Allium cepa. Sci Total Environ 407:5243–5246
Maurer-Jones MA, Gunsolus IL, Murphy CJ, Haynes CL (2013) Toxicity of engineered nanoparticles in the environment. Anal Chem 85(6):3036–3049
Mehmood A, Murtaza G (2017) Application of SNPs to improve yield of Pisum sativum L. (pea). IET Nanobiotechnol 11(4):390–394
Mirzajani F, Askari H, Hamzelou S, Farzaneh M, Ghassempour A (2013) Effect of silver nanoparticles on Oryza sativa L. and its rhizosphere bacteria. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 88:48–54
Mukherjee A, Peralta-Videa JR, Bandyopadhyay S, Rico CM, Zhao L, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2014) Physiological effects of nanoparticulate ZnO in green peas (Pisum sativum L.) cultivated in soil. Metallomics 6(1):132–138
Mukherjee P, Ahmad A, Mandal D, Senapati S, Sainkar SR, Khan MI, Parishcha R, Ajaykumar PV, Alam M, Kumar R, Sastry M (2001) Fungus-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their immobilization in the mycelial matrix: a novel biological approach to nanoparticle synthesis. Nano Lett 1(10):515–519
Murugan K, Benelli G, Ayyappan S, Dinesh D, Panneerselvam C, Nicoletti M, Hwang JS, Kumar PM, Subramaniam J, Suresh U (2015) Toxicity of seaweed-synthesized silver nanoparticles against the filariasis vector Culex quinquefasciatus and its impact on predation efficiency of the cyclopoid crustacean Mesocyclops longisetus. Parasitol Res 114(6):2243–2253
Nair PMG, Chung IM (2014) Physiological and molecular level effects of silver nanoparticles exposure in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Chemosphere 112:105–113
Navarro E, Baun A, Behra R, Hartmann NB, Filser J, Miao AJ, Quigg A, Santschi PH, Sigg L (2008) Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 17:372–386
Okupnik A, Pflugmacher S (2016) Oxidative stress response of the aquatic macrophyte Hydrilla verticillata exposed to TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Chem 35:2859–2866
Pasupuleti VR, Prasad TN, Shiekh RA, Balam SK, Narasimhulu G, Reddy CS, Rahman I, Gan SH (2013) Biogenic silver nanoparticles using Rhinacanthus nasutus leaf extract: synthesis, spectral analysis, and antimicrobial studies. Int J Nanomed 8:3355–3364
Patil BC, Bhat GI (1992) A comparative study of MH and EMS in the induction of chromosomal aberration on lateral root meristem in Clitoria ternatea L. CYTOLOGIA 57:295–264
Patlolla AK, Berry A, May L, Tchounwou PB (2012) Genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in Vicia faba: A pilot study on the environmental monitoring of nanoparticles. Int J Environ Res Public Health 9(5):1649–1662
Paul NS, Yadav RP (2015) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant seeds and their antimicrobial activity. Asian J Biomed Pharm Sci 5(45):26–28
Potapova T, Gorbsky GJ (2017) The Consequences of chromosome segregation errors in mitosis and meiosis. Biology 6(1):1–33
Rajeshkumar S, Malarkodi C, Vanaja M, Annadurai G (2016) Anticancer and enhanced antimicrobial activity of biosynthesizd silver nanoparticles against clinical pathogens. J Mol Struct 1116:165–173
Rastogi A, Zivcak M, Sytar O, Kalaji HM, He X, Mbarki S, Bristic M (2017) Impact of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on plant: a critical review. Front Chem 5:78. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2017.00078
Rico CM, Majumdar S, Duarte-Gardea M, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea Torresdey JL (2011) Interaction of nanoparticles with edible plants and their possible implications in the food chain. J Agr Food Chem 59:3485–3498
Roco MC (2003) Broader societal issue on nanotechnology. J Nanopart Res 5:181–189
Roy F, Boye JI, Simpson BK (2010) Bioactive proteins and peptides in pulse crops: pea, chickpea and lentil. Food Res Int 43:432–442
Sadeghi B, Gholamhoseinpoor F (2015) A Study on the stability and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ziziphora tenuior (Zt) extract at room temperature. Spectrochim Acta 134:310–315
Salama HMH (2012) Effects of silver nanoparticles in some crop plants, common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and corn (Zea mays L.). Int Res J Biotechnol 3:190–197
Satry M, Patil V, Sainkar SR (1998) Electrostatically controlled diffusion of carboxylic acid derivatized silver colloidal particles in thermally evaporated fatty amine films. J Phy Chem B 102(8):1404–1410
Saxena PN, Chauhan LKS, Gupta SK (2005) Cytogenetic effects of commercial formulation of cypermethrin in root meristem cells of Allium sativum: spectroscopic basis of chromosome damage. Toxicology 216(2–3):244–252
Sengottaiyan A, Mythili R, Selvankumar T, Aravinthan A, Kamala Kannan S, Manoharan K, Thiyagarajan P, Govarthanan M, Kim JH (2016) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Solanum indicum L. and their antibacterial, splenocyte cytotoxic potentials. Res Chem Intermediat 42(4):3095–3103
Singhal G, Bhavesh R, Kasariya K, Sharma AR, Singh RP (2011) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi) leaf extract and screening its antimicrobial activity. J Nanopart Res 13:2981–2988
Smaka-Kincl V, Stegnar P, Lovka M, Toman MJ (1996) The evaluation of waste, surface and ground water quality using the Allium test procedure. Mutat Res 368:171–179
Srividya K, Mohanty K (2009) Biosorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by Catlacatla scale: equilibrium and kinetics studies. Chem Eng J 155:666–673
Stampoulis D, Sinha SK, White JC (2009) Assay-dependent phytotoxicity of nanoparticles to plants. Environ Sci Tech 43:9473–9479
Sun RW, Chen R, Chung NP, Ho CM, Lin CL, Che CM (2005) Silver nanoparticles fabricated in Hepes buffer exhibit cytoprotective activities toward HIV‑1 infected cells. Chem Commun 28(40):5059–5061
Tripathi DK, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Chauhan DK, Dubey NK (2015) Silicon nanoparticles (SiNps) alleviate chromium (VI) phytotoxicity in Pisum sativum (L.) seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 96:189–198
Tripathi DK, Singh S, Srivastava PK, Singh VP, Singh S, Prasad SM, Singh PK, Dubey NK, Pandey AC, Chauhan DK (2017a) Nitric oxide alleviates silver nanoparticles (AgNps)-induced phytotoxicity in Pisum sativum seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:167–177
Tripathi DK, Tripathi A, Shweta , Singh S, Singh Y, Vishwakarma K, Yadav G, Sharma S, Singh VK, Mishra RK, Upadhyay RG, Dubey NK, Lee Y, Chauhan DK (2017b) Uptake, accumulation and toxicity of silver nanoparticle in autotrophic plants, and heterotrophic microbes: a concentric review. Front Microbiol 8:1–16
Vannini C, Domingo G, Onelli E, De Mattia F, Bruni I, Marsoni M, Bracale M (2014) Phytotoxic and genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles exposure on germinating wheat seedlings. J Plant Physiol 171:1142–1148
Yi H, Meng Z (2003) Genotoxicity of hydrated sulfur dioxide on root tips of Allium sativum and Vicia faba. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 537:109–114
Yin L, Cheng Y, Espinasse B, Colman BP, Auffan M, Wiesner M, Rose J, Liu J, Bernhardt ES (2011) More than the ions: the effects of silver nanoparticles on Lolium multiflorum. Environ Sci Tech 45(6):2360–2367
Yin L, Colman BP, McGill BM, Wright JP, Bernhard ES (2012) Effects of silver nanoparticle exposure on germination and early growth of eleven wetland plants. Plos One 7(10):1–7
Youssef MS, Elamawi RM (2018) Evaluation of phytotoxicity, cytotoxicity, and genotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles in Vicia faba. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3250-1
Zhu ZJ, Wang H, Yan B, Zheng H, Jiang Y, Miranda OR, Rotello VM, Xing B, Vachet RW (2012) Effect of surface charge on the uptake and distribution of gold nanoparticles in four plant species. Environ Sci Tech 46:12391–12398
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
M. Labeeb, A. Badr, S.A. Haroun, M.Z. Mattar, A.S. El-Kholy and I.M. El-Mehasseb declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labeeb, M., Badr, A., Haroun, S.A. et al. Ecofriendly Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Effects on Early Growth and Cell Division in Roots of Green Pea (Pisum sativum L.). Gesunde Pflanzen 72, 113–127 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-019-00491-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-019-00491-5