Abstract
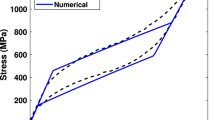
In this study the superelastic behavior of porous shape memory alloys has been simulated in a finite element procedure. The Boyd and Lagoudas plasticity like phenomenological model (Lecce and Concilio in Shape memory alloy engineering: for aerospace, structural and biomedical application, Elsevier, Oxford, 2016) has been developed by incorporating the pore volume fraction parameter to describe the behavior of porous shape memory alloys. Accordingly, to homogenize the porous media, Young’s modulus and the phase transformation function have been defined as functions of pore volume fraction. Furthermore, for random distribution of pores, Bernoulli process has been implemented. A numerical procedure was proposed and executed by a finite element code based on the proposed constitutive model. In finite element models, each pore was defined as a negligible stiffness element. Simulations show that the proposed model could precisely simulate the superelastic behavior of porous SMAs under tensile loading.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashrafi, M.J., Arghavani, J., Naghdabadi, R., Sohrabpour, S., Auricchio, F.: Theoretical and numerical modeling of dense and porous shape memory alloys accounting for coupling effects of plasticity and transformation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 88–89, 248–262 (2016)
Ayers, R., Burkes, D., Gottoli, G., Yi, H.C., Moore, J.J.: The application of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis of engineered porous composite biomedical materials. Mater. Manuf. Process 22, 481–488 (2007)
Bansiddhi, A., Dunand, D.C.: Shape-memory NiTi foams produced by solid-state replication with NaF. Materials Science and Engineering 15(12), 1612–1622 (2007)
Boyd, J.G., Lagoudas, D.C.: A thermodynamic constitutive model for the shape memory alloy materials, Part I: the monolithic shape memory alloy. Int. J. Plast 12(6), 805–842 (1996)
Charalambakis, N.: Homogenization techniques and micromechanics, a survey and perspectives. ASME Appl. Mech. Rev. 63(3), 030803 (2010)
Chiu, S.N., Stoyan, D., Kendall, W.S., Mecke, J.: Stochastic Geometry and Its Applications. Wiley, UK (2013)
DeGiorgi, V.G., Qidwai, M.A.: A computational mesoscale evaluation of material characteristics of porous shape memory alloys. Smart Mater. Struct. 11(3), 435–443 (2002)
Entchev, P.B., Lagoudas, D.C.: Modeling porous shape memory alloys using micromechanical averaging techniques. Mech. Mater. 34(1), 1–24 (2002)
Entchev, P.B., Lagoudas, D.C.: Modeling of transformation-induced plasticity and its effect on the behavior of porous shape memory alloys, part II: porous SMA response. Mech. Mater. 36(9), 893–913 (2004)
Gautam, A., Callejas, M.A., Acharyya, A., Acharyya, S.G.: Shape-memory-alloy-based smart knee spacer for total knee arthroplasty: 3D CAD modelling and a computational study. Med. Engineering & Physics 55, 43–51 (2018)
Gibson, L.J., Ashby, M.F.: Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1999)
Greiner, C., Oppenheimer, S.M., Dunand, D.C.: High strength, low stiffness, porous NiTi with superelastic properties. Acta Biomater. 1(6), 705–716 (2005)
Kim, Y.W., Do, D.: Shape memory characteristics of highly porous Ti-rich TiNi alloys. Mater. Lett. 162, 1–4 (2016)
Krone, L., Schüller, E., Bram, M., Hamed, O., Buchkremer, H.P., Stöver, D.: Mechanical behaviour of NiTi parts prepared by powder metallurgical methods. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 378, 185–190 (2004)
Lagoudas, D.C.: Shape Memory Alloys: Modeling and Engineering Applications. Springer, New York (2008)
Lecce, L., Concilio, A.: Shape Memory Alloy Engineering: For Aerospace, Structural and Biomedical Application. Elsevier, Oxford (2016)
Liu, B., Dui, G., Zhu, Y.: On phase transformation behavior of porous shape memory alloys. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 5(1), 9–15 (2012)
Moss, W.: On the computational significance of the strain space formulation of plasticity theory. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 20, 1703–1709 (1984)
Nemat-Nasser, S., Su, Y., Guob, W.G., Isaacsa, J.: Experimental characterization and micromechanical modeling of superelastic, response of a porous NiTi shape-memory alloy. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 53(10), 2320–2346 (2005)
Olsen, J.S., Zhang, Z.L.: Effect of spherical micro-voids in shape memory alloys subjected to uniaxial loading. Int. J. Solids Struct. 49(14), 1947–1960 (2012)
Panico, M., Brinson, L.C.: Computational modeling of porous shape memory alloys. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45(21), 5613–5626 (2008)
Ponsonnet, L., Treheux, D., Lissac, M., Jaffrezic, N., Grosgogeat, B.: Review of in vitro studies on the biocompatibility of NiTi alloys. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 23(3–4), 147–151 (2006)
Qidwai, M.A., Entchev, P.B., Logoudas, D.C., DeGiorgi, V.G.: Modeling of the thermomechanical behavior of porous Shape memory alloy. Int. J. Solids Struct. 38(48–49), 8653–8671 (2001)
Sayed, T., Gurses, E., Siddiq, A.: A phenomenological two-phase constitutive model for porous shape memory alloys. Comput. Mater. Sci. 60, 44–52 (2012)
Sepe, V., Marfia, S., Auricchio, F.: Response of porous SMA: a micromechanical study. Frattura ed Integrità Strutturale 8(29), 85–96 (2014)
Sepe, V., Auricchio, F., Marfia, S., Sacco, E.: Micromechanical analysis of porous SMA. Smart Mater. Struct. 24(8), 1–20 (2015)
Sepe, V., Auricchio, F., Marfia, S., Sacco, E.: Homogenization techniques for the analysis of porous SMA. Comput. Mech. 57(5), 755–772 (2016)
Shearwood, C., Fu, Y.Q., Yu, L., Khor, K.A.: Spark plasma sintering of TiNi nano-powder. Script Mater. 52, 455–460 (2005)
Starosvetsky, D., Gotman, I.: Corrosion behavior of titanium nitride coated Ni–Ti shape memory surgical alloy. Biomaterials 22, 1853–1859 (2001)
Tanaka, K.: Thermomechanical sketch of shape memory effect: one-dimensional tensile behavior. International Journal of Structural Mechanics and Materials Science 18(3), 251–263 (1986)
Teppei, W., Yoshimi, W., Hiroshi, O.: Development of Fe–Mn–Si–Cr shape memory alloy fiber reinforced plaster based smart composites. Mater. Sci. Forum 475, 2063–2066 (2005)
Turner, C.H., Rho, J., Takano, Y., Tsui, T.Y., Pharr, G.M.: The elastic properties of trabecular and cortical bone tissues are similar: results from two microscopic measurement techniques. J. Biomech. 32(4), 437–441 (1999)
Whitney, M., Corbin, S.F., Gorbet, R.B.: Investigation of the mechanisms of reactive sintering and combustion synthesis of NiTi using differential scanning calorimetry and microstructural analysis. Acta Mater. 56, 559–570 (2008)
Zhao, Y., Taya, M.: Analytical modeling for stress–strain curve of a porous NiTi. J. Appl. Mech. 74(2), 291–297 (2007)
Zhao, Y., Taya, M., Izui, H.: Study on energy absorbing composite structure made of concentric NiTi spring and porous NiTi. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43(9), 2497–2512 (2006)
Zhu, Y., Dui, G.: A model considering hydrostatic stress of porous NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mech. Solida Sinica 24(4), 289–298 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdollahzadeh, M., Hoseini, S.H. & Faroughi, S. Modeling of superelastic behavior of porous shape memory alloys. Int J Mech Mater Des 16, 109–121 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-019-09457-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-019-09457-x