Abstract
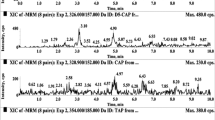
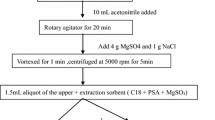
In this study, a preliminary food quality and safety assessment was performed on organic and cage-free egg samples marketed in the state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, that were analyzed concerning veterinary drug and pesticide residues using high performance and ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. The polyether ionophore salinomycin was detected in two organic egg samples (25% of the organic samples), one with an estimated concentration even higher than the maximum permissible amount of 3 µg kg−1 established for conventional eggs by the European Commission. The other sample presented a concentration higher than the limit of detection of 0.3 µg kg−1, but lower than the lowest calibration level of 1.5 µg kg−1. Regarding pesticide residues, spiroxamine, pirimiphos, mephosfolan and pyraclostrobin were identified at residual levels below the lowest calibration level of 4.5 µg kg−1, except for one organic egg sample, presenting 8.3 µg kg−1 of spiroxamine. Spiroxamine was identified in 62% of the assessed samples. These findings indicate that non-conformities were found even with a limited number of samples, impacting the confidence in the quality of organic and cage-free alternative systems in egg production. The hazard index (HI) approach demonstrated that chemical food safety might be at risk, since a mixture of the detected analytes may pose a risk for children up to 27 kg, through egg consumption.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABNT (2016) Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas. Avicultura, Produção, classificação e identificação do ovo caipira, colonial ou capoeira. NBR 16437. ABNT, Rio de Janeiro
Akhtar MH, El-Sooud KA, Shehata MAA (1996) Concentrations of salinomycin in eggs and tissues of laying chickens fed medicated feed for 14 days followed by withdrawal for 3 days. Food Addit Contam A 13(8):897–907
ANVISA (2018) Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. Programa de Análise de Resíduos de Agrotóxicos em Alimentos (PARA). http://portal.anvisa.gov.br/programa-de-analise-de-registro-de-agrotoxicos-para. Accessed 10 May 2019
Baars AJ, Theelen RMC, Janssen PJCM, Hesse JM, van Apeldoorn ME, Meijerink MCM et al (2001) Re-evaluation of human-toxicological maximum permissible risk levels. https://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/rapporten/711701025.pdf. Accessed 11 Oct 2019
Botsoglou NA, Fletouris DJA (2001) Stability of residues during food storage, cooking, and processing. In: Fletouris DJ (ed) Drug residues in foods: pharmacology, food safety and analysis. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 515–535
Brasil (1999) Ministério da Agricultura e do Abastecimento. Secretaria de Defesa Agropecuária. Ofício Circular/DIPOA nº 60/99 de 04/11/1999. Registro do Produto “Ovos Caipira” ou “Ovos Tipo ou Estilo Caipira” ou “Ovos Colonial” ou “Ovos Tipo ou Estilo Colonial”
Brasil (2011) Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Instrução normativa nº 46, de 06 de outubro de 2011. Estabelece o Regulamento Técnico para os Sistemas Orgânicos de Produção, bem como as listas de substâncias e práticas permitidas para uso nos Sistemas Orgânicos de Produção. D O U Brasil. Brasília. Seção 1
Brasil (2019) Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Plano Nacional de Controle de Resíduos e Contaminantes—PNCRC/Animal. http://www.agricultura.gov.br/assuntos/inspecao/produtos-animal/plano-de-nacional-de-controle-de-residuos-e-contaminantes. Accessed 18 July 2019
CAC (2014) Codex Alimentarius Commission. Guidelines for the design and implementation of national regulatory food safety assurance programme associated with the use of veterinary drugs in food producing animals. CAC/GL 71-2009. Revision 2014. http://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/en/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCAC%2BGL%2B71-2009%252FCXG_071e_2014.pdf. Accessed 18 June 2018
CEC (2008) Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 889/2008 of 5 September 2008 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 834/2007 on organic production and labelling of organic products with regard to organic production, labelling and control. Off J Eur Union L250:1-84. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=uriserv:OJ.L_.2008.250.01.0001.01.ENG&toc=OJ:L:2008:250:TOC. Accessed 18 June 2018
CEC (2009) Commission of the European Communities. Commission Regulation (EC) No. 124/2009 of 10 February 2009 setting maximum levels for the presence of coccidiostats or histomonostats in food resulting from the unavoidable carry-over of these substances in non-target feed. Off J Eur Commun L40:7–11
Dorne JLCM, Fernández-Cruz ML, Bertelsen U, Renshaw DW, Peltonen K, Anadon A et al (2013) Risk assessment of coccidostatics during feed cross-contamination: animal and human health aspects. Toxicol Appl Pharm 270(3):196–208
EC (2002) European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No. 657/2002 of 12 August 2002 on implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off J Eur Commun L 221:8–36
EC (2010) European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No. 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin. Off J Eur Commun L15:1–72
EC (2018) European Commission. Plants EU—Pesticides database. http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/public/?event=pesticide.residue.CurrentMRL&language=EN. Accessed 11 May 2018
Hernández AF, Parrón T, Tsatsakis AM, Requena M, Alarcón R, López-Guarnido O (2013) Toxic effects of pesticide mixtures at a molecular level: their relevance to human health. Toxicology 307:136–145
Landoni MF, Albarellos G (2015) The use of antimicrobial agents in broiler chickens. Vet J 205(1):21–27
Leclercq R (2002) Mechanisms of resistance to macrolides and lincosamides: nature of the resistance elements and their clinical implications. Clin Infect Dis 34(4):482–492
Luo P, Liu X, Kong F, Chen L, Wang Q, Li W et al (2019) Simultaneous determination of 169 veterinary drugs in chicken eggs with EMR-Lipid clean-up using ultra-high performance liquid chromatograph tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Methods 11:1657–1662
MAPA (2019) Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento. Fichas Agroecológicas. http://www.agricultura.gov.br/assuntos/sustentabilidade/organicos/fichas-agroecologicas/capa-fichas-agroecologicas. Accessed 14 May 2019
Mertzig K, Hardebusch B, Obrecht K, Lippold R (2012) Comparison of 3 different MRM methods for analysing pesticide residues in eggs. In: Paper presented at: EPRW 2012. Proceedings of the 9th European Pesticide Residue Workshop; June 25–28; Vienna, Austria
Organicsnet (2016) Mercado de orgânicos cresce o dobro no Brasil. http://www.organicsnet.com.br/2016/01/mercado-de-organicos-cresce-o-dobro-no-brasil. Accessed 7 June 2018
Palermo-Neto J (2005) Resíduos de Medicamentos Veterinários em Carne de Frango e Ovos. In: Palermo-Neto J, Spinosa HS, Górniak SL (eds) Farmacologia Aplicada à Avicultura: Boas Práticas do Manejo de Medicamentos. Roca, São Paulo, pp 287–302
Piatkowska M, Jedziniak P, Zmudzki J (2016) Multiresidue method for the simultaneous determination of veterinary medicinal products, feed additives and illegal dyes in eggs using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 197:571–580
SANTE (2018) Guidance document on analytical quality control and method validation procedures for pesticide residues analysis in food and feed. Document No SANTE/11813/2017. Implemented by 01 January 2018
SINDAN (2018) Sindicato Nacional da Indústria de Produtos para Saúde Animal. Compêndio de Produtos Veterinários Edição eletrônica de produtos veterinários de uso permitido no Brasil. http://www.cpvs.com.br/cpvs. Accessed 26 Feb 2018
Šinigoj-GačniK K, Zorman RO (2008) Salinomycin concentration in eggs and tissues of laying hens. Acta Vet 77(3):423–429
Song NE, Lee JY, Mansur OR, Jang HW, Lim MC, Lee Y et al (2019) Determination of 60 pesticides in hen eggs using the QuEChERS procedure followed by LC–MS/MS and GC–MS/MS. Food Chem 298:125050
Souza MCM (2001) Certificação de Produtos Orgânicos. Secretaria de Agricultura e Abastecimento do Estado de São Paulo: Instituto de Economia Agrícola. http://www.iea.sp.gov.br/out/verTexto.php?codTexto=260. Accessed 20 June 2018
Spisso BF, Ferreira RG, Pereira MU, Monteiro MA, Cruz TA, Costa RP et al (2010a) Simultaneous determination of polyether ionophores, macrolides and lincosamides in hen eggs by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry using a simple solvent extraction. Anal Chim Acta 682(1–2):82–92
Spisso BF, Pereira MU, Ferreira RG, Monteiro MA, Costa RP, Cruz TA et al (2010b) Pilot survey of hen eggs consumed in the metropolitan area of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, for polyether ionophores, macrolides and lincosamides residues. Food Addit Contam B 3(4):212–219
Tiryaki O (2017) Pesticide residues and organic production. J Biol Environ Sci 11:11–23
USDA (2015) United States Department of Agriculture. Agricultural Marketing Service. Guidelines for Organic Certification of Poultry. https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media/Poultry%20-%20Guidelines.pdf. Accessed 7 June 2018
WHO (2017) World Health Organization. Critically important antimicrobials for human medicine: Ranking of antimicrobial agents for risk management of antimicrobial resistance due to non-human use. http://www.who.int/foodsafety/areas_work/antimicrobial-resistance/cia/en. Accessed 7 June 2018
Xu X, Xi Xu, Han M, Qiu S, Hou X (2019) Development of a modified QuEChERS method based on magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for the simultaneous determination of veterinary drugs, pesticides and mycotoxins. Food Chem 276:419–426
Zhang X, Song Y, Jia Q, Zhang L, Zhang W, Mu P et al (2019) Simultaneous determination of 58 pesticides and relevant metabolites in eggs with a multi-functional filter by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1593:81–90
Acknowledgements
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, M.U., Cândido, F.S., de Oliveira, A.C. et al. A preliminary study of simultaneous veterinary drug and pesticide residues in eggs produced in organic and cage-free alternative systems using LC–MS/MS. J Food Sci Technol 57, 1719–1730 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04205-7
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-04205-7