Abstract
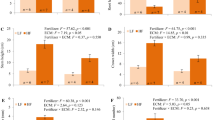
Seedling quality is important for subtropical tree species endangered by the degradation of natural habitats in southern China. At present, the cultural regime for raising these seedlings involving fertilizer levels and size of container is not clear. In this study, seedlings of three endangered species, red-seed tree (Ormosia hosiei), Zhejiang phoebe (Phoebe chekiangensis), and Zhejiang camphor (Cinnamomum japonicum) were evaluated along with red-bark oak (Cyclobalanopsis gilva) as a reference, a species which is not endangered. Seedlings were raised in 2.8, 3.6, 5.1, and 6.3 L containers and fertilizer applied at 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and 4.0 kg m−3. Seedling height and leaf biomass increased in response to higher fertilizer levels while larger containers resulted in greater stem and root biomass. Root biomass of endangered species seedlings did not respond to neither treatments. Zhejiang phoebe seedlings responded to nitrogen and phosphorus uptake but red-seed tree seedlings were unaffected by any nutrient levels. Red-bark oak seedlings had high nitrogen-use efficiency. Based on the results, it is recommended using at least 5.1 L containers to culture Zhejiang phoebe and Zhejiang camphor seedlings with fertilizer at 3.0 kg m−3. Red-bark oak and red-seed tree seedlings should be cultured with 2.0 kg m−3 in smaller containers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aphalo P, Rikala R (2003) Field performance of silver birch planting-stock grown at different spacing and in containers of different volume. New For 25:93–108
Chirino E, Vilagrosa A, Hernández EI, Matos A, Vallejo VR (2008) Effects of a deep container on morpho-functional characteristics and root colonization in Quercus suber L. seedlings for reforestation in Mediterranean climate. For Ecol Manag 256:779–785
Close DC, Paterson S, Corkrey R, McArthur C (2010) Influence of seedling size, container type and mammal browsing on the establishment of Eucalyptus globulus in plantation forestry. New For 39:105–115
De La Fuente LM, Ovalle JF, Arellano EC, Ginocchio R (2017) Use of alternative containers for promoting deep rooting of native forest species used for dryland restoration: the case of Acacia caven. iForest Biogeosci For 10:776–782
De Oliveira JRG, Silva EME, Teixeira-Rios T, De Melo NF, Yano-Melo AM (2015) Response of an endangered tree species from Caatinga to mycorrhization and phosphorus fertilization. Acta Bot Bras 29:94–102
Dos Santos UM, Goncalves JFD, Feldpausch TR (2006) Growth, leaf nutrient concentration and photosynthetic nutrient use efficiency in tropical tree species planted in degraded areas in central Amazonia. For Ecol Manag 226:299–309
Dumroese RK, Davis AS, Jacobs DF (2011) Nursery response of Acacia koa seedlings to container type, irrigation method, and fertilization rate. J Plant Nutr 34:877–887
Frournier A, Barbet-Massin M, Rome Q, Courchamp F (2017) Predicting species distribution combining multi-scale drivers. Global Ecol Conserv 12:215–216
Guo J, Wu YQ, Wang B, Lu Y, Cao FL, Wang GB (2016) The effect of fertilization on the growth and physiological characteristics of Ginkgo biloba L. Forests 7:293
Haywood JD, Susana Sung SJ, Sword Sayer MA (2011) Copper root pruning and container cavity size influence longleaf pine growth through five growing seasons. South J Appl For 36:146–151
Hess L, De Kroon H (2017) Effects of rooting volume and nutrient availability as an alternative explanation for root self/non-self discrimination. Br Ecol Soc 95:241–251
Hu YB, Fernández V, Ma L (2014) Nitrate transporters in leaves and their potential roles in foliar uptake of nitrogen dioxide. Fron Plant Sci 5:360
Hu YB, Peuke AD, Zhao XY, Yan JX, Li CM (2019) Effects of simulated atmospheric nitrogen deposition on foliar chemistry and physiology of hybrid poplar seedlings. Plant Physiol Bioch 143:94–108
Kostopoulou P, Radoglou K, Papanastasi OD, Adamidou C (2011) Effect of mini-plug container depth on root and shoot growth of four forest tree species during early developmental stages. Turk J Agric For 35:379–390
Li XW, Gao Y, Wei HX, Xia HT, Chen QX (2017) Growth, biomass accumulation and foliar nutrient status in fragrant rosewood (Dalbergia odorifera T.C. Chen) seedlings cultured with conventional and exponential fertilizations under different photoperiod regimes. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 63:153–162
Li XW, Chen QX, Lei HQ, Wang JW, Yang S, Wei HX (2018) Nutrient uptake and utilization by fragrant rosewood (Dalbergia odorifera) seedlings cultured with oligosaccharide addition under different lighting spectra. Forests 9:29
Liao JX, Chen J, Jiang MX, Huang HD (2012) Leaf traits and persistence of relict and endangered tree species in a rare plant community. Funct Plant Ecol 39:512–518
Luo J, Qin JJ, He FF, Li H, Liu TX, Polle A, Peng CH, Luo ZB (2013) Net fluxes of ammonium and nitrate in association with H+ fluxes in fine roots of Populus popularis. Planta 237:19–31
Mariotti B, Maltoni A, Chiarabaglio PM, Giorcelli A, Jacobs DF, Tognetti R, Tani A (2015a) Can the use of large, alternative nursery containers aid in field establishment of Juglans regia and Quercus robur seedlings? New For 46:773–794
Mariotti B, Maltoni A, Jacobs DF, Tani A (2015b) Container effects on growth and biomass allocation in Quercus robur and Juglans regia seedlings. Scand J For Res 30:401–415
NeSmith DS, Duval JR (1998) The effect of container size. Am Soc Hortic Sci 8:495–498
Oliet JA, Puértolas J, Lanelles R, Jacobs DF (2013) Nutrient loading of forest tree seedlings to promote stress resistance and field performance: a Mediterranean perspective. New For 44:649–669
Pinto JR, Marshall JD, Dumroese RK, Davis AS, Cobos DR (2011) Establishment and growth of container seedlings for reforestation: a function of stocktype and edaphic conditions. For Ecol Manag 261:1876–1884
Pokharel P, Chang SX (2016) Exponential fertilization promotes seedling growth by increasing nitrogen retranslocation in trembling aspen planted for oil sands reclamation. For Ecol Manag 372:35–43
Poorter H, Bühler J, van Dusschoten D, Climent J, Postma JA (2012) Pot size matters: a meta-analysis of the effects of rooting volume on plant growth. Funct Plant Biol 39:839–850
Qingyuan People’s Government (2018) The general description of Qingyuan County, China. http://www.zjqy.gov.cn/zjqy/qygk/. Accessed 23 Dec 2018
Salifu KF, Timmer VR (2003) Optimizing nitrogen loading of Picea mariana seedlings during nursery culture. Can J For Res 33:1287–1294
Salto CS, Harrand L, Javier Oberschelp GP, Ewens M (2016) Growth of Prosopis alba seedlings on different substrates, containers and nursery conditions. Bosque 37:527–537
Thomas BR, Schreiber SG, Kamelchuk DP (2016) Impact of planting container type on growth and survival of three hybrid poplar clones in central Alberta, Canada. New For 47:815–827
Tian N, Fang SZ, Yang WX, Shang XL, Fu XX (2017) Influence of container type and growth medium on seedling growth and root morphology of Cyclocarya paliurus during nursery culture. Forests 8:387
United Nations (2015) Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World urbanization prospects: the 2014 revision. United Nations, New York, USA, pp 1–3. Working Paper No. ST/ESA/SER.A/366
United Nations (2017) Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects: The 2017 revision, key findings and advance tables. United Nations, New York, USA, pp 1–4. Working Paper No. ESA/P/WP/248
Wan JZ, Wang CJ, Qu H, Liu R, Zhang QX (2018) Vulnerability of forest vegetation to anthropogenic climate change in China. Sci Total Environ 621:1633–1641
Wang Z, Zhao Y, Wei HX (2017) Chitosan oligosaccharide addition affects current-year shoot of post-transplant Buddhist pine (Podocarpus macrophyllus) seedlings under contrasting photoperiods. iForest Biogeosci For 10:715–721
Warren CR (2011) How does P affect photosynthesis and metabolite profiles of Eucalyptus globulus? Tree Physiol 31:727–739
Wei HX, Ren J, Zhou JH (2013) Effect of exponential fertilization on growth and nutritional status in Buddhist pine (Podocarpus macrophyllus [Thunb.] D. Don) seedlings cultured in natural and prolonged photoperiods. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 59:933–941
Wei HX, Xu CY, Ma LY, Duan J, Jiang LN, Ren J (2014) Effect of late-season fertilization on nutrient reserves and carbohydrate accumulation in bareroot Larix olgensis seedlings. J Plant Nutr 37:279–293
Wei HX, Guo P, Zheng HF, He XY, Wang PJ, Ren ZB, Zhai C (2017) Micro-scale heterogeneity in urban forest soils affects fine root foraging by ornamental seedlings of Buddhist pine and Northeast yew. Urban For Urban Green 28:63–72
World Conservation Monitoring Centre (1998a) Ormosia hosiei. The IUCN Red list of threatened species e.T32432A9706557. Accessed 07 Apr 2018
World Conservation Monitoring Centre (1998b) Phoebe chekiangensis. The IUCN Red list of threatened species e.T32438A9707020. Accessed 07 Apr 2018
World Conservation Monitoring Centre (1998c) Cinnamomum japonicum. The IUCN Red list of threatened species e.T32390A9696302. Accessed 07 Apr 2018
Zhao Y, Wang Z, Wei HX, Bao YJ, Guo P (2017) Effect of prolonged photoperiod on morphology, biomass accumulation and nutrient utilization in post-transplant Taxus Cuspidata seedlings. Pak J Bot 49:1285–1290
Zhu KY, Liu HC, Wei HX, Zhou JH, Zou QC, Ma GY, Zhang JQ (2016) Prediction of nutrient leaching from culture of containerized Buddhist pine and Japanese maple seedlings exposed to extended photoperiod. Int J Agric Biol 18:425–434
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Rongzhou Man and MyaRice, both of them are from Ontario Forest Research Institute in Canada, for the polishing work and suggestions for the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project funding: This work was supported by “Forestry Science and Technology Cooperation Project between Zhejiang Province and Chinese Academy of Forestry (2017SY19)” and “Fundamental Research Funds of CAF” (CAFYBB2018GC003).
The online version is available at https://www.springerlink.com.
Corresponding editor: Yanbo Hu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, X., Wang, X., Zhang, D. et al. Effects of fertilization and container-type on nutrient uptake and utilization by four subtropical tree seedlings. J. For. Res. 31, 1201–1213 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-019-01070-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-019-01070-0