Abstract
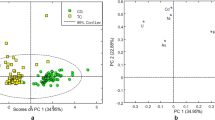
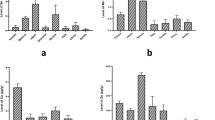
The background level of lead (Pb) in drinking water in Serbia represents a significant health issue. The aim of study was to examine the content of significant toxic and essential trace metals (Mn, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Cd, Pb, Th, and U) in the thyroid tissues with diagnosed colloid goiter (CG). Different variables were investigated (sex, age, smoking habits, goiter size, and previous history of any thyroid disease). The study was designed to compare the goiter tissues (GTs) to sex- and age-matched healthy- and malignant-thyroid tissues (HTTs and MTTs, respectively). All trace metals were quantified by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The reduced content of essential elements (Mn and Se) and increased content of toxic metals (Pb, Th, and U) were found in GTs compared with HTTs. The increased content of the same toxic metals separated GTs from MTTs, as well as reduced content of Mn and Cd. Our results indicated that Pb acts as the main goitrogen, which could highlight its role in the unknown etiology of CG disease. Pb/Se ratio could be considered as a relevant parameter for the tissue separation of GTs from HTTs and/or MTTs. This research also provides novel data on the effects of metal pollutants on thyroid health hazards.
Graphical Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ademova IG, Chumachenko AN (2007) Morphological characteristics of various thyroid pathologies in the population living in a technogenically polluted area. Arkh Patol 69:24–28
Badiei K, Nikghadam P, Mostaghni K, Zarifi M (2009) Effect of lead on thyroid function in sheep. Iran J Vet Res 10:223–227
Bahn RS, Castro MR (2011) Approach to the patient with nontoxic multinodular goiter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:1202–1212
Barany E, Bergdahl IA, Bratterby LE, Lundh T, Samuelson G, Schutz A, Skerfving S, Oskarsson A (2002) Relationship between trace element concentrations in human blood and serum. Toxicol Lett 134:177–184
Blazewicz A, Dolliver W, Sivsammye S, Deol A, Randhawa R, Orlicz-Szczesna G, Blazewicz R (2010) Determination of cadmium, cobalt, copper, iron, manganese, and zinc in thyroid glands of patients with diagnosed nodular goiter using ion chromatography. J Chromatogr B 878:34–38
Borković-Mitić S, Pavlović S, Perendija B, Despotović S, Gavrić J, Gačić Z, Saičić Z (2013) Influence of some metal concentrations on the activity of antioxidant enzymes and concentrations of vitamin E and SH-groups in the digestive gland and gills of the freshwater bivalve Unio tumidus from the Serbian part of Sava River. Ecol Indic 32:212–221
Buha A, Matovic V, Antonijevic B, Bulat Z, Curcic M, Renieri EA, Tsatsakis AM, Schweitzer A, Wallace D (2018) Overview of cadmium thyroid disrupting effects and mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci 19:1–19
Bursalioglu EO, Alkan FA, Barutcu UB, Demir M, Karabul Y, Balkan B, Oz E, Icelli O (2017) Prediction of electron density and trace element concentrations in human blood serum following radioiodine therapy in differentiated thyroid cancer patients. Measurement 100:19–25
Canas AI, Cervantes-Amat M, Esteban M, Ruiz-Moraga M, Perez-Gomez B, Mayor J, Castano A (2014) Blood lead levels in a representative sample of the Spanish adult population: The BIOAMBIENT.ES project. Int J Hyg Envir Health 217:452–459
Chen A, Kim SS, Chung E, Dietrich KN (2013) Thyroid hormones in relation to lead, mercury, and cadmium exposure in the National health and nutrition examination survey, 2007-2009. Environ Health Persp 121:181–186
Chung HK, Nam JS, Ahn CW, Lee YS, Kim KR (2016) Some elements in thyroid tissue are associated with more advanced stage of thyroid cancer in Korean women. Biol Trace Elem Res 171:54–62
Dundar B, Oktem F, Arslan MK, Delibas N, Baykal B, Arslan C, Gultepe M, Ilhan IE (2006) The effect of long-term low-dose lead exposure on thyroid function in adolescents. Environ Res 101:140–145
Frilling A, Liu C, Weber F (2004) Benign multinodular goiter. Scan J Surg 93:278–281
Fuhrer D, Bockisch A, Schmid KW (2012) Euthyroid goiter with and without nodules-diagnosis and treatment. Dtsch Arztebl Int 109:506–516
Giray B, Arnaud J, Sayek I, Favier A, Hincal F (2010) Trace elements status in multinodular goiter. J Trace Elem Med Biol 24:106–110
Goulle JP, Saussereau E, Mahieu L, Guerbet M (2014) Current role of ICP-MS in clinical toxicology and forensic toxicology: a metallic profile. Bioanalysis 6:2245–2259
Gustafson A, Hedner P, Schutz A, Skerfving S (1989) Occupational lead exposure and pituitary function. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 61:277–281
Hegedus L, Bonnema SJ, Bennedbeak FN (2003) Management of simple nodular goiter: current status and future perspectives. Endocr Rev 24:102–132
Hon Z, Osterreicher J, Navratil L (2015) Depleted uranium and its effects on humans. Sustainability 7:4063–4077
Izah SC, Chakrabarty N, Srivastav AL (2016) A review on heavy metal concentration in potable water sources in Nigeria: human health effects and mitigating measures. Expo Health 8:285–304
Jomova K, Valko M (2011) Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 283:65–87
Kampa M, Castanas E (2008) Human health effects of air pollution. Environ Pollut 151:362–367
Kim HJ, Lim HS, Lee KR, Choi MH, Kang NM, Lee CH, Oh EJ, Park HK (2017) Determination of trace metal levels in the general population of Korea. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:1–12
Kucharzewski M, Braziewicz J, Majewska U, Gozdz S (2002) Concentration of selenium in the whole blood and the thyroid tissue of patients with various thyroid diseases. Biol Trace Elem Res 88:25–30
Kucharzewski M, Braziewicz J, Majewska U, Gozdz S (2003) Copper, zinc, and selenium in whole blood and thyroid tissue of people with various thyroid diseases. Biol Trace Elem Res 93:9–18
Lam S, Lang BHH (2014) A review of the pathogenesis and management of multinodular goiter. In: Diaz Soto G (ed) Thyroid disorders: focus on hyperthyroidism. Rijeka, Croatia, Intech, pp 25–35
Lasisz B, Zdrojewicz Z, Marcinkowski Z (1992) Effect of lead on thyroid function. Wiad Lek 45:116–119
Lazarević K, Nikolić D, Lj Stošić, Milutinović S, Videnović J, Bogdanović D (2012) Determination of lead and arsenic in tobacco and cigarettes: an important issue of public health. Cent Eur J Public Health 20:62–66
Mahato MK, Singh PK, Tiwari AK, Singh AK (2016) Risk assessment due to intake of metals in groundwater of East Bokaro Coalfield, Jharkhand, India. Expo Health 8:265–275
Makokha VA, Qi Y, Shen Y, Wang J (2016) Concentrations, distribution, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the East Dongting and Honghu Lake, China. Expo Health 8:31–41
Maksimović ZJ, Djujić I, Jović V, Ršumović M (1992) Selenium deficiency in Yugoslavia. Biol Trace Elem Res 33:187–196
Manojlović M, Singh BR (2012) Trace elements in soils and food chains of the Balkan region. Acta Agric Scand B. 62:673–695
Marcelo MA, Malandrino P, Almeida JFM, Martins MB, Cunha LL, Bufalo NE, Pellegriti G, Ward LS (2014) The influence of the environment on the development of thyroid tumors: a new appraisal. Endocr-Relat Cancer 21:235–254
McHenry CR, Phitayakorn R (2011) Follicular adenoma and carcinoma of the thyroid gland. Oncologist 16:585–593
Pavlović Z, Miletić I, Jokić Ž, Stevanović J, Šobajić S, Bulat Z (2013) The influence of selenium supplementation of animal feed on human selenium intake in Serbia. Biotechnol Anim Husb 29:345–352
Pellegriti G, Frasca F, Regalbuto C, Squatrito S, Vigneri R (2013) Worldwide increasing incidence of thyroid cancer: update on epidemiology and risk factors. J Cancer Epidemiol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/965212
Skrbić B, Živančev J, Mrmoš N (2013) Concentrations of arsenic, cadmium and lead in selected foodstuffs from Serbian market basket: estimated intake by the population from the Serbia. Food Chem Toxicol 58:440–448
Soldin OP, Aschner M (2007) Effects of manganese on thyroid hormone homeostasis. Neurotoxicology 28:951–956
Stojsavljević A, Borković-Mitić S, Lj Vujotić, Grujičić D, Gavrović-Jankulović M, Manojlović D (2019) The human biomonitoring study in Serbia: background levels for arsenic, cadmium, lead, thorium and uranium in the whole blood of adult Serbian population. Ecotox Environ Safety 169:402–409
Zaichick V, Zaichick S (2018) Associations between age and 50 trace element contents and relationships in intact thyroid of males. Aging Clin Exp Res 30:1059–1070
Acknowledgement
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia, Project No. 172030.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stojsavljević, A., Rovčanin, B., Krstić, Đ. et al. Risk Assessment of Toxic and Essential Trace Metals on the Thyroid Health at the Tissue Level: The Significance of Lead and Selenium for Colloid Goiter Disease. Expo Health 12, 255–264 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00309-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00309-9