Abstract
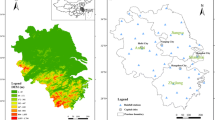
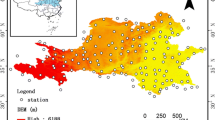
Changes in overall observed precipitation have been recognized in many parts of the world in recent decades, leading to the argument on climate change and its impact on extreme precipitation. However, the concept of natural variations and the complex physical mechanisms hidden in the observed data sets must also be taken into consideration. This study aims to examine the matter further with reference to inter-decadal variability in extreme precipitation quantiles appropriate for risk analysis. Temporal changes in extreme precipitation are assessed using a parametric approach incorporating a regional method in region-of-influence form. The index-flood method with the application of generalized extreme value distribution is used to estimate the decadal extreme precipitation. The study also performs a significance test to determine whether the decadal extremes are significant. A case study is performed on the Yangtze River Basin, where annual maximum 1-day precipitation data for 180 stations were analyzed over a 50-year period from 1961 to 2010. Extreme quantiles estimated from the 1990s data emerged as the significant values on several occasions. The immediate drop in the quantile values in the following decade, however, suggested that it is not practical to assign more weight to recent data for the quantile estimation process. The temporal patterns identified are in line with the previous studies conducted in the region and thus make it an alternative way to perform decadal analysis with an advantage that the scheme can be transferred to ungauged conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, L. V., Zhang, X., Peterson, T. C., et al. (2006). Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres,111, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD006290.
Bengtsson, L., & Rana, A. (2014). Long-term change of daily and multi-daily precipitation in southern Sweden. Hydrological Processes,28, 2897–2911. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9774.
Bülow, I., Henrik, G., & Dan, M. (2015). Long term variations of extreme rainfall in Denmark and southern Sweden. Climate Dynamics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2276-4.
Burn, D. H. (1990). Evaluation of regional flood frequency analysis with a region of influence approach. Water Resources Research,26, 2257–2265.
Chen, H., Sun, J., & Fan, K. (2012). Decadal features of heavy rainfall events in eastern China. Acta Meteorologica Sinica,26, 289–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-012-0303-0.
Dalrymple, T. (1960). Flood frequency methods. U. S. Geological Survey,1543, 11–51.
Das, S. (2017). Performance of region-of-influence approach of frequency analysis of extreme rainfall in monsoon climate conditions. International Journal of Climatology,37, 612–623. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5025.
Das, S. (2018a). Goodness-of-fit tests for generalized normal distribution for use in hydrological frequency analysis. Pure and Applied Geophysics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-1877-y.
Das, S. (2018b). Extreme rainfall estimation at ungauged sites: Comparison between region-of-influence approach of regional analysis and spatial interpolation technique. International Journal of Climatology. https://doi.org/10.1002/JOC.5819.
Das, S., & Cunnane, C. (2011). Examination of homogeneity of selected Irish pooling groups. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,15, 819–830. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-15-819-2011.
Das, S., & Cunnane, C. (2012). Performance of flood frequency pooling analysis in a low CV context. Hydrological Sciences Journal,57, 433–444. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2012.666635.
Das, S., Millington, N., & Simonovic, S. P. (2013). Distribution choice for the assessment of design rainfall for the city of London (Ontario, Canada) under climate change. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering,40, 121–129. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjce-2011-0548.
Feng, S., Nadarajah, S., & Hu, Q. (2007). Modeling annual extreme precipitation in China using the generalized extreme value distribution. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan,85, 599–613. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.85.599.
Fu, G., Yu, J., Yu, X., et al. (2013). Temporal variation of extreme rainfall events in China, 1961–2009. Journal of Hydrology,487, 48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.02.021.
Gaál, L., & Kyselý, J. (2009). Comparison of region-of-influence methods for estimating high quantiles of precipitation in a dense dataset in the Czech Republic. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,13, 2203–2219. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-13-2203-2009.
Gocic, M., & Trajkovic, S. (2013). Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann–Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Global and Planetary Change,100, 172–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.10.014.
Gong, D.-Y., & Ho, C.-H. (2002). Shift in the summer rainfall over the Yangtze River valley in the late 1970s. Geophysical Research Letters,29, 78-1–78-4. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001gl014523.
Gong, D. Y., & Wang, S. W. (2000). Severe summer rainfall in China associated with the enhanced global warming. Climate Research,16, 51–59. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr016051.
Gultepe, I., Heymsfield, A. J., Gallagher, M., et al. (2017). Ice fog: The current state of knowledge and future challenges. Meteorological Monographs,58, 41–424. https://doi.org/10.1175/amsmonographs-d-17-0002.1.
Gultepe, I., Isaac, G. A., Joe, P., et al. (2014). Roundhouse (RND) mountain top research site: Measurements and uncertainties for winter alpine weather conditions. Pure and Applied Geophysics,171, 59–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-012-0582-5.
Guo, J., Chen, H., Xu, C. Y., et al. (2012). Prediction of variability of precipitation in the Yangtze River Basin under the climate change conditions based on automated statistical downscaling. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment,26, 157–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-011-0464-x.
Guo, J., Guo, S., Li, Y., et al. (2013). Spatial and temporal variation of extreme precipitation indices in the Yangtze River basin, China. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment,27, 459–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-012-0643-4.
Guo, P., Zhang, X., Zhang, S., et al. (2014). Decadal variability of extreme precipitation days over northwest China from 1963 to 2012. Journal of Meteorological Research,28, 1099–1113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-014-4022-6.1.
Hosking, J. R. M., & Wallis, J. R. (1993). Some statistics useful in regional frequency analysis. Water Resources Research,29, 271–281.
Hosking, J. R. M., & Wallis, J. R. (1997). Regional frequency analysis: An approach based on L-moments. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Huang, H., Winter, J. M., Osterberg, E. C., et al. (2017). Total and extreme precipitation changes over the Northeastern United States. Journal of Hydrometeorology,18, 1783–1798. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-16-0195.1.
Institute of Hydrology. (1999). Flood Estimation Handbook (Vol. 1-5). Wallingford: Institute of Hydrology.
IPCC. (2001). Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Jiang, T., Su, B., & Hartmann, H. (2007). Temporal and spatial trends of precipitation and river flow in the Yangtze River Basin, 1961–2000. Geomorphology,85, 143–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.03.015.
Ju, Q., Yu, Z., Hao, Z., et al. (2014). Response of hydrologic processes to future climate changes in the Yangtze River Basin. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)he.1943-5584.0000770.
Jung, Y., Shin, J. Y., Ahn, H., & Heo, J. H. (2017). The spatial and temporal structure of extreme rainfall trends in South Korea. Water (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100809.
Kay, A. L., Jones, D. A., Crooks, S. M., et al. (2007). An investigation of site-similarity approaches to generalisation of a rainfall–runoff model. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,11, 500–515. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-11-500-2007.
Kyselý, J., Gaál, L., & Picek, J. (2011). Comparison of regional and at-site approaches to modelling probabilities of heavy precipitation. International Journal of Climatology,31, 1457–1472. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2182.
Liu, Y., Huang, G., & Huang, R. (2011). Inter-decadal variability of summer rainfall in Eastern China detected by the Lepage test. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-011-0442-8.
Nichols, M. H., Renard, K. G., & Osborn, H. B. (2002). Precipitation changes from 1956 to 1996 on the Walnut Gulch Experimental Watershed. Journal of the American Water Resources Association,38, 161–172.
Ntegeka, V., & Willems, P. (2008). Trends and multidecadal oscillations in rainfall extremes, based on a more than 100-year time series of 10 min rainfall intensities at Uccle, Belgium. Water Resources Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007wr006471.
Pedron, I. T., Silva Dias, M. A. F., de Paula, Dias S., et al. (2017). Trends and variability in extremes of precipitation in Curitiba—Southern Brazil. International Journal of Climatology,37, 1250–1264. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4773.
Qian, W., Fu, J., & Yan, Z. (2007). Decrease of light rain events in summer associated with a warming environment in China during 1961–2005. Geophysical Research Letters,34, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL029631.
Rasmussen, R., Baker, B., Kochendorfer, J., et al. (2012). How well are we measuring snow: The NOAA/FAA/NCAR winter precipitation test bed. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society,93, 811–829. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00052.1.
Reed, D. W., Faulkner, D. S., & Stewart, E. J. (1999). The FORGEX method of rainfall growth estimation II: Description. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,3, 197–203. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-3-205-1999.
Scherrer, S. C., Fischer, E. M., Posselt, R., Liniger, M. A., Croci-Maspoli, M., & Knutti, R. (2016). Emerging trends in heavy precipitation and hot temperature extremes in Switzerland. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 121(6), 2626–2637. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD024634.
Serinaldi, F., & Kilsby, C. G. (2016). The importance of prewhitening in change point analysis under persistence. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment,30, 763–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-015-1041-5.
Soltani, M., Laux, P., Kunstmann, H., et al. (2016). Assessment of climate variations in temperature and precipitation extreme events over Iran. Theoretical and Applied Climatology,126, 775–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1609-5.
Su, B., Gemmer, M., & Jiang, T. (2008). Spatial and temporal variation of extreme precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin. Quaternary International,186, 22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2007.09.001.
Su, B. D., Jiang, T., & Jin, W. B. (2006). Recent trends in observed temperature and precipitation extremes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Theoretical and Applied Climatology,83, 139–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-005-0139-y.
Svensson, C., & Jones, D. A. (2010). Review of rainfall frequency estimation methods. Journal of Flood Risk Management. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-318x.2010.01079.x/abstract.
Tabari, H., AghaKouchak, A., & Willems, P. (2014). A perturbation approach for assessing trends in precipitation extremes across Iran. Journal of Hydrology,519, 1420–1427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.09.019.
Tabari, H., & Willems, P. (2016). Daily precipitation extremes in Iran: Decadal anomalies. Journal of the American Water Resources Association. https://doi.org/10.1111/1752-1688.12403.
Tsonis, A. A. (1996). Widespread increases in low-frequency variability of precipitation over the past century. Nature,382, 700.
Turkes, M. (1996). Spatial and temporal analysis of annual rainfall variations I. Journal of Climatology,1076, 1057–1076.
Viglione, A., Laio, F., & Claps, P. (2007). A comparison of homogeneity tests for regional frequency analysis. Water Resources Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006WR005095.
Wallis, J. R., Schaefer, M. G., Barker, B. L., & Taylor, G. H. (2007). Regional precipitation-frequency analysis and spatial mapping for 24-hour and 2-hour durations for Washington State. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,11, 415–442. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-11-415-2007.
Wang, Y., & Zhou, L. (2005). Observed trends in extreme precipitation events in China during 1961–2001 and the associated changes in large-scale circulation. Geophysical Research Letters,32, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL022574.
Willems, P. (2013). Adjustment of extreme rainfall statistics accounting for multidecadal climate oscillations. Journal of Hydrology,490, 126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.03.034.
Yilmaz, A. G., Hossain, I., & Perera, B. J. C. (2014). Effect of climate change and variability on extreme rainfall intensity–frequency–duration relationships: A case study of Melbourne. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,1, 1. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-18-4065-2014.
Zhai, P., Zhang, X., Wan, H., & Pan, X. (2005). Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China. Journal of Climate,18, 1096–1108. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-3318.1.
Zhang, Q., Xu, C. Y., Zhang, Z., et al. (2008). Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation maxima during 1960–2005 in the Yangtze River basin and possible association with large-scale circulation. Journal of Hydrology,353, 215–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.11.023.
Zhang, X., Zwiers, F. W., Hegerl, G. C., et al. (2007). Detection of human influence on twentieth-century precipitation trends. Nature,448, 461–465. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06025.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology in the form of a grant (grant no. 2243141501015) to the first author. Comments and suggestions from two anonymous reviewers are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S., Zhu, D. & Cheng, CH. A Regional Approach of Decadal Assessment of Extreme Precipitation Estimates: A Case Study in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Pure Appl. Geophys. 177, 1079–1093 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-019-02354-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-019-02354-6