Abstract
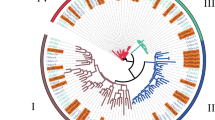
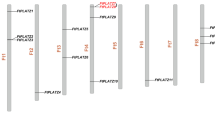
TALE (Three Amino-acid Loop Extension) transcription factors belong to a large gene family in plants and are also widespread in other Eukaryotes, including animals. We have in detail studied TALE genes in the economically important crop plant pineapple (Ananas comosus) but also compared these gene sequences with other plant TALE-genes. Using the webtool HMMER we found 18 TALE gene sequences in the pineapple genome, 33 genes in rice genome and 27 genes in Arabidopsis thaliana genome, 25 genes in Brachypodium distachyon genome, 22 genes in Vitis vinifera genome and 36 genes in Populus trichocarpa genome. The found TALE genes in pineapple genome were assigned to four groups (A, B, C, and D) based on similarity. The 18 TALE genes in pineapple were located on 11 of the 25 chromosomes. Structural heterogeneity was observed for the pineapple TALE genes and number of introns varied from 1 to 3 while the number of exons was 2–4. The pineapple TALE genes showed tissue specific expression. AcoTALE1 and AcoTALE15 were highly expressed in roots while AcoTALE16, AcoTALE2, and AcoTALE18 were highly expressed in fruit tissues. AcoTALE4 and AcoTALE7 were highly expressed at two different stages of stamen development. Abiotic shock treatment revealed that AcoTALE17 and AcoTALE8 were moderately upregulated by cold shock while heat shock firmly upregulated AcoTALE16 and AcoTALE5. AcoTALE2, AcoTALE4, AcoTALE12 and AcoTALE16 was highly expressed in response to salt shock while AcoTALE5 and AcoTALE12 was upregulated in response to osmotic (mannitol) shock. None of the TALE gene was differentially regulated in response to sudden darkness. Our study, identifying these TALE transcription factors and their involvement in different stress responses lays a foundation for the possible use of genetic modifications of TALE genes for pineapple crop improvements.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TFs:
-
Transcription factors
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- IP:
-
Isoelectric point
- RNA-Seq:
-
RNA sequencing
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time PCR
- NaCl:
-
Sodium chloride
References
Ali H, Liu Y, Azam SM, Rahman ZU, Priyadarshani SVGN, Li W, Huang X, Hu B, Xiong J, Ali U, Qin Y. (2017) Genomic survey, characterization, and expression profile analysis of the SBP genes in pineapple (Ananas comosus L.). Int J Genomics United States 2017:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1032846
Azam SM, Liu Y, Rahman Z u, Ali H, Cheng Y, Wang L, Priyadarshani SVGN, Hu B, Huang X, Xiong J, Qin Y, (2018) Identification, characterization and expression profiles of Dof transcription factors in pineapple (Ananas comosus L). Trop Plant Biol Springer US 11:49–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-018-9200-8
Bellaoui M, Pidkowich MS, Samach A, Kushalappa K, Kohalmi SE, Modrusan Z, Crosby WL, Haughn GW (2001) The Arabidopsis BELL1 and KNOX TALE home- odomain proteins interact through a domain conserved between plants and animals. Plant Cell 13:2455–2470
Bürglin TR (1997) Analysis of TALE superclass homeobox genes (MEIS, PBC, KNOX, Iroquois, TGIF) reveals a novel domain conserved between plants and animals. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4173–4180
Chen C, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Luan A, Mao Q, Feng J, Xie T, Gong X, Wang X, Chen H, He Y (2016) Transcriptome profiling of the pineapple under low temperature to facilitate its breeding for cold tolerance. PLoS One 11:e0163315. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163315
Chen P, Li Y, Zhao L, Hou Z, Yan M, Hu B, Liu Y, Azam SM, Zhang Z, Rahman Z, Liu L, Qin Y (2017) Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter gene family in pineapple (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.) reveal the role of AcABCG38 in pollen development. Front Plant Sci 8:2150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.02150
Dai X, Bai Y, Zhao L, Dou X, Liu Y, Wang L, Li Y, Li W, Hui Y, Huang X, Wang Z, Qin Y (2017) H2A.Z represses gene expression by modulating promoter nucleosome structure and enhancer histone modifications in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 10:1274–1292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2017.09.007
Dale RK, Matzat LH, Lei EP (2014) Metaseq: a Python package for integrative genome-wide analysis reveals relationships between chromatin insulators and associated nuclear mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res 42:9158–9170
Firoozabady E, Gutterson N (2003) Cost-effective in vitro propagation methods for pineapple. Plant Cell Rep Germany 21:844–850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-003-0577-x
Gangopadhyay S, Harding BL, Rajagopalan B, Lukas JJ, Fulp TJ (2009) A nonparametric approach for paleohydrologic reconstruction of annual streamflow ensembles. Water Resour Res 45. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007201
Gasteiger E (2003) ExPASy: the proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3784–3788. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg563
Guo Y, Qiu LJ (2013) Genome-wide analysis of the Dof transcription factor gene family reveals soybean-specific duplicable and functional characteristics. PLoS One 8:e76809. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076809
Kawahara Y, de la Bastide M, Hamilton JP et al (2013) Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice (N Y) 6:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1939-8433-6-4
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lucas WJ, Bouché-Pillon S, Jackson DP et al (1995) Selective trafficking of KNOTTED1 homeodomain protein and its mRNA through plasmodesmata. Science 270:1980–1983. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.270.5244.1980
Ming R, VanBuren R, Wai CM et al (2015) The pineapple genome and the evolution of CAM photosynthesis. Nat Genet 47:1435–1442. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3435
Mittler R (2006) Abiotic shock, the field environment and shock combination. Trends Plant Sci 11:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2005.11.002
Müller J, Wang Y, Franzen R, Santi L, Salamini F, Rohde W (2001) In vitro interactions between barley TALE home- odomain proteins suggest a role for protein-protein associa- tions in the regulation of Knox gene function. Plant J 27:13–23
Nagasaki H, Sakamoto T, Sato Y, Matsuoka M (2001) Func- tional analysis of the conserved domains of a rice KNOX homeodomain protein, OSH15. Plant Cell 13:2085–2098
Rahman Z u, Azam SM, Liu Y, Yan C, Ali H, Zhao L et al (2017) Expression profiles of Wuschel-related Homeobox gene family in pineapple (Ananas comosus L). Trop Plant Biol Springer US 10:204–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-017-9192-9
Shu YJ, Song LL, Zhang J, Liu Y, Guo CH (2015) Genome-wide identification and characterization of the Dof gene family in Medicago truncatula. Genet Mol Res 14:10645–10657. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.September.9.5
Smith HM, Hake S (2003) The interaction of two homeobox genes, BREVIPEDICELLUS and PENNYWISE, regulates internode patterning in the Arabidopsis inflores- cence. Plant Cell 15:1717–1727
Smith HM, Boschke I, Hake S (2002) Selective interaction of plant homeodomain proteins mediates high DNA-binding affinity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:9579–9584
Song A, Gao T, Li P, Chen S, Guan Z, Wu D, Xin J, Fan Q, Zhao K, Chen F (2016) Transcriptome-wide identification and expression profiling of the DOF transcription factor gene family in Chrysanthemum morifolium. Front Plant Sci 7:199. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00199
Su Z, Wang L, Li W, Zhao L, Huang X, Azam SM, Qin Y (2017) Genome-wide identification of auxin response factor (ARF) genes family and its tissue-specific prominent expression in pineapple (Ananas comosus). Trop Plant Biol 10:86–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-017-9187-6
Tamaoki M, Kusaba S, Kano-Murakami Y, Matsuoka M (1997) Ectopic expression of a tobacco homeobox gene, NTH15, dramatically alters leaf morphology and hormone levels in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Physiol 38: 917–927
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular biology and evolution, 28(10), 2731–2739.
Vollbrecht E, Veit B, Sinha N, Hake S (1991) The developmental gene KNOTTED-1 is a member of a maize homeobox gene family. Nature. 350. 241-3. https://doi.org/10.1038/350241a0
Wu Z, Cheng J, Cui J et al (2016) Genome-wide identification and expression profile of Dof transcription factor gene family in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Front Plant Sci 7:574. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00574
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 100 Talent Programs of Fujian Province and NSFC (U1605212).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H. Ali performed experiments, data analysis and manuscript writing, Y. Liu and W. Li carried out bioinformatics assistance, U. Ali and I. Ali organized figures, H.J. Ashraf and Y. Jie worked on qRT-PCR, SM. Azam helped and observed RNA-Seq analysis. S. Olsson and Y. Qin conceived the study. H. Ali and S. Olsson wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Communicated by: Hongwei Cai
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yanhui Liu is co-first author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, H., Liu, Y., Azam, S.M. et al. Genome Wide Identification and Expression Profiles of TALE Genes in Pineapple (Ananas comosus L). Tropical Plant Biol. 12, 304–317 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-019-09232-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-019-09232-4