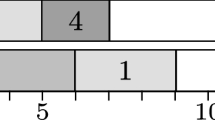
Abstract
In this paper, we prove that parallel machine scheduling problems where jobs have unit processing time and level-order precedence constraints are NP-complete, while minimizing the makespan or the total completion time. These problems are NP-complete even when preemption is allowed. We then adapt the proof to other open problems with out-tree or opposing-forests precedence constraints.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baptiste, P., & Timkovsky, V. G. (2001). On preemption redundancy in scheduling unit processing time jobs on two parallel machines. Operations Research Letters, 28(5), 205–212.
Brucker, P., Garey, M. R., & Johnson, D. S. (1977). Scheduling equal-length tasks under treelike precedence constraints to minimize maximum lateness. Mathematics of Operations Research, 2(3), 275–284.
Brucker, P., Heitmann, S., & Hurink, J. (2003). How useful are preemptive schedules? Operations Research Letters, 31(2), 129–136.
Dolev, D., & Warmuth, M. K. (1985). Profile scheduling of opposing forests and level orders. SIAM Journal on Algebraic Discrete Methods, 6(4), 665–687.
Garey, M. R., & Johnson, D. S. (2002). Computers and intractability (Vol. 29). New York: WH Freeman.
Garey, M. R., Johnson, D. S., Tarjan, R. E., & Yannakakis, M. (1983). Scheduling opposing forests. SIAM Journal on Algebraic Discrete Methods, 4(1), 72–93.
Graham, R. L., Lawler, E. L., Lenstra, J. K., & Kan, A. H. G. R. (1979). Optimization and approximation in deterministic sequencing and scheduling: A survey. Annals of Discrete Mathematics, 5, 287–326.
Hu, T. C. (1961). Parallel sequencing and assembly line problems. Operations Research, 9(6), 841–848.
Pinedo, M. (2012). Scheduling. Berlin: Springer.
Prot, D., & Bellenguez-Morineau, O. (2018). A survey on how the structure of precedence constraints may change the complexity class of scheduling problems. Journal of Scheduling, 21(1), 3–16.
Van Bevern, R., Bredereck, R., Bulteau, L., Komusiewicz, C., Talmon, N., & Woeginger, G.J. (2016). Precedence-constrained scheduling problems parameterized by partial order width. In International conference on discrete optimization and operations research (pp. 105–120). Springer.
Wang, T., & Bellenguez-Morineau, O. (2017). Complexity of parallel scheduling problem with equal processing time and particular precedence constraints while minimizing the mean flow time. Journal of Scheduling. ref: hal-01800804 (submitted).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the China Scholarship Council (Grant No. 201404490037).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Bellenguez-Morineau, O. The Complexity of Parallel Machine Scheduling of Unit-Processing-Time Jobs under Level-Order Precedence Constraints. J Sched 22, 263–269 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10951-018-0596-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10951-018-0596-7