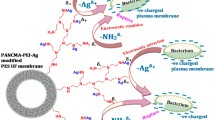
Abstract
A novel surface-modified nanofiltration (NF) membrane was prepared by layer-by-layer (LbL) self-assembly of positively charged polyethylenimine (PEI) and glutaraldehyde (GA) and negatively charged carboxymethyl chitosan (NO-CMC) alternately on the polyethersulfone (PES) membrane surfaces. The alteration aimed at improving the membrane separation performance, which was investigated in the study. In order to enhance antibiological fouling performance of the NF membrane, the silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were coated on the modified membrane in two different modes. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), zeta potential measurement, and water contact angle measurements were employed to characterize the formed membrane surface chemical composition and morphology. The rejection of different single nonheavy metal salts, yielded from the modified membrane, followed the order of MgCl2 > MgSO4 > CaCl2 > Na2CO3 > NaCl > Na2SO4. Additionally, the rejection of single heavy metal salts Cr3+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Ni2+ was 88.95%, 84.04%, 82.69% and 83.47%, respectively, whereas the rejection of Cr3+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Ni2+ increased to 91.77%, 90.70%, 89.74% and 87.22%, respectively, in the mixed salt solution. Moreover, the rejection of Cu2+ and Cd2+ increased to 96.12% and 94.38% after adjusting pH. As a result of loading the AgNPs on the modified membrane with a suitable mode, the antibiological fouling ability of the membrane was immensely improved by AgNPs.
Graphic abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goddek, S, Keesman, KJ, “The necessity of desalination technology for designing and sizing multi-loop aquaponics systems.” Desalination, 428 76–85 (2018)
Zhao, FY, An, QF, Ji, YL, Gao, CJ, “A novel type of polyelectrolyte complex/MWCNT hybrid nanofiltration membranes for water softening.” J. Membr. Sci., 492 412–421 (2015)
Nan, Q, Li, P, Cao, B, “Fabrication of positively charged nanofiltration membrane via the layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide and polyethylenimine for desalination.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 387 521–528 (2016)
Tepanosyan, G, Sahakyan, L, Belyaeva, O, Asmaryan, S, Saghatelyan, A, “Continuous impact of mining activities on soil heavy metals levels and human health.” Sci. Total Environ., 639 900–909 (2018)
Babel, S, Kurniawan, TA, “Cr(VI) removal from synthetic wastewater using coconut shell charcoal and commercial activated carbon modified with oxidizing agents and/or chitosan.” Chemosphere, 54 (7) 951–967 (2004)
Setiawan, L, Shi, L, Wang, R, “Dual layer composite nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for low-pressure water softening.” Polymer, 55 (6) 1367–1374 (2014)
Eccles, H, “Treatment of metal-contaminated wastes: why select a biological process?” Trends Biotechnol., 17 (12) 462–465 (1999)
Attia, H, Alexander, S, Wright, CJ, Hilal, N, “Superhydrophobic electrospun membrane for heavy metals removal by air gap membrane distillation (AGMD).” Desalination, 420 318–329 (2017)
Padaki, M, Isloor, AM, Wanichapichart, P, “Polysulfone/N-phthaloylchitosan novel composite membranes for salt rejection application.” Desalination, 279 (1–3) 409–414 (2011)
Waszak, M, Gryta, M, “The ultrafiltration ceramic membrane used for broth separation in membrane bioreactor.” Chem. Eng. J., 305 (4) 129–135 (2016)
Nayak, V, Geetha-Balakrishna, R, Padaki, M, Soontarapa, K, “Zwitterionic ultrafiltration membranes for As (V) rejection.” Chem. Eng. J., 308 347–358 (2017)
Hu, L, Zhang, S, Han, R, Jian, X, “Preparation and performance of novel thermally stable polyamide/PPENK composite nanofiltration membranes.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 258 (22) 9047–9053 (2012)
Werber, JR, Osuji, CO, Elimelech, M, “Erratum: materials for next-generation desalination and water purification membranes.” Nat. Rev. Mater., 1 (5) 16018–16030 (2016)
Zhu, WP, Sun, SP, Gao, J, Fu, FJ, Chung, TS, “Dual-layer polybenzimidazole/polyethersulfone (PBI/PES) nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for heavy metals removal from wastewater.” J. Membr. Sci., 456 117–127 (2014)
Liao, Y, Bokhary, A, Maleki, E, Liao, B, “A review of membrane fouling and its control in algal-related membrane processes.” Bior. Technol., 264 343–358 (2018)
Shafi, HZ, Matin, A, Khan, Z, Khalil, A, Gleason, KK, “Surface modification of reverse osmosis membranes with zwitterionic coatings: a potential strategy for control of biofouling.” Surf. Coat. Tech., 279 171–179 (2015)
Liu, YJ, Ma, XY, Zhou, TT, Wang, RB, Hou, JW, Tang, J, Zhu, BS, Su, Y, Zhu, XY, “Layer by layer assembled phosphorylcholine groups on paclitaxel/chitosan nanofibers coatings for hemocompatibility improvement.” Surf. Coat. Tech., 357 984–992 (2018)
Wasim, M, Sabir, A, Shafiq, M, Islam, A, Jamil, T, “Preparation and characterization of composite membrane via layer by layer assembly for desalination.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 396 259–268 (2017)
Zhao, H, Ju, H, “Multilayer membranes for glucose biosensing via layer-by-layer assembly of multiwall carbon nanotubes and glucose oxidase.” Analyt. Biochem., 350 (1) 138–144 (2006)
Feng, C, Xu, J, Li, M, Tang, Y, Gao, C, “Studies on a novel nanofiltration membrane prepared by cross-linking of polyethyleneimine on polyacrylonitrile substrate.” J. Membr. Sci., 451 103–110 (2014)
Xu, J, Wang, Z, Wang, J, Wang, S, “Positively charged aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membrane with high anti-fouling property prepared by polyethylenimine grafting.” Desalination., 365 398–406 (2015)
Min, M, Wang, X, Yang, Y, Liu, Z, Zhou, Z, Zhu, M, Chen, Y, Hsiao, BS, “Fabrication of micro-nano structure nanofibers by solvent etching.” J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 11 (8) 6919–6925 (2011)
Gao, J, Sun, SP, Zhu, WP, Chung, TS, “Chelating polymer modified P84 nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for high efficient heavy metal removal.” Water Res., 63 252–261 (2014)
Moran, HBT, Turley, JL, Andersson, M, Lavelle, EC, “Immunomodulatory properties of chitosan polymers.” Biomaterials, 184 1–9 (2018)
Ekambaram, K, Doraisamy, M, “Fouling resistant PVDF/Carboxymethyl chitosan composite nanofiltration membranes for humic acid removal.” Carb. Polym., 173 431–440 (2017)
Musale, DA, Kumar, A, Pleizier, G, “Formation and characterization of poly(acrylonitrile)/Chitosan composite ultrafiltration membranes.” J. Membr. Sci., 154 (2) 163–173 (1999)
Gao, FS, Gao, XL, Jian, W, Xia, GS, Gao, CJ, “Preparation and characterization of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) composite nanofiltration membrane.” Mod. Chem. Ind., 33 (6) 86–90 (2013)
Mirzajani, F, Ghassempour, A, Aliahmadi, A, Esmaeili, MA, “Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on staphylococcus aureus.” Res. Microbiol., 162 (5) 542–549 (2011)
Du, L, Zeng, S, Xu, Q, Feng, JX, “Biosynthesis of Ag nanoparticles using liquefied cassava mash and its antibacterial activity against staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli.” J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 16 (8) 8741–8747 (2016)
Long, Y, Wang, Y, Liu, Y, Zeng, Q, Li, Y, “Maintenance of the activity of mono-dispersed Au and Ag nano-particles embedded in agar gel for ion-sensing and antimicrobial applications.” Sci. Ch. Chem., 58 (4) 1–7 (2015)
Muzzarelli, RAA, “N-(carboxymethylidene) chitosans and N-(carboxymethyl) chitosans: novel chelating polyampholytes obtained from chitosan gloxylate.” Carbohydr. Res., 107 199–214 (1982)
Chen, XG, Park, HJ, “Chemical characteristics of O-carboxymethyl chitosans related to the preparation conditions.” Carb. Polym., 53 (4) 355–359 (2003)
Samuels, RJ, “Solid state characterization of the structure of chitosan films.” J. Polym. Sci. Part Polym. Chem., 19 (7) 1081–1105 (1981)
Belfer, S, Fainchtain, R, Purinson, Y, Kedem, O, “Surface characterization by FTIR-ATR spectroscopy of polyethersulfone membranes-unmodified, modified and protein fouled.” J. Membr. Sci., 172 (1) 113–124 (2000)
Simakov, NA, Kurnikova, MG, “Membrane Position Dependency of the pKa and Conductivity of the Protein Ion Channel.” J. Membr. Bio., 251 (6) 1–12 (2018)
Bandehali, S, Parvizian, F, Moghadassi, AR, “Copper and lead ions removal from water by new PEI based NF membrane modified by functionalized POSS nanoparticles.” J. Polym. Res., 26 (9) 211–218 (2019)
Han, RL, Wang, YQ, “Zhang X Z, Preparation of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Sodium/PEI Nanofiltration Membrane.” Adv. Mater. Res., 800 580–583 (2013)
Van Zwol, PJ, Palasantzas, G, De Hosson, JT, “Influence of roughness on capillary forces between hydrophilic surfaces.” Phys. Rev., 78 (3 Pt 1) 031606–031618 (2008)
Bharathidasan, T, Kumar, SV, Bobji, MS, Chakradhar, RPS, Basu, BJ, “Effect of wettability and surface roughness on ice-adhesion strength of hydrophilic, hydrophobic and superhydrophobic surfaces.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 314 (31) 241–250 (2014)
Zhao, MH, Chen, XP, Wang, Q, “Wetting failure of hydrophilic surfaces promoted by surface roughness.” Sci. Rep., 4 5376–5387 (2014)
Biswas, P, Bandyopadhyaya, R, “Biofouling prevention using silver nanoparticle impregnated polyethersulfone (PES) membrane: E. coli cell-killing in a continuous cross-flow membrane module.” J. Colloid Interface Sci., 491 13–26 (2016)
Li, RJ, Wu, YT, Shen, LG, Chen, JR, Lin, HJ, “A novel strategy to develop antifouling and antibacterial conductive Cu/polydopamine/polyvinylidene fluoride membranes for water treatment.” J. Colloid Interface Sci., 531 493–501 (2018)
Wang, T, Lu, J, Mao, L, Wang, Z, “Electric field assisted layer-by-layer assembly of graphene oxide containing nanofiltration membrane.” J. Membr. Sci., 515 125–133 (2016)
Li, M, Xu, J, Chang, CY, Feng, C, Zhang, L, Tang, Y, Gao, CJ, “Bioinspired fabrication of composite nanofiltration membrane based on the formation of DA/PEI layer followed by cross-linking.” J. Membr. Sci., 459 62–71 (2014)
Galama, AH, Post, JW, Stuart, MAC, Biesheuvel, PM, “Validity of the Boltzmann equation to describe Donnan equilibrium at the membrane–solution interface.” J. Membr. Sci., 442 (1) 131–139 (2013)
Huang, R, Chen, G, Sun, M, Hu, Y, Gao, C, “Studies on nanofiltration membrane formed by diisocyanate cross-linking of quaternized chitosan on poly(acrylonitrile) (PAN) support.” J. Membr. Sci., 286 (1) 237–244 (2006)
Li, XL, Zhu, LP, Jiang, JH, Yi, Z, Zhu, BK, Xu, YY, “Hydrophilic nanofiltration membranes with self-polymerized and strongly-adhered polydopamine as separating layer.” Ch. J. Polym. Sci., 30 (2) 152–163 (2012)
Lv, Y, Yang, HC, Liang, HQ, Wan, LS, Xu, ZK, “Nanofiltration membranes via co-deposition of polydopamine/polyethylenimine followed by cross-linking.” J. Membr. Sci., 476 50–58 (2015)
Zhang, R, Su, Y, Zhao, X, Li, Y, Zhao, J, Jiang, Z, “A novel positively charged composite nanofiltration membrane prepared by bio-inspired adhesion of polydopamine and surface grafting of poly(ethylene imine).” J. Membr. Sci., 470 9–17 (2014)
Huang, ZH, Li, MK, Li, N, Tang, XY, Ouyang, ZY, “Antibacterial properties enhancement of layer-by-layer self-assembled nanofiltration membranes.” J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 18 4524–4533 (2018)
Ouyang, ZY, Huang, ZH, Tang, XY, Xiong, CH, Tang, MD, Lu, YT, “A dually charged nanofiltration membrane by pH-responsive polydopamine for pharmaceuticals and personal care products removal.” Sep. Purif. Technol., 211 90–97 (2019)
Tansel, B, “Significance of thermodynamic and physical characteristics on permeation of ions during membrane separation: hydrated radius, hydration free energy and viscous effects.” Sep. Purif. Technol., 86 119–126 (2012)
Huang, ZH, Yin, YN, Aikebaier, GL, Zhang, Y, “Preparation of a novel positively charged nanofiltration composite membrane incorporated with silver nanoparticles for pharmaceuticals and personal care product rejection and antibacterial properties.” Water Sci. Technol., 73 (8) 1910–1922 (2016)
Zhang, Y, Zhang, L, Hou, L, “Modeling of the variations of permeate flux, concentration polarization, and solute rejection in nanofiltration system.” AIChE J., 65 (3) 1076–1087 (2019)
Comerton, AM, Andrews, RC, Bagley, DM, Hao, C, “The rejection of endocrine disrupting and pharmaceutically active compounds by NF and RO membranes as a function of compound and water matrix properties.” J. Membr. Sci., 313 (1) 323–335 (2008)
Bellona, C, Drewes, JE, “The role of membrane surface charge and solute physico-chemical properties in the rejection of organic acids by NF membranes.” J. Membr. Sci., 249 (1) 227–234 (2005)
Xu, Y, Lebrun, RE, “Investigation of the solute separation by charged nanofiltration membrane: effect of pH, ionic strength and solute type.” J. Membr. Sci., 158 (1–2) 93–104 (1999)
Thong, Z, Han, G, Cui, Y, Chung, TS, Chan, SY, Wei, S, “Novel nanofiltration membranes consisting of a sulfonated pentablock copolymer rejection layer for heavy metal removal.” Environ. Sci. Technol., 48 13880–13887 (2014)
Dong, G, Zhu, G, Shida, LI, Hong, QI, “Research on rejection of heavy metal ions with TiO2 nanofiltration membranes.” Membr. Sci. Technol., 46 1–7 (2012)
Al Rashdi, BAM, Johnson, DJ, Hilal, N, “Removal of heavy metal ions by nanofiltration.” Desalination, 315 2–17 (2013)
Yurekli, Y, “Removal of heavy metals in wastewater by using zeolite nano-particles impregnated polysulfone membranes.” J. Haz. Mater., 309 53–64 (2016)
Mondal, M, Dutta, M, De, S, “A novel ultrafiltration grade nickel iron oxide doped hollow fiber mixed matrix membrane: spinning, characterization and application in heavy metal removal.” Sep. Purif. Technol., 188 155–166 (2017)
Shukla, AK, Alam, J, Alhoshan, M, Dass, LA, Ali, FAA, Muthumareeswaran, MR, Mishra, U, Ansari, MA, “Removal of heavy metal ions using a carboxylated graphene oxide-incorporated polyphenylsulfone nanofiltration membrane.” Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol., 4 438–448 (2018)
Anderson, RC, Haverkamp, RG, Yu, PL, “Investigation of morphological changes to Staphylococcus aureus induced by ovine-derived antimicrobial peptides using TEM and AFM, FEMS.” Microbiol. Lett., 240 (1) 105–110 (2004)
Rasul, R, Cole, N, Balasubramanian, D, Chen, R, Kumar, N, Willcox, MDP, “Interaction of the antimicrobial peptide melimine with bacterial membranes.” Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, 35 (6) 566–572 (2010)
Stanley, EF, “Magainin 2, a natural antibiotic from frog skin, forms ion channels in lipid bilayer membranes.” Eur. J. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol., 226 (4) 287–296 (1992)
Con, TH, “Preparation of silver nano-particles and use as a material for water sterilization.” Environmentasia, 4 (1) 62–66 (2011)
Jung, YJ, Park, CB, Kim, Y, Kim, S, Pflugmacher, S, Baik, S, “Application of multi-species microbial bioassay to, assess the effects of engineered nanoparticles in the, aquatic environment: potential of a luminous microbial array for toxicity risk assessment (LumiMARA) on testing for surface-coated silver nanoparticles.” Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 12 (7) 8172–8186 (2015)
Wu, D, Fan, W, Kishen, A, Gutmann, JL, Fan, B, “Evaluation of the antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis biofilm.” J. Endodont., 40 (2) 285–290 (2014)
Rudakiya, DM, Pawar, K, “Bactericidal potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized using cell-free extract of Comamonas acidovorans: in vitro and in silico approaches.” Biotech, 7 (2) 92–102 (2017)
Cancino, J, Nobre, TM, Jr, OO, “A new strategy to investigate the toxicity of nanomaterials using Langmuir monolayers as membrane models.” Nanotoxicology, 7 (1) 61–70 (2013)
Acknowledgments
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51208259) financially supported this study. The facility was mainly supported by Jiangsu Key Laboratory of New Membrane Materials, Key Laboratory of New Membrane Materials, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, School of Environmental and Biological Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology (Grant No. 30920140122008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, C., Huang, Z., Ouyang, Z. et al. Improvement of the separation and antibiological fouling performance using layer-by-layer self-assembled nanofiltration membranes. J Coat Technol Res 17, 731–746 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-019-00298-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-019-00298-z