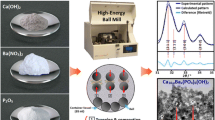
Abstract
Many attempts have been conducted for green synthesis of biofunctional scaffolds and implant coatings. Hydroxyapatite Ca5(OH)(PO4)3 (HA), is an excellent material for these purposes. HA is a major mineral component of vertebrate bones and teeth; it constitutes 70 wt% of human bones. This paper reports on the sustainable fabrication of HA particles in different morphologies including nanoplates (400 nm L and 150 nm W), and nanorods (10 nm D and 500 nm L). XRD diffractogram revealed highly crystalline structure. HA nanoplates were surface modified with poly(ethylene-co-AA) polymeric surfactant; organic modified HA nanoplates demonstrated complete change in surface properties from hydrophilic to hydrophobic. It demonstrated effective phase transfer from aqueous phase to organic phase, with decrease in nanoplate size to 100 nm L, 50 nm W. Layered HA plates were further developed via surface modification with dodecanedioic acid; this approach can offer laminated or exfoliated plates for effective integration into bio-compatible polymers. This manuscript shaded the light on facile green synthesis of HA nanoparticles with controlled morphology and surface properties.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Kozlowska et al., Preliminary in vitro and in vivo assessment of modified collagen/hydroxyapatite composite. Mater. Lett. 221, 74–76 (2018)
M. Schiavoni et al., Focus on the catalytic performances of Cu-functionalized hydroxyapatites in NH3-SCR reaction. Appl. Catal. A 563, 43–53 (2018)
A. Dündar et al., Effects of citric acid modified with fluoride, nano-hydroxyapatite and casein on eroded enamel. Arch. Oral Biol. 93, 177–186 (2018)
A. Sobczak-Kupiec et al., Synthesis and characterization of ceramic—polymer composites containing bioactive synthetic hydroxyapatite for biomedical applications. Ceram. Int. 44(12), 13630–13638 (2018)
K. Sangeetha et al., Strontium and ciprofloxacin modified hydroxyapatites as functional grafts for bone prostheses. Ceram. Int. 44(12), 13782–13789 (2018)
M. Harja, G. Ciobanu, Studies on adsorption of oxytetracycline from aqueous solutions onto hydroxyapatite. Sci. Total Environ. 628–629, 36–43 (2018)
B. Kaczmarek et al., In vivo study on scaffolds based on chitosan, collagen, and hyaluronic acid with hydroxyapatite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 118, 938–944 (2018)
G. Ciobanu, M. Harja, Cerium-doped hydroxyapatite/collagen coatings on titanium for bone implants. Ceramics International (2018)
A. Szcześ, L. Hołysz, E. Chibowski, Synthesis of hydroxyapatite for biomedical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 249, 321–330 (2017)
K. Nakagawa et al., Template effect of phosphate surfactant on formation of hydroxyapatite nanostructures with various shapes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 213, 183–190 (2018)
E. Skwarek et al., Heats of immersion of hydroxyapatite and hydroxyapatite/fumed oxides composites in water and n-decane. Mater. Chem. Phys. 215, 99–103 (2018)
F.E. Baştan et al., Electrophoretic co-deposition of PEEK-hydroxyapatite composite coatings for biomedical applications. Colloids Surf. B 169, 176–182 (2018)
Z. Chen et al., Effect of cation doping on the structure of hydroxyapatite and the mechanism of defluoridation. Ceram. Int. 44(6), 6002–6009 (2018)
H.-P. Yu, Y.-J. Zhu, B.-Q. Lu, Highly efficient and environmentally friendly microwave-assisted hydrothermal rapid synthesis of ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires. Ceram. Int. 44(11), 12352–12356 (2018)
Q. Wang et al., Universal and biocompatible hydroxyapatite coating induced by phytic acid-metal complex multilayer. Colloids Surf. B 169, 478–485 (2018)
T. Adschiri, Y. Hakuta, K. Arai, Hydrothermal synthesis of metal oxide fine particles at supercritical conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 39(12), 4901–4907 (2000)
E. Lester et al., Reaction engineering: the supercritical water hydrothermal synthesis of nano-particles. J. Supercrit. Fluids 37(2), 209–214 (2006)
S. Elbasuney, Dispersion characteristics of dry and colloidal nano-titania into epoxy resin. Powder Technol. 268, 158–164 (2014)
S. Elbasuney, Surface engineering of layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanoparticles for polymer flame retardancy. Powder Technol. 277, 63–73 (2015)
S. Elbasuney, Continuous hydrothermal synthesis of AlO(OH) nanorods as a clean flame retardant agent. Particuology 22, 66–71 (2015)
S. Elbasuney, Sustainable steric stabilization of colloidal titania nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 409, 438–447 (2017)
S. Elbasuney, Novel multi-component flame retardant system based on nanoscopic aluminium-trihydroxide (ATH). Powder Technol. 305, 538–545 (2017)
S. Elbasuney, Novel colloidal molybdenum hydrogen bronze (MHB) for instant detection and neutralization of hazardous peroxides. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 102, 272–279 (2018)
S. Elbasuney, Novel colloidal nanothermite particles (MnO2/Al) for advanced highly energetic systems. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28(5), 1793–1800 (2018)
S. Elbasuney et al., Stabilized super-thermite colloids: a new generation of advanced highly energetic materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 419, 328–336 (2017)
S. Elbasuney, H.E. Mostafa, Synthesis and surface modification of nanophosphorous-based flame retardant agent by continuous flow hydrothermal synthesis. Particuology 22, 82–88 (2015)
S. Elbasuney, S.F. Mostafa, Continuous flow formulation and functionalization of magnesium di-hydroxide nanorods as a clean nano-fire extinguisher. Powder Technol. 278, 72–83 (2015)
S. Farrokhpay, A review of polymeric dispersant stabilisation of titania pigment. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 151(1–2), 24–32 (2009)
J. Fleer, A. Cohen, M. Scheutjens, Polymers at Interfaces (Chapman & Hall, London, 1993)
X. Yu, P. Somasundaran, Role of polymer conformation in interparticle-bridging dominated flocculation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 177(2), 283–287 (1996)
S. Farrokhpay, Interaction of Polymeric Dispersants with Titania Pigment Particles 2004 (University of South Australia, Adelaide, 2004)
D. Skog, F. Holler, Principles of Instrumental Analysis (Sunders Golden, Philadelphia, 1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elbasuney, S. Green Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles with Controlled Morphologies and Surface Properties Toward Biomedical Applications. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 899–906 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01247-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01247-4