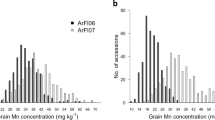
Abstract
Rice is a major dietary source of essential mineral nutrients and toxic elements (aka ionome) for humans. However, the genetic basis underlying the variation in ionome is still largely unknown. Here, we mapped 51 and 61 quantitative trait loci (QTLs) controlling the concentrations of 13 and 15 elements in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grain and straw, respectively, using a recombinant inbred lines (RILs) that were grown at three different field sites in 3 years. Several QTLs were repeatedly detected in both grain and straw or in multiple years; the resulting 87 unique QTLs with 17 of them (20%) were co-localized with previously reported corresponding QTLs and 70 were novel ionomic QTLs. At least, 14 genomic clusters that controlled the concentrations of multiple elements were identified. Furthermore, we identified a molybdate transporter gene OsMOT1;1 as the putative causal gene for a QTL controlling molybdenum concentration in both straw and grain. QTL analyses based on the concentrations of multiple elements in both grain and straw of RIL population grown in three field sites in 3 years allow us to identify tissue common QTLs and reproducible QTLs that were validated in multiple years. The identification of ionomic QTLs will be useful in revealing the molecular mechanisms underlying the accumulation of elements in rice and providing the opportunity to reduce the accumulation of toxic elements and enrich the accumulation of beneficial elements in rice grain.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- As:
-
Arsenic
- B:
-
Boron
- Ca:
-
Calcium
- CIM:
-
Composite interval mapping
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- cM:
-
Centimorgan
- Co:
-
Cobalt
- Chr:
-
Chromosome
- Cu:
-
Copper
- HD:
-
Heading date
- ICP-MS:
-
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
- K:
-
Potassium
- LOD:
-
Logarithm of the odds
- Mg:
-
Magnesium
- Mn:
-
Manganese
- Mo:
-
Molybdenum
- Na:
-
Sodium
- Ni:
-
Nickel
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- Pb:
-
Lead
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait locus
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- Zn:
-
Zinc
References
Arao T, Kawasaki A, Baba K, Mori S, Matsumoto S (2009) Effects of water management on cadmium and arsenic accumulation and dimethylarsinic acid concentrations in Japanese rice. Environ Sci Technol 43:9361–9367
Baxter I, Hermans C, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Tikhonova M, Verbruggen N, Chao DY, Salt DE (2012) Biodiversity of mineral nutrient and trace element accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 7:e35121
Baxter IR, Gustin JL, Settles AM, Hoekenga OA (2013) Ionomic characterization of maize kernels in the intermated B73 x Mo17 population. Crop Sci 53:208–220
Baxter IR, Ziegler G, Lahner B, Mickelbart MV, Foley R, Danku J, Armstrong P, Salt DE, Hoekenga OA (2014) Single-kernel ionomic profiles are highly heritable indicators of genetic and environmental influences on elemental accumulation in maize grain (Zea mays). PLoS ONE 9:e87628
Bentsink L, Yuan K, Koornneef M, Vreugdenhil D (2003) The genetics of phytate and phosphate accumulation in seeds and leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana, using natural variation. Theor Appl Genet 106:1234–1243
Chen H, Zhang W, Yang X, Wang P, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2018) Effective methods to reduce cadmium accumulation in rice grain. Chemosphere 207:699–707
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Dai WM, Zhang KQ, Wu JR, Wang L, Duan BW, Zheng KL, Cai R, Zhuang JY (2008) Validating a segment on the short arm of chromosome 6 responsible for genetic variation in the hull silicon content and yield traits of rice. Euphytica 160:317–324
Frossard E, Bucher M, Machler F, Mozafar A, Hurrell R (2000) Potential for increasing the content and bioavailability of Fe, Zn and Ca in plants for human nutrition. J Sci Food Agric 80:861–879
Ghandilyan A, Ilk N, Hanhart C, Mbengue M, Barboza L, Schat H, Koornneef M, El-Lithy M, Vreugdenhil D, Reymond M, Aarts MG (2009) A strong effect of growth medium and organ type on the identification of QTLs for phytate and mineral concentrations in three Arabidopsis thaliana RIL populations. J Exp Bot 60:1409–1425
Gomez-Coronado F, Almeida AS, Santamaria O, Cakmak I, Poblaciones MJ (2019) Potential of advanced breeding lines of bread-making wheat to accumulate grain minerals (Ca, Fe, Mg and Zn) and low phytates under Mediterranean conditions. J Agron Crop Sci 205:341–352
Gu R, Chen F, Liu B, Wang X, Liu J, Li P, Pan Q, Pace J, Soomro AA, Lubberstedt T, Mi G, Yuan L (2015) Comprehensive phenotypic analysis and quantitative trait locus identification for grain mineral concentration, content, and yield in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 128:1777–1789
Huang XY, Salt DE (2016) Plant ionomics: from elemental profiling to environmental adaptation. Mol Plant 9:787–797
Huang XY, Deng F, Yamaji N, Pinson SR, Fujii-Kashino M, Danku J, Douglas A, Guerinot ML, Salt DE, Ma JF (2016) A heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA4 prevents copper accumulation in rice grain. Nat Commun 7:12138
Huang XY, Liu H, Zhu YF, Pinson SRM, Lin HX, Guerinot ML, Zhao FJ, Salt DE (2019) Natural variation in a molybdate transporter controls grain molybdenum concentration in rice. New Phytol 221:1983–1997
Ishikawa S, Ae N, Yano M (2005) Chromosomal regions with quantitative trait loci controlling cadmium concentration in brown rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 168:345–350
Ishikawa S, Ishimaru Y, Igura M, Kuramata M, Abe T, Senoura T, Hase Y, Arao T, Nishizawa NK, Nakanishi H (2012) Ion-beam irradiation, gene identification, and marker-assisted breeding in the development of low-cadmium rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:19166–19171
Kamiya T, Borghi M, Wang P, Danku JM, Kalmbach L, Hosmani PS, Naseer S, Fujiwara T, Geldner N, Salt DE (2015) The MYB36 transcription factor orchestrates Casparian strip formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:10533–10538
Kumssa DB, Joy EJM, Ander EL, Watts MJ, Young SD, Walker S, Broadley MR (2015) Dietary calcium and zinc deficiency risks are decreasing but remain prevalent. Sci Rep 5:10974
Li RY, Stroud JL, Ma JF, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2009) Mitigation of arsenic accumulation in rice with water management and silicon fertilization. Environ Sci Technol 43:3778–3783
Li G, Sun GX, Williams PN, Nunes L, Zhu YG (2011) Inorganic arsenic in Chinese food and its cancer risk. Environ Int 37:1219–1225
Lu K, Li L, Zheng X, Zhang Z, Mou T, Hu Z (2008) Quantitative trait loci controlling Cu, Ca, Zn, Mn and Fe content in rice grains. J Genet 87:305–310
Luo JS, Huang J, Zeng DL, Peng JS, Zhang GB, Ma HL, Guan Y, Yi HY, Fu YL, Han B, Lin HX, Qian Q, Gong JM (2018) A defensin-like protein drives cadmium efflux and allocation in rice. Nat Commun 9:645
Ma JF, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Xu XY, Su YH, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2008) Transporters of arsenite in rice and their role in arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:9931–9935
McCouch SR, CGSNL (Committee on Gene Symbolization, Nomenclature and Linkage, Rice Genetics Cooperative) (2008) Gene nomenclature system for rice. Rice 1:72–84
Miyadate H, Adachi S, Hiraizumi A, Tezuka K, Nakazawa N, Kawamoto T, Katou K, Kodama I, Sakurai K, Takahashi H, Satoh-Nagasawa N, Watanabe A, Fujimura T, Akagi H (2011) OsHMA3, a P1B-type of ATPase affects root-to-shoot cadmium translocation in rice by mediating efflux into vacuoles. New Phytol 189:190–199
Norton GJ, Deacon CM, Xiong LZ, Huang SY, Meharg AA, Price AH (2010) Genetic mapping of the rice ionome in leaves and grain: identification of QTLs for 17 elements including arsenic, cadmium, iron and selenium. Plant Soil 329:139–153
Norton GJ, Duan GL, Lei M, Zhu YG, Meharg AA, Price AH (2012) Identification of quantitative trait loci for rice grain element composition on an arsenic impacted soil: influence of flowering time on genetic loci. Ann Appl Biol 161:46–56
Norton GJ, Douglas A, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Guerinot ML, Pinson SR, Tarpley L, Eizenga GC, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ, Islam MR, Islam S, Duan G, Zhu Y, Salt DE, Meharg AA, Price AH (2014) Genome wide association mapping of grain arsenic, copper, molybdenum and zinc in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown at four international field sites. PLoS One 9:e89685
Pinson SRM, Tarpley L, Yan WG, Yeater K, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Huang XY, Zhang M, Guerinot ML, Salt DE (2015) Worldwide genetic diversity for mineral element concentrations in rice grain. Crop Sci 55:294–311
Rude RK, Gruber HE (2004) Magnesium deficiency and osteoporosis: animal and human observations. J Nutr Biochem 15:710–716
Sasaki A, Yamaji N, Yokosho K, Ma JF (2012) Nramp5 is a major transporter responsible for manganese and cadmium uptake in rice. Plant Cell 24:2155–2167
Song Y, Wang Y, Mao W, Sui H, Yong L, Yang D, Jiang D, Zhang L, Gong Y (2017) Dietary cadmium exposure assessment among the Chinese population. PLoS ONE 12:e0177978
Stangoulis JCR, Huynh BL, Welch RM, Choi EY, Graham RD (2007) Quantitative trait loci for phytate in rice grain and their relationship with grain micronutrient content. Euphytica 154:289–294
Thacher TD, Fischer PR, Strand MA, Pettifor JM (2006) Nutritional rickets around the world: causes and future directions. Ann Trop Paediatr 26:1–16
Ueno D, Koyama E, Kono I, Ando T, Yano M, Ma JF (2009) Identification of a novel major quantitative trait locus controlling distribution of Cd between roots and shoots in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 50:2223–2233
Ueno D, Yamaji N, Kono I, Huang CF, Ando T, Yano M, Ma JF (2010) Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:16500–16505
Uraguchi S, Mori S, Kuramata M, Kawasaki A, Arao T, Ishikawa S (2009) Root-to-shoot Cd translocation via the xylem is the major process determining shoot and grain cadmium accumulation in rice. J Exp Bot 60:2677–2688
Vreugdenhil D, Aarts MGM, Koornneef M, Nelissen H, Ernst WHO (2004) Natural variation and QTL analysis for cationic mineral content in seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 27:828–839
Wang Z, Chen JY, Zhu YJ, Fan YY, Zhuang JY (2017) Validation of qGS10, a quantitative trait locus for grain size on the long arm of chromosome 10 in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Integr Agric 16:16–26
Waters BM, Grusak MA (2008) Quantitative trait locus mapping for seed mineral concentrations in two Arabidopsis thaliana recombinant inbred populations. New Phytol 179:1033–1047
Welch RM, Graham RD (2005) Agriculture: the real nexus for enhancing bioavailable micronutrients in food crops. J Trace Elem Med Biol 18:299–307
White PJ, Broadley MR (2009) Biofortification of crops with seven mineral elements often lacking in human diets—iron, zinc, copper, calcium, magnesium, selenium and iodine. New Phytol 182:49–84
Whitt L, Ricachenevsky FK, Ziegler G, Clemens S, Walker E, Maathuis F, Kear P, Baxter I (2018) A curated list of genes that control elemental accumulation in plants. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/456384
Xu XY, McGrath SP, Meharg AA, Zhao FJ (2008) Growing rice aerobically markedly decreases arsenic accumulation. Environ Sci Technol 42:5574–5579
Yamamoto T, Kuboki Y, Lin SY, Sasaki T, Yano M (1998) Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci Hd-1, Hd-2 and Hd-3, controlling heading date of rice, as single Mendelian factors. Theor Appl Genet 97:37–44
Yang M, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Hu J, Zhang X, Lu K, Dong H, Wang D, Zhao FJ, Huang CF, Lian X (2014) OsNRAMP5 contributes to manganese translocation and distribution in rice shoots. J Exp Bot 65:4849–4861
Yang M, Lu K, Zhao FJ, Xie W, Ramakrishna P, Wang G, Du Q, Liang L, Sun C, Zhao H, Zhang Z, Liu Z, Tian J, Huang XY, Wang W, Dong H, Hu J, Ming L, Xing Y, Wang G, Xiao J, Salt DE, Lian X (2018) Genome-wide association studies reveal the genetic basis of ionomic variation in rice. Plant Cell 30:2720–2740
Yano M, Harushima Y, Nagamura Y, Kurata N, Minobe Y, Sasaki T (1997) Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling heading date in rice using a high-density linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 95:1025–1032
Zhang M, Pinson SR, Tarpley L, Huang XY, Lahner B, Yakubova E, Baxter I, Guerinot ML, Salt DE (2014) Mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci associated with concentrations of 16 elements in unmilled rice grain. Theor Appl Genet 127:137–165
Zhao FJ, Ma JF, Meharg AA, McGrath SP (2009) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants. New Phytol 181:777–794
Zhao FJ, Ma Y, Zhu YG, Tang Z, McGrath SP (2015) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies. Environ Sci Technol 49:750–759
Funding
The work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFD0800206), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31772382, 31520103914), the Innovative Research Team Development Plan of the Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. IRT_17R56), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. KYT201802) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. KB20180023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
F-JZ and X-YH conceived and designed research, CW, Zhong T and Zhu T conducted experiments, J-YZ provided the RIL population, and X-YH, F-JZ and CW wrote the manuscript with contribution from J-YZ. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study did not involve human participants or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Tang, Z., Zhuang, JY. et al. Genetic mapping of ionomic quantitative trait loci in rice grain and straw reveals OsMOT1;1 as the putative causal gene for a molybdenum QTL qMo8. Mol Genet Genomics 295, 391–407 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01632-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01632-1