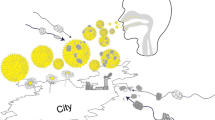
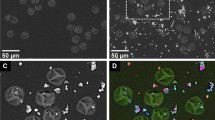
Abstract
From anther dehiscence to its atmospheric journey, airborne pollen grains can come into contact with other particulate matter (PM) and the external wall of pollen grains can be polluted by adhered atmospheric particles. Pollen and PM are some of the most common asthma triggers. The aim of this review was to discuss literature reporting pollen–particle complexes in the outdoor environment so their potential role in enhancing the risk of allergy could be examined. Twenty-five studies report pollen–particle complexes observed in outdoor conditions. PM adhesion onto the pollen surface was investigated in the literature by three different experimental approaches: direct collection from anthers, bulk exposure of pollen to PM in polluted areas, and direct sampling of airborne pollen during pollination. Four processes are proposed to explain deposition of PM on the surface of pollen grains: sticking of particles to anthers and pollen during dehiscence, airborne pollen-particles coagulation, wet and dry scavenging of pollen and particles, and co-deposition of PM and pollen in the respiratory system. Despite potential adverse health effects, the magnitude of pollution of pollen by PM is poorly understood. To address this issue, we suggest the following guidelines for research: (1) Possible artifacts during sampling and handling of anthers must be carefully avoided; (2) Control pollen grains (i.e. non-polluted) should be carefully selected; (3) A better knowledge of pollen atmospheric deposition and resuspension is needed; (4) The health effects of pollen-particles complexes need more attention regarding symptoms and allergic sensitization; (5) Use of individual pollen samplers could give a depiction of the degree of pollution of pollen that is actually inhaled.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amjad, L., & Shafighi, M. (2012). The Effect of Air Pollution on Chenopodium album L. Pollen Structure. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology A, 2(001), 143–148.
Aoyagi, H., & Ugwu, C. U. (2011). Fullerene fine particles adhere to pollen grains and affect their autofluorescence and germination. Nanotechnology, science and applications,4, 67.
Aylor, D. E. (1976). Resuspension of particles from plant surfaces by wind. Atmosphere Surface Exchange of Particulate and Gaseous Pollutants; Proceedings of a Symposium. http://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=US201303053458. Accessed 26 April 2018
Azzazy, M. (2016). Environmental Impacts of Industrial Pollution on Pollen Morphology of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. (Myrtaceae). Journal of Applied Biology & Biotechnology Vol, 4(05), 057–062.
Behrendt, H., Becker, W. M., Friedrichs, K. H., Darsow, U., & Tomingas, R. (1992). Interaction between Aeroallergens and Airborne Particulate Matter. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology,99(2–4), 425–428.
Behrendt, H., Becker, W. M., Fritzsche, C., Sliwa-Tomczok, W., Tomczok, J., Friedrichs, K. H., et al. (1997). Air Pollution and Allergy: Experimental Studies on Modulation of Allergen Release from Pollen by Air Pollutants. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology,113(1–3), 69–74.
Behrendt, H., Friedrich, K., Kainka-Stanicke, E., Darsow, U., Becker, W., & Tomingas, R. (1991). Allergens and pollutants in the air- A complex interaction. New Trends in Allergy,III, 467.
Bianchimano, A., Murray, M., Aztiria, M., Montes, B., Calfuán, M., & Prat, M. (2014). Morphological and immunochemical characterization of the pollen grains of Chenopodium album L.(Chenopodiaceae) in a temperate urban area in Argentina. FYTON, 9457(83), 9–15.
Bowker, G. E., & Crenshaw, H. C. (2007a). Electrostatic forces in wind-pollination—Part 1: Measurement of the electrostatic charge on pollen. Atmospheric Environment,41(8), 1587–1595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.10.047.
Bowker, G. E., & Crenshaw, H. C. (2007b). Electrostatic forces in wind-pollination—Part 2: Simulations of pollen capture. Atmospheric Environment,41(8), 1596–1603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.10.048.
Cerceau-Larrival, M. T., Bocquel, C., Carbonnier-Jarreau, M., & Verhille, A. (1996). Pollen: bio-indicator of pollution. Journal of Aerosol Science,27(1001), 227–228.
Cerceau-Larrival, M. T., Nilsson, S., Berggren, B., Carbonnier-Jarreau, M.-C., Derouet, L., & Verhille, A.-M. (1990). Influence de l’environnement sur les pollens de Betula verrucosa Ehrl. Bulletin de la Société Botanique de France. Actualités Botaniques, 137(2), 137–143.
Cerceau-Larrival, M. T., Nilsson, S., Cauneau-Pigot, A., Berggren, B., Derouet, L., Verhille, A.-M., et al. (1991). The influence of the environment (natural and experimental) on the composition of the exine of allergenic pollen with respect to the deposition of pollutant mineral particles. Grana,30(2), 532–545.
Chehregani, A., Majd, A., Moin, M., Gholami, M., Ali Shariatzadeh, M., & Nassiri, H. (2004). Increasing allergy potency of Zinnia pollen grains in polluted areas. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,58(2), 267–272.
Choël, M., Deboudt, K., & Flament, P. (2007). Evaluation of quantitative procedures for X-ray microanalysis of environmental particles. Microscopy Research and Technique,70(11), 996–1002.
Davidson, C. I., Phalen, R. F., & Solomon, P. A. (2005). Airborne Particulate Matter and Human Health: A Review. Aerosol Science and Technology,39(8), 737–749.
Dobson, H. E. (1988). Survey of Pollen and Pollenkitt Lipids–Chemical Cues to Flower Visitors? American Journal of Botany, 170–182.
Duque, L., Guimarães, F., Ribeiro, H., Sousa, R., & Abreu, I. (2012). Airborne Platanus Pollen Analysis by EPMA. Microscopy and Microanalysis,18(S5), 39–40.
Duque, L., Guimarães, F., Ribeiro, H., Sousa, R., & Abreu, I. (2013). Elemental characterization of the airborne pollen surface using Electron Probe Microanalysis (EPMA). Atmospheric Environment,75, 296–302.
Frank, U., & Ernst, D. (2016). Effects of NO2 and Ozone on Pollen Allergenicity. Plant Physiology,7, 91.
González-Díaz, S. N., Arias-Cruz, A., Macouzet-Sánchez, C., & Partida-Ortega, A. B. (2017). Impact of air pollution in respiratory allergic diseases. Medicina Universitaria. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S166557961730011X
Gottardini, E., Cristofolini, F., Paoletti, E., Lazzeri, P., & Pepponi, G. (2004). Pollen Viability for Air Pollution Bio-Monitoring. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry,49(1), 149–159.
Guedes, A., Ribeiro, N., Ribeiro, H., Oliveira, M., Noronha, F., & Abreu, I. (2009). Comparison between urban and rural pollen of Chenopodium alba and characterization of adhered pollutant aerosol particles. Journal of Aerosol Science,40(1), 81–86.
Helbig, N., Vogel, B., Vogel, H., & Fiedler, F. (2004). Numerical modelling of pollen dispersion on the regional scale. Aerobiologia,20(1), 3–19.
Hirst, J. M. (1952). An Automatic Volumetric Spore Trap. Annals of Applied Biology,39(2), 257–265.
Jaconis, S. Y., Culley, T. M., & Meier, A. M. (2017). Does particulate matter along roadsides interfere with plant reproduction? A comparison of effects of different road types on Cichorium intybus pollen deposition and germination. Environmental Pollution,222, 261–266.
Kalkar Surekha, A., & Renu, J. (2014). Effects of industrial pollution on pollen morphology of Cassia species. International journal of Life Sciences,2(1), 17–22.
Khattab, A., & Levetin, E. (2008). Preliminary studies on the effect of the Burkard alternate orifice on airborne fungal spore concentrations. Aerobiologia,24(3), 165–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-008-9096-0.
Kim, K.-H., Jahan, S. A., & Kabir, E. (2013). A review on human health perspective of air pollution with respect to allergies and asthma. Environment International,59, 41–52.
Kim, K.-H., Kabir, E., & Kabir, S. (2015). A review on the human health impact of airborne particulate matter. Environment International,74, 136–143.
Knox, R. B., Suphioglu, C., Taylor, P., Desai, R., Watson, H. C., Peng, J. L., et al. (1997). Major grass pollen allergen Lol p 1 binds to diesel exhaust particles: implications for asthma and air pollution. Clinical and Experimental Allergy,27(3), 246–251.
Kweon, H., Yiacoumi, S., & Tsouris, C. (2015). The role of electrostatic charge in the adhesion of spherical particles onto planar surfaces in atmospheric systems. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,481, 583–590.
Lin, H., Gomez, I., & Meredith, J. C. (2013). Pollenkitt Wetting Mechanism Enables Species-Specific Tunable Pollen Adhesion. Langmuir,29(9), 3012–3023. https://doi.org/10.1021/la305144z.
Majd, A., Chehregani, A., Moin, M., Gholami, M., Kohno, S., Nabe, T., et al. (2004). The Effects of Air Pollution on Structures, Proteins and Allergenicity of Pollen Grains. Aerobiologia,20(2), 111–118.
Namork, E., Johansen, B. V., & Løvik, M. (2006). Detection of allergens adsorbed to ambient air particles collected in four European cities. Toxicology Letters,165(1), 71–78.
Nilsson, S. (1988). Poursuite des analyses de la pollution particulaire des pollens. Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Botanique,9, 125–132.
Okuyama, Y., Matsumoto, K., Okochi, H., & Igawa, M. (2007). Adsorption of Air Pollutants on the Grain Surface of Japanese Cedar Pollen. Atmospheric Environment,41(2), 253–260.
Ormstad, H. (2000). Suspended particulate matter in indoor air: adjuvants and allergen carriers. Toxicology,152(1–3), 53–68.
Pacini, E., & Hesse, M. (2005). Pollenkitt - Its Composition, Forms and Functions. Flora-Morphology, Distribution, Functional Ecology of Plants,200(5), 399–415.
Peel, R. G., Hertel, O., Smith, M., & Kennedy, R. (2013). Personal exposure to grass pollen: relating inhaled dose to background concentration. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology,111(6), 548–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anai.2013.09.002.
Peltre, G. (1998). Inter-relationship between allergenic pollens and air pollution. Allerg Immunol (Paris),30(10), 324–326.
Phosri, A., Ueda, K., Tasmin, S., Kishikawa, R., Hayashi, M., Hara, K., et al. (2017). Interactive effects of specific fine particulate matter compositions and airborne pollen on frequency of clinic visits for pollinosis in Fukuoka, Japan. Environmental Research,156, 411–419.
Polosa, R. (2001). The interaction between particulate air pollution and allergens in enhancing allergic and airway responses. Current Allergy and Asthma Reports,1(2), 102–107.
Rezanejad, F. (2007). The effect of air pollution on microsporogenesis, pollen development and soluble pollen proteins in Spartium junceum L. (Fabaceae). Turk. J. Bot, 31(3), 183–191.
Rezanejad, F., Majd, A., Shariatzadeh, S., Moein, M., Aminzadeh, M., & Mirzaeian, M. (2003). Effect of air pollution on soluble proteins, structure and cellular material release in pollen of Lagerstroemia indicaL. (Lytraceae). Acta Biol. Cracovien, 45(1), 129–132.
Ribeiro, H., Duque, L., Guimarães, F., Abreu, I., & Noronha, F. (2014). Airborne Acer pollen wall elemental analysis and adhered particulate matter. Comunicações Geológicas, 101(Especial III), 1355–1358.
Ribeiro, H., Guimarães, F., Duque, L., Noronha, F., & Abreu, I. (2015). Characterisation of Particulate Matter on Airborne Pollen Grains. Environmental Pollution,206, 7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.06.015.
Riedl, M., & Diaz-Sanchez, D. (2005). Biology of diesel exhaust effects on respiratory function. Journal of allergy and clinical immunology,115(2), 221.
Ruggiero, F., & Bedini, G. (2018). Systematic and morphologic survey of orbicules in allergenic angiosperms. Aerobiologia, 1–18.
Saxon, A., & Diaz-Sanchez, D. (2005). Air pollution and allergy: you are what you breathe. Nature Immunology,6(3), 223–226.
Schäppi, G. F., Monn, C., Wüthrich, B., & Wanner, H. U. (1996). Analysis of allergens in ambient aerosols: comparison of areas subjected to different levels of air pollution. Aerobiologia,12(1), 185–190.
Schiavoni, G., D’Amato, G., & Afferni, C. (2017). The dangerous liaison between pollens and pollution in respiratory allergy. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1081120616314065. Accessed 7 February 2017
Sedghy, F., Sankian, M., Moghadam, M., Ghasemi, Z., Mahmoudi, M., & Varasteh, A.-R. (2016). Impact of traffic-related air pollution on the expression of Platanus orientalis pollen allergens. International Journal of Biometeorology, 1–9.
Seinfeld, J. H., & Pandis, S. N. (2012). Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change. John Wiley & Sons.
Sénéchal, H., Visez, N., Charpin, D., Shahali, Y., Peltre, G., Bioley, J.-P., et al. (2015). A Review of the Effects of Major Atmospheric Pollutants on Pollen Grains, Pollen Content and Allergenicity. The Scientific World Journal, 2015, ID 940243.
Shahali, Y., Pourpak, Z., Moin, M., Zare, A., & Majd, A. (2009). Impacts of Air Pollution Exposure on the Allergenic Properties of Arizona Cypress Pollens. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,151(1), 012027.
Sofiev, M., Siljamo, P., Ranta, H., Linkosalo, T., Jaeger, S., Rasmussen, A., et al. (2013). A numerical model of birch pollen emission and dispersion in the atmosphere. Description of the emission module. International Journal of Biometeorology, 57(1), 45–58.
Solomon, W. R. (2002). Airborne pollen: A brief life. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology,109(6), 895–900.
Taylor, P. E., Jacobson, K. W., House, J. M., & Glovsky, M. M. (2007). Links between pollen, atopy and the asthma epidemic. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology,144(2), 162–170.
Vaknin, Y., Gan-Mor, S., Bechar, A., Ronen, B., & Eisikowitch, D. (2000). The role of electrostatic forces in pollination. Plant Systematics and Evolution,222(1–4), 133–142.
Wang, Q., Nakamura, S., Lu, S., Xiu, G., Nakajima, D., Suzuki, M., et al. (2012). Release behavior of small sized daughter allergens from Cryptomeria japonica pollen grains during urban rainfall event. Aerobiologia,28(1), 71–81.
Wolters, J., & Martens, M. (1987). Effects of Air Pollutants on Pollen. The Botanical Review,53(3), 372–414.
World Health Organization. (2018). Ambient (outdoor) air quality and health. World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ambient-(outdoor)-air-quality-and-health. Accessed 14 June 2018
Acknowledgements
MC and NV thank the Université de Lille and the Institut de Recherches Pluridisciplinaires en Sciences de l’Environnement (IREPSE Fed 4129) for financial support. The CaPPA project (Chemical and Physical Properties of the Atmosphere) is funded by the French National Research Agency (ANR) through the PIA (Programme d’Investissement d’Avenir) under contract ANR-11-LABX-005-01. This work is a contribution to the CPER research project CLIMIBIO. The authors thank the French Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche, the Hauts de France Region and the European Funds for Regional Economical Development for their financial support to this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Visez, N., Ivanovsky, A., Roose, A. et al. Atmospheric particulate matter adhesion onto pollen: a review. Aerobiologia 36, 49–62 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-019-09616-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-019-09616-9