Abstract
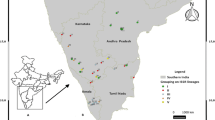
In previous works, significant variation in morphometric and molecular characteristics was detected among populations of M. beecheii. Here RFLP tests of the internal transcribed spacer 1 of the ribosomal gene were performed to confirm those results and to evaluate the intraspecific variability within the species. The complete ITS1 region and the flanking regions showed length variation (1720 to 1670) and also three different restriction patterns that allowed differentiation of three groups of colonies with different geographic distribution. Mexican colonies from Yucatán, Campeche and Chiapas, together with one colony from northern Guatemala formed one group, a second was composed of colonies from southern Guatemala, El Salvador and Costa Rica and a third one corresponded to one colony from San Marcos (Guatemala but close to the Mexican border). Such test could be used to characterize locally adapted ecotypes subject to conservation efforts.
Zusammenfassung
Molekulare Analysen an Melipona beecheii, einer in den amerikanischen Tropen einheimischen Stachellosen Biene, ermöglichten die Charakterisierung der Populationen über das gesamte Verbreitungsgebiet von Mexiko bis Costa Rica (Tab. I). Als molekularen Marker wählten wir die interne transkribierte Region 1 eines ribosomalen Gens. Dieser Marker wurde bereits zur populationsgenetischen Charakteri-sierung von drei brasilianischen Melipona-Arten eingesetzt (Fernandes-Salomão et al., 2005) und erwies sich auch als nützlich in intraspezifischen Untersuchungen der brasilianischen Art M. subnitida (Cruz et al., 2006). Die ITS1-Region der von uns untersuchten Art erwies sich als besonders komplex und lang (1670–1720 Basenpaare), so dass einfache Analysen zu Restriktionsfragment-Längenpolymorphismen (RFLP) möglich waren. Von den zehn verwendeten Restriktionsenzymen erwiesen sich vier als besonders geeignet und erlaubten die Trennung von drei RFLP-Mustern (Abb. 1 und 2). Die geographische Verteilung der Kolonien, von denen die Proben stammten, stimmte mit der Verteilung der unterschiedlichen RFLP-Muster überein und bestätigte damit die Unterschiedlichkeit von drei Populationen (Abb. 3). Diese können deshalb als an jeweils lokale Umweltbedingungen angepasste Ökotypen aufgefasst werden. Die Kolonien aus Mexiko (Yucatán, Campeche und Chiapas) bildeten zusammen mit den Kolonien des nördlichen Guatemala eine gemeinsame Gruppe, eine zweite umfasste Völker aus dem Süden Guatemalas, aus El Salvador und Costa Rica, und eine dritte Gruppe bildeten Völker aus San Marcos (eine nahe der mexikanischen Grenze gelegenen Region Guatemalas). Da wilde Melipona-Populationen von einer Habitatfragmentierung der Wälder stark betroffen sein können, bildet die genetische Information aus den RFLP-Analysen der ITS1 Region der M. beecheii Völker eine Grundlage für die Etablierung von Managementstrategien und Schutzmassnahmen für die Erhaltung dieser Art.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayala R. (1999) Revisión de las abejas sin aguijón de México (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Meliponini), Folia Entomol. Mex. 106, 1–123.
Bennett E.T. (1831) Some accounts of the habits of a mexican bee, in: Beechey F.W. (Ed.), Narrative of a voyage to the Pacific and Bering’s Strait, to co-operate with the Polar Expeditions, Vol. 2, London, UK, pp. 357–365.
Camargo JMF, Moure J.S, Roubik D.W. (1988) Melipona yucatanica New Species (Himenoptera: Apidae: Meliponinae): stingless bee dispersal across the Caribbean Arc and Post-Eucene Vicariance, Pan-Pacific Entomol. 64, 147–157.
Carrillo A., Quezada-Euán J.J.G., Moo-Valle H. (2001) Estudio preliminar sobre la variabilidad morfológica de Melipona beecheii (Apidae: Meliponini) en su rango de distribución de México, América Central y el Caribe, in: Quezada-Euán J.J.G., May-Itzá W. de J., Moo-Valle H., Chab-Medina J.C. (Eds.), II Seminario Mexicano sobre abejas sin aguijón, Mérida Yucatán, México, pp. 73–78.
Cruz D.O., Jorge D.M.M., Pereira J.O.P., Torres D.C., Soares A.E.A., Freitas B.M., Grangeiro T.B. (2006) Intraspecific variation in the first internal transcribed spacer (ITS1) of the nuclear ribosomal DNA in Melipona subnitida (Hymenoptera, Apidae), an endemic stingless bee from northeastern Brazil, Apidologie 37, 376–386.
De la Rúa P., Fuchs S., Serrano J. (2007) A scientific note on the ITS-1 region of Apis mellifera subspecies, Apidologie 38, 378–379.
De la Rúa P., May-Itzá W. de J., Serrano J., Quezada-Euán J.J.G. (2007) Sequence and RFLP analysis of the ITS2 ribosomal DNA in two Neotropical social bees, Melipona beecheii and Melipona yucatanica (Apidae: Meliponini), Insectes Soc. 54, 418–423.
Fernandes-Salomão T.M., Muro-Abad J.I., Campos L.A.O., Araújo E.F. (2002) Mitochondrial and nuclear DNA characterization in Melipona species (Hymenoptera, Meliponini) by RFLP analysis, Hereditas 137, 229–233.
Fernandes-Salomão T.M., Rocha R.B., Campos L.A.O., Araújo E.F. (2005) The first internal transcribed spacer (ITS-1) of Melipona species (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Meliponini): characterization and phylogenetic analysis, Insectes Soc. 52, 11–18.
González-Acereto J.A. (1999) La meliponicultura yucateca en crisis: una actividad indígena a punto de desaparecer, 1er Seminario Nacional sobre Abejas sin Aguijón, Boca del Río Ver, México, pp. 9–12.
González-Acereto J.A. (2008) Cría y manejo de abejas nativas sin aguijón en México. Impresiones Planeta, 177 p.
González-Acereto J.A., De Araujo F.Ch. (2005) Manual de Meliponicultura Mexicana, Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán, Facultad de Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia, Fundación Produce Guerrero A.C. Imp Gramma, 46 p.
Heard T. (1999) The role of stingless bees in crop pollination, Annu. Rev. Entomol. 44, 183–206.
Ji Y., Zhang D., He L. (2003) Evolutionary conservation and versatility of a new set of primers for amplifying the ribosomal internal transcribed spacer regions in insects and other invertebrates, Mol. Ecol. Notes 3, 581–585.
Morrone J.J. (2006) Biogeographic areas and transition zones of Latin America and the Caribbean Islands based on panbiogeographic and cladistic analyses of the entomofauna, Annu. Rev. Entomol. 51, 467–494.
Quezada-Euán J.J.G., May-Itzá W. de J., González-Acereto J.A. (2001) Meliponiculture in Mexico: Problems and perspectives for development, Bee World 82, 160–167.
Quezada-Euán J.J.G., Paxton R.J., Palmer K.A., May-Itzá W. de J., Tay W.T., Oldroyd B.P. (2007) Morphological and molecular characters reveal differentiation in a Neotropical social bee, Melipona beecheii (Apidae: Meliponini), Apidologie 38, 247–258.
Sappal N.P., Jeng R.S., Hubbes M., Liu F. (1995) Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in polymerase chain reaction amplified ribosomal DNAs of three Trichogramma (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) species, Genome 38, 419–425.
Sheppard W.S., McPheron B.A. (1991) Ribosomal DNA diversity in Apidae, in: Smith D.R. (Ed.), Diversity in the Genus Apis, Westview Press, Boulder, Colorado pp. 89–102.
Villanueva G.R., Roubik D.W., Collí-Ucán W. (2005) Extinction of Melipona beecheii and traditional beekeeping in the Yucatán peninsula, Bee World 86, 35–41.
Von der Schulenburg J.H.G., Hancock J.M., Pagnamenta A., Sloggett J.J., Majerus M.E.N., Hurst D.D. (2001) Extreme length and length variation in the first ribosomal internal transcribed spacer of ladybird beetles (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), Mol. Biol. Evol. 18, 648–660.
Weaver N., Weaver E.C. (1981) Beekeeping with the stingless bee Melipona beecheii by the Yucatecan Maya, Bee World 62, 7–19.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript editor: Walter S. Sheppard
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
May-Itzá, W.d.J., Quezada-Euán, J.J.G., Enriquez, E. et al. Intraspecific variation in the stingless bee Melipona beecheii assessed with PCR-RFLP of the ITS1 ribosomal DNA. Apidologie 40, 549–555 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1051/apido/2009036
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/apido/2009036