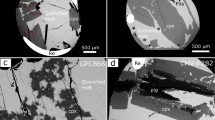
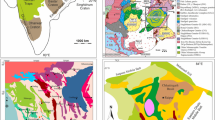
Abstract
This paper investigates the Jigede gabbros from the Shalazhashan tectonic belt, Alxa Block. Laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) zircon U-Pb dating reveals that they were emplaced in the Middle Permian (ca. 262 Ma). All the gabbro samples collected from the intrusion exhibit low contents of TiO2 (0.24–0.37 wt %) and \({\text{F}}{{{\text{e}}}_{{\text{2}}}}{\text{O}}_{{\text{3}}}^{{\text{T}}}\) (4.87–5.41 wt %), but high levels of MgO (11.15–12.15 wt %), CaO (11.45–12.75 wt %), Al2O3 (14.18–17.08 wt %) and high Mg# (0.81–0.83). Relative to HREEs and LILEs, the gabbros are enriched in LREEs and depleted in Th, Nb, Ce, Zr, Hf, and Ti, with positive Eu, Sr and U anomalies. In contrast to MORB, the Jigede intrusion has higher initial 87Sr/86Sr values of 0.7046 to 0.7054 and lower εNd(T) of + 1.8 to + 4.8. Elemental and isotopic data suggest that the intrusion was likely to have been produced by partial melting of a shallow lithospheric mantle source modified by slab-derived fluids, with subsequent cumulation of plagioclase. Thus, the Jigede intrusion was emplaced in a back-arc setting, in response to the Paleo-Asian oceanic subduction. In addition, the final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean did not occur prior to the Middle Permian.










Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andersen, T., Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb, Chem. Geol., 2002, vol. 192, pp. 59–79.
Brenan, J.M., Shaw, H.F., Ryerson, F.J., and Phinney, D.L., Mineral-aqueous fluid partitioning of trace elements at 900oC and 2.0 GPa: constraints on the trace element chemistry of mantle and deep crystal fluids, Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 1995a, vol. 59, pp. 3331–3350.
Brenan, J.M., Shaw, H.F., and Ryerson, F.J., Experimental evidence for the origin of lead enrichment in convergent margin magmas, Nature, 1995b, vol. 378, pp. 54–56.
Black,L.P. dand Gulson, B.L., The age of the Mud Tank carbonatite, Strangways Range, Northern Territory, BMR, J. Austral. Geol. Geophys., 1978, vol. 3, pp. 227–232.
Bryan, S., Silicic large igneous provinces, Episodes, 2007, vol. 30, pp. 20–31.
Dan, W., Li, X.H., Wang, Q., Tang, G.J., and Liu, Y., An Early Permian (ca. 280 Ma) silicic igneous province in the Alxa Block, NW China: a magmatic flare-up triggered by a mantle-plume?, Lithos, 2014a, vol. 204, pp. 144–158.
Falloon, T.J., Green, D.H., Hatton, C.J., and Harris, K.L., Anhydrous partial melting of a fertile and depleted peridotite from 2 to 30 kb and application to basalt petrogenesis, J. Petrol., 1988, vol. 29, pp. 1257–1282.
Feng, J.Y., Xiao, W.J., Windley, B., Han, C.M., Wan, B., Zhang, J.E., Ao, S.J., Zhang, Z.Y., and Lin, L.N., Field geology, geochronology and geochemistry of mafic–ultramafic rocks from Alxa, China: implications for Late Permian accretionary tectonics in the southern Altaids, J. Asian Earth Sci., 2013, vol. 78, pp. 114–142.
Gao, J.F., Lu, J.J., Lai, M.Y., Lin, Y.P., and Pu, W., Analysis of trace elements in rock samples using HR-ICPMS, J. Nanjing Univ. (Natural Sciences), 2003, vol. 39, pp. 844–850 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Han, B.F., He, G.Q., Wang, X.C., and Guo, Z.J., “Late Carboniferous collision between the Tarim and Kazakhstan-Yili terranes in the western segment of the South Tian Shan Orogen, Central Asia, and implications for the Northern Xinjiang, western China,” Earth Sci. Rev., 2011, vol. 109, pp. 74–93.
He, X.H., Zhong, H., Zhao, Z.F., Tan, S.C., Zhu, W.G., Yang, S.Q., Hu, W.J., Tang, Z., and Bao, C.F., U-Pb geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd isotopic geochemistry of the Houyaoyu granite porphyries: implications for the genesis of Early Cretaceous felsic intrusions in East Qinling, J. Earth Sci., 2018, vol. 29, pp. 920–938.
Hunter, R.H., Texture development in cumulate rocks, Layered Intrusions, Cawthorn, R.G., Ed., Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1996, pp. 77–101.
Jahn, B.-M., The Central Asian Orogenic Belt and growth of the continental crust in the Phanerozoic, Geol. Soc., London, Spec. Publ., 2004, vol. 226, pp. 73–100
Jackson, S.E., Pearson, N.J., Griffin, W.L., and Be-lousova, E.A., The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology, Chem. Geol., 2004, vol. 211, pp. 47–69.
Kepezhinskas, P., McDermott, F., Defant, M., Hochstaedter, A., Drummond, M.S., Hawdesworth, C.J., Koloskov, A., Maury, R.C., Bellon, H., Trace element and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic constraints on a three-component model of Kamchatka Arc petrogenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1997, vol. 61, pp. 577–600.
Khain, E.V., Bibikova, E.V., Salnikova, E.B., Kröner, A., Gibsher, A.S., Didenko, A.N., Degtyarev, K.E., and Fedotova, A.A., The Palaeo-Asian ocean in the Neoproterozoic and early Palaeozoic: new geochronologic data and palaeotectonic reconstructions, Precambrian Res., 2003, vol. 122, pp. 329–358.
Kovach, V.P., Matukov, D.I., Berezhnaya, N.G., Kotov, A.B., Levitsky, V.I., Barash, I.G., Kozakov, I.K., Levsky, L.K., and Sergeev, S.A., SHRIMP zircon age of the Gargan block tonalites – find Early Precambrian basement of the Tuvino-Mongolian microcontinent, Central Asia mobile belt 32th Intern. Geological Congress, Florence: 2004, Pt 2, no. 1263.
Kozakov, I.K., Stuctural features and metamorphism of the Precambrian granitoids of the Sangilen highland, Tuva, Geol. Geofiz., 1976, no. 12, pp. 159–160.
Kozakov, I.K. and Azimov, P.Ya., Geodynamics of the origin of granulites in the Sangilen Block of the Tuva–Mongolian Terrane, Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Petrology, 2017, vol. 25, no. 6, pp. 615–624.
Kozakov, I.K., Kotov, A.B., Salnikova, E.B., et al., Metamorphic age of crystalline complexes of the Tuva–Mongolia massif: the U–Pb geochronology of granitoids, Petrology, 1999, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 177–191.
Kröner, A., Kovach, V., Belousova, E., Hegner, E., Armstrong, R., Dolgopolova, A., Seltmann, R., Alexeiev, D.V., Hoffmann, J.E., Wong, J., Sun, M., Cai, K., Wang, T., Tong, Y., Wilde, S.A., Degtyarev, K.E., and Rytsk, E., Reassessment of continental growth during the accretionary history of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Gondwana Res., 2014, vol. 25, pp. 103–125.
Kröner, A., Kovach, V., Alexeiev, D., Wang, K.L., Wong, J., Degtyarev, K., and Kozakov, I., 2017. No excessive crustal growth in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Further evidence from field relationships and isotopic data, Gondwana Res., 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2017.04.006
Le Maitre, R.W., Igneous Rocks: A Classification and Glossary of Terms, 2nd. Ed, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002.
Liao, S.Y., Wang, D.B., Tang, Y., Yin, F.G., Cao, S.N., Wang, L.Q., Wang, B.D., and Sun, Z.M., Late Paleozoic Woniusi basaltic province from Sibumasu terrane: Implications for the breakup of eastern Gondwana’s northern margin, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 2015. https://doi.org/10.1130/B31210.1
Lin, L.N., Xiao, W.J., Wan, B., Windley, B.F., Ao, S.J., Han, C.M., Feng, J.Y., Zhang, J.E., and Zhang, Z.Y., Geochronology and geological evidence for persistence of south-dipping subduction to Late Permian time, Langshan area, Inner Mongolia (China): significance for termination of accretionary orogenesis in the southern Altaids, Am. J. Sci., 2014, vol. 314, pp. 679–703.
Liu, Z., Zhou, Q., Lai, Y., Qing, C.S., Li, Y.X., Wu, J.Y., and Xia, X.B., Petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous Laguila bimodal intrusive rocks from the Tethyan Himalaya: Implications for the break-up of Eastern Gondwana, Lithos, 2015, vol. 236–237, pp. 190–202.
Liu, Q., Zhao, G.C., Han, Y.G., Eizenhöfer, P.R., Zhu, Y.L., Hou, W.Z., and Zhang, X.R., Timing of the final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean in the Alxa Terrane: Constraints from geochronology and geochemistry of Late Carboniferous to Permian gabbros and diorites. Lithos, 2017a, vol. 274—275, pp. 19—30.
Liu, Q., Zhao, G.C., Han, Y.G., Eizenhöfer, P.R., Zhu, Y.L., Hou, W.Z., Zhang, X.R., and Wang, B., Geochronology and geochemistry of Permian to Early Triassic granitoids in the Alxa Terrane: constraints on the final closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean, Lithosphere, 2017b. https://doi.org/10.1130/L646.1
Liu, Z., Liao, S.Y., Zhou, Q., and Zhang, X., Petrogenesis of ore-bearing porphyry in non-subduction setting: a case study of the Eocene potassic intrusions in the western Yangtze Block, Mineral. Petrol., 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-018-0597-4
Lu, J.C., Wei, X.Y., Li, Y.H., and Wei, J.S., Geochemical characteristics of CarboniferousPermian hydrocarbon source rocks of Xiangtan 9 well in Ejin Banner, western Inner Mongolia, Geol. Bull. China, 2012, vol. 31, no. 10, pp. 1628–1638 (in Chinese with English abstract).
McKenzie, D.A.N. and O’Nions, R.K., Partial melt distributions from inversion of rare earth element concentrations, J. Petrol., 1991, vol. 32, pp. 1021–1091.
Pearce, J.A., Harris, N.B.W., and Tindle, A.G., Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks, J. Petrol., 1984, vol. 25, pp. 956–983.
Pu, W., Zhao, K.D., Ling, H.F., and Jiang, S.Y., High precision Nd isotope measurement by Triton TI Mass Spectrometry, Acta Geosci. Sinica, 2004, vol. 25, pp. 271–274 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Pu, W., Gao, J.F., Zhao, K.D., Ling, H.F., Jiang, S.Y., Separation method of Rb–Sr, Sm–Nd using DCTA and HIBA, J. Nanjing Univ. (Natural Sciences), 2005, vol. 41, pp. 445–450 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Robinson, J.A.C. and Wood, B.J., The depth of the spinel to garnet transition at the peridotite solidus, Earth Plane. Sci. Lett., 1998, vol. 164, pp. 277–284.
Rollinson, H.R., Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation, London: Longman Publishing Group, 1993.
Rudnick, R.L. and Gao, S., Composition of the continental crust, Treatise on Geochemistry, Volume 3, Holland, H.D. and Turekian, K.K., Eds., Elsevier, 2003, p. 1–64.
Shervais, J.W., Ti–V plots and the petrogenesis of modern and ophiolitic lavas, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1982, vol. 59, pp. 101–118.
Şengör, A.M.C., Natal’in, B.A., and Burtman, V.S., Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia, Nature, 1993, vol. 364, pp. 299–307.
Shi, X.J., Tong, Y., Wang, T., Zhang, J.J., Zhang, Z.C., Zhang, L., Guo, L., Zeng, T., and Geng, J.Z., LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age and geochemistry of the Early Permian Halinudeng granite in northern Alxa area, western Inner Mongolia, Geol. Bull. China, 2012, vol. 31, pp. 662–670.
Shi, X.J., Wang, T., Zhang, L., Castro, A., Xiao, X.C., Tong, Y., Zhang, J.J., Guo, L., and Yang, Q.D., Timing, petrogenesis and tectonic setting of the Late Paleozoic gabbro–granodiorite–granite intrusions in the Shalazhashan of northern Alxa: constraints on the southernmost boundary of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Lithos, 2014, 208–209, pp. 158–177.
Sun, S.S. and McDonough, W.F., Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes, Geol. Soc., London, Spec. Publ., 1989, vol. 42, pp. 313–345.
Sun, J., Liu, Z., Zhang, S., Li, X.G., and Qi, J.F., Large-scale removal of lithosphere underneath the North China Craton in the Early Cretaceous: geochemical constraints from volcanic lavas in the Bohai Bay Basin, Lithos, 2017, vol. 292–293, pp. 69–80.
Thirlwall, M.F., Smith, T.E., Graham, A.M., Theodorou, N., Hollings, P., Davidson, J.P., and Arculus, R.J., High field strength element anomalies in arc lavas: source or process? J. Petrol., 1994, vol. 35, pp. 819–838.
Wang, T.Y., Wang, S.Z., and Wang, J.R., The Formation and Evolution of Paleozoic Continental Crust in Alxa Region, Lanzhou: Lanzhou University Press, 1994. (in Chinese).
Williams, I.S., Buick, A., and Cartwright, I., An extended episode of early Mesoproterozoic metamorphic fluid flow in the Reynold Region, central Australia, J. Metamorph. Geol., 1996, vol. 14, pp. 29–47.
Windley, B.F., Alexeiev, D., Xiao, W.J., Kröner, A., and Badarch, G., Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt, J. Geol. Soc. London, 2007, vol. 164, pp. 31–47.
Wu, T.R., He, G.Q., and Zhang, C., On Paleozoic tectonics in the Alxa region, Acta Geol. Sinica, 1998, vol. 72, pp. 256–263.
Xiao, W.J., Windley, B.F., Huang, B.C., Han, C.M., Yuan, C., Chen, H.L., Sun, M., Sun, S., and Li, J.L., End-Permian to mid-Triassic termination of the accretionary processes of the southern Altaids: implications for the geodynamic evolution, Phanerozoic continental growth, and metallogeny of Central Asia, Int. J. Earth Sci., 2009, vol. 98, no. 6, pp. 1189–1217.
Xiao, W.J., Windley, B., Sun, S., Li, J.L., Huang, B.C., Han, C.M., Yuan, C., Sun, M., and Chen, H.L., A tale of amalgamation of three Permo-Triassic collage systems in Central Asia: oroclines, sutures, and terminal accretion, Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci., 2015, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 477–507.
Xu, X.S., Griffin, W.L., Ma, X., O’Reilly, S.Y., He, Z.Y., and Zhang, C.L., The Taihua group on the southern margin of the North China craton: further insights from U-Pb ages and Hf isotope compositions of zircons, Mineral. Petrol., 2009, vol. 97, pp. 43–59.
Zhang, L., Shi, X.J., Zhang, J.J., Yang, Q.D., Tong, Y., and Wang, T., LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age and geochemical characteristics of the Taohaotuoxiquan gabbro in northern Alxa, Inner Mongolia, Geol. Bull. China, 2013, vol. 32, pp. 1536–1547.
Zhang, X.R., Zhao, G.C., Eizenhöfer, P.R., Sun, M., Han, Y.G., Hou, W.Z., Liu, D.X., Wang, B., Liu, Q., and Xu, B., Paleozoic magmatism and metamorphism in the Central Tianshan block revealed by U–Pb and Lu–Hf isotope studies of detrital zircons from the South Tianshan belt, NW China, Lithos, 2015a, vol. 233, pp. 193–208.
Zhang, X.R., Zhao, G.C., Eizenhöfer, P.R., Sun, M., Han, Y.G., Hou, W.Z., Liu, D.X., Wang, B., Liu, Q., and Xu, B., Latest Carboniferous closure of the Junggar Ocean constrained by geochemical and zircon U–Pb-Hf isotopic data of granitic gneisses from the Central Tianshan block, NW China, Lithos, 2015b, vol. 238, pp. 26–36.
Zhao, J.H. and Zhou, M.F., Geochemistry of Neoproterozoic mafic intrusions in the Panzhihua district (Sichuan Province, SW China): implications for subduction related metasomatism in the upper mantle, Precambrian Res., 2007, vol. 132, pp. 27–47.
Zheng, R.G., Wu, T.R., Zhang, W., Xu, C., Meng, Q.P., and Zhang, Z.Y., Late Paleozoic subduction system in the northern margin of the Alxa block, Altaids: geochronological and geochemical evidences from ophiolites, Gondwana Res., 2014, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 842–858.
FUNDING
This study is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 41703022), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (lzujbky-2018-52), Plateau mountain ecology and Earth’s environment discipline construction project (grants C176240107), Joint Foundation Project between Yunnan Science and Technology Department and Yunnan University (grants C176240210019), and Geology Discipline Construction Project of Yunnan University (C176210227).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng Liu, Zhang, X., Tan, SC. et al. The Timing of the Paleo-Asian Oceanic Closure: Geochemical Constraints from the Jigede Gabbro in the Alxa Block. Petrology 27, 425–437 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869591119040076
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0869591119040076