Abstract
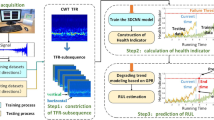
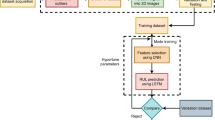
Remaining useful life (RUL) prediction plays an important role in guaranteeing safe operation and reducing maintenance cost in modern industry. In this paper, we present a novel deep learning method for RUL estimation based on time empirical mode decomposition (EMD) and temporal convolutional networks (TCN). The proposed framework can effectively reveal the non-stationary characteristics of bearing degradation signals and acquire time-series degradation signals which namely intrinsic mode functions through empirical mode decomposition. Furthermore, the feature information is used as the input to convolution layer and trained by TCN to predict remaining useful life. The proposed EMD–TCN model structure maintains a superior result compared to several state-of-the-art convolutional algorithms on public data sets. Experimental results show that the average score of EMD–TCN model is improved by 10–20% than traditional convolutional algorithms.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heng, A., Tan, A.C., Mathew, J., Montgomery, N., Banjevic, D., Jardine, A.K.: Intelligent condition-based prediction of machinery reliability. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 23(5), 1600–1614 (2009)
Zhang, J., Jiang, N., Li, H., Li, N.: Online health assessment of wind turbine based on operational condition recognition. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 41(10), 2970–2981 (2019)
Fan, M., Zeng, Z., Zio, E., Kang, R., Chen, Y.: A sequential bayesian approach for remaining useful life prediction of dependent competing failure processes. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 68(1), 317–329 (2018)
Khorasgani, H., Kulkarni, C., Biswas, G., Celaya, J.R., Goebel, K.: Degredation modeling and remaining useful life prediction of electrolytic capacitors under thermal overstress condition using particle filters. In: Annual Conference of the Prognostics and Health Management Society (PHM’13) (2013)
Zheng, Z., Podobnik, B., Feng, L., Li, B.: Changes in cross-correlations as an indicator for systemic risk. Sci Rep 2, 888 (2012)
Zhang, C., Hong, G.S., Xu, H., Tan, K.C., Zhou, J.H., Chan, H.L., Li, H.: A data-driven prognostics framework for tool remaining useful life estimation in tool condition monitoring. In 2017 22nd IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2017)
Si, X.-S., Wang, W., Hu, C.-H., Zhou, D.-H.: Remaining useful life estimation—a review on the statistical data driven approaches. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 213(1), 1–14 (2011)
Fu, D., Zheng, Z., Gui, J., Xiao, R., Huang, G., Li, Y.: Development of a fuel management model for a multi-source district heating system under multi-uncertainty and multi-dimensional constraints. Energy Convers. Manag. 153, 243–256 (2017)
Li, X., Ding, Q., Sun, J.-Q.: Remaining useful life estimation in prognostics using deep convolution neural networks. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 172, 1–11 (2018)
Huang, N.E., Shen, Z., Long, S.R., Wu, M.C., Shih, H.H., Zheng, Q., Yen, N.-C., Tung, C.C., Liu, H.H.: The empirical mode decomposition and the hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 454(1971), 903–995 (1998)
Nectoux, P., Gouriveau, R., Medjaher, K., Ramasso, E., Chebel-Morello, B., Zerhouni, N., Varnier, C.: Pronostia: an experimental platform for bearings accelerated degradation tests. In: IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management, PHM’12. IEEE Catalog Number: CPF12PHM-CDR, pp. 1–8 (2012)
Ahmadzadeh, F., Lundberg, J.: Remaining useful life estimation. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 5(4), 461–474 (2014)
Gao, Z., Cecati, C., Ding, S.X.: A survey of fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant techniques—part I: fault diagnosis with model-based and signal-based approaches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 62(6), 3757–3767 (2015)
Luo, J., Bixby, A., Pattipati, K., Qiao, L., Kawamoto, M., Chigusa, S.: An interacting multiple model approach to model-based prognostics. In: SMC’03 Conference Proceedings. 2003 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. Conference Theme-System Security and Assurance (Cat. No. 03CH37483), vol. 1, pp. 189–194. IEEE (2003)
Li, Y., Kurfess, T., Liang, S.: Stochastic prognostics for rolling element bearings. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 14(5), 747–762 (2000)
Baillie, D., Mathew, J.: Nonlinear model-based fault diagnosis of bearings. NDT e Int. 5(30), 328 (1997)
Tobon-Mejia, D.A., Medjaher, K., Zerhouni, N., Tripot, G.: A data-driven failure prognostics method based on mixture of gaussians hidden markov models. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 61(2), 491–503 (2012)
Cheng, F., Qu, L., Qiao, W., Hao, L.: Enhanced particle filtering for bearing remaining useful life prediction of wind turbine drivetrain gearboxes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(6), 4738–4748 (2018)
Banjevic, D., Jardine, A.: Calculation of reliability function and remaining useful life for a markov failure time process. IMA J. Manag. Math. 17(2), 115–130 (2006)
Sankararaman, S., Goebel, K.: Uncertainty quantification in remaining useful life of aerospace components using state space models and inverse form. In: 54th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, p. 1537 (2013)
Zhang, J., Wang, S., Chen, L., Guo, G., Chen, R., Vanasse, A.: Time-dependent survival neural network for remaining useful life prediction. In: Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 441–452. Springer (2019)
Tian, Z.: An artificial neural network method for remaining useful life prediction of equipment subject to condition monitoring. J. Intell. Manuf. 23(2), 227–237 (2012)
Soualhi, A., Medjaher, K., Zerhouni, N.: Bearing health monitoring based on Hilbert–Huang transform, support vector machine, and regression. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 64(1), 52–62 (2014)
Zhu, M., Ye, K., Wang, Y., Xu, C.-Z.: A deep learning approach for network anomaly detection based on AMF-LSTM. In: IFIP International Conference on Network and Parallel Computing, pp. 137–141. Springer (2018)
Zhu, M., Ye, K., Xu, C.-Z.: Network anomaly detection and identification based on deep learning methods. In: International Conference on Cloud Computing, pp. 219–234. Springer (2018)
Lin, P., Ye, K., Xu, C.-Z.: Dynamic network anomaly detection system by using deep learning techniques. In: International Conference on Cloud Computing, pp. 161–176. Springer (2019)
Ye, K., Liu, Y., Xu, G., Xu, C.-Z.: Fault injection and detection for artificial intelligence applications in container-based clouds. In: International Conference on Cloud Computing, pp. 112–127. Springer (2018)
Pinheiro, H., Jain, P., Joos, G.: Series-parallel resonant converter in the self-sustained oscillating mode for unity power factor applications. In: Proceedings of APEC 97-Applied Power Electronics Conference, vol. 1, pp. 477–483. IEEE (1997)
Bai, S., Kolter, J. Z., Koltun, V.: An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling (2018). arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.01271
Deng, S., Zhang, N., Zhang, W., Chen, J., Pan, J. Z., Chen, H.: Knowledge-driven stock trend prediction and explanation via temporal convolutional network. In: Companion Proceedings of The 2019 World Wide Web Conference, pp. 678–685. ACM (2019)
Nair, V., Hinton, G.E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In: Proceedings of the 27th international conference on machine learning (ICML-10), pp. 807–814 (2010)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFB1004804), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61702492), Shenzhen Discipline Construction Project for Urban Computing and Data Intelligence, and Shenzhen Basic Research Program (No. JCYJ20170818153016513).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Yao, Q., Ye, K. et al. Empirical Mode Decomposition and Temporal Convolutional Networks for Remaining Useful Life Estimation. Int J Parallel Prog 48, 61–79 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10766-019-00650-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10766-019-00650-1