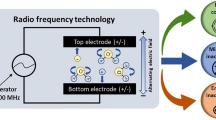
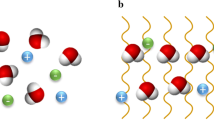
Abstract
Fresh foods, such as vegetables, fruits, and aquatic products, have high water activity and are highly heat-sensitive. Thermal processing of fresh foods is often employed to extend shelf-life without chemical treatment in order to avoid any chemical residues in the preserved food. Radio frequency (RF) heating is one of the most promising heating methods applicable to fresh foods due to rapid heating, low cost, deep thermal penetration, and possibility of better quality control. This paper reviews the recent literature on applications of RF heating in fresh food processing, including cooking, microorganism reduction, disinfestation, thawing, and blanching. The heating efficiency and product quality of aforementioned applications were further discussed. Moreover, recommendations were made for future research on RF to effectively achieve enhanced thermal processing and reliable scale-up. The present study provides some useful information for the use of RF heating in industry and the future study of RF application in fresh food processing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alholy M, Wang Y, Tang J, Rasco B (2005) Dielectric properties of salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) and sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus) caviar at radio frequency (RF) and microwave (MW) pasteurization frequencies. J Food Eng 70:564–570
Armstrong JW (1994) Insect pest and fresh horticultural products: treatments and responses. In: Paull RE, Armstrong JW (eds) Heat and cold disinfestation treatments. CAB International, Wallingford, United Kingdom, pp 103–109
Awuah GB, Ramaswamy HS, Tang J (2014) Radio frequency heating in food processing: principles and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Basaran P, Basaran-Akgul N, Rasco BA (2010) Dielectric properties of chicken and fish muscle treated with microbial transglutaminase. Food Chem 120:361–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.09.050
Bedane TF, Chen L, Marra F, Wang S (2017) Experimental study of radio frequency (RF) thawing of foods with movement on conveyor belt. J Food Eng 201:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.01.010
Birla SL, Wang S, Tang J (2008) Computer simulation of radio frequency heating of model fruit immersed in water. J Food Eng 84:270–280
Birla SL, Wang S, Tang J, Hallman G (2004) Improving heating uniformity of fresh fruit in radio frequency treatments for pest control. Postharvest Biol Technol 33:205–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2004.02.010
Brackeet RE (1994) Microbial spoilage and pathogens. In: Wiley RC (ed) Minimally processed refrigerated fruits and vegetables. Chapman & Hall, New York, pp 269–312
Brunton NP, Lyng JG, Li W, Cronin DA, Morgan D, Mckenna B (2005) Effect of radio frequency (RF) heating on the texture, colour and sensory properties of a comminuted pork meat product. Food Res Int 38:337–344
Challis LJ (2005) Mechanisms for interaction between RF fields and biological tissue. Bioelectromagnetics 26(Suppl 7):S98–S106
Chiewchan N, Mujumdar AS, Devahastin S (2015) Application of drying technology to control aflatoxins in foods and feeds: a review. Dry Technol 33:1700–1707
Cleary SF, Cao G, Liu LM (1996) Effects of isothermal 2.45 GHz microwave radiation on the mammalian cell cycle: comparison with effects of isothermal 27 MHz radiofrequency radiation exposure. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 39:167–173
Culkin KA, Fung DYC (1975) Destruction of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium in microwave-cooked soups. J Milk Food Technol 55:151–152
Dasan BG, Mutlu M, Boyaci IH (2016) Decontamination of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus spores on hazelnuts via atmospheric pressure fluidized bed plasma reactor. Int J Food Microbiol 216:50–59
Drake SR, Heidt ML, Hansen JD, Watkins MA, Tang J, Wang S (2005) Evaluation of radio frequency-hot water treatments for postharvest control of codling moth in 'Bing' sweet cherries. Horttechnology 15:613–616
Erdogdu F, Altin O, Marra F, Bedane TF (2017) A computational study to design process conditions in industrial radio-frequency tempering/thawing process. J Food Eng 213:99–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.05.003
Falade AO, Oboh G, Okoh AI (2017) Potential health implications of the consumption of thermally-oxidized cooking oils—a review. Pol J Food Nutr Sci 67:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjfns-2016-0028
Farag KW, Duggan E, Morgan DJ, Cronin DA, Lyng JG (2009) A comparison of conventional and radio frequency defrosting of lean beef meats: effects on water binding characteristics. Meat Sci 83:278–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2009.05.010
Farag KW, Lyng JG, Morgan DJ, Cronin DA (2008) A comparison of conventional and radio frequency tempering of beef meats: effects on product temperature distribution. Meat Sci 80:488–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2008.01.015
Farag KW, Lyng JG, Morgan DJ, Cronin DA (2011) A comparison of conventional and radio frequency tempering of beef meats: effects on product temperature distribution. Food Bioprocess Tech 4:1128–1136
Ferrari-John RS, Katrib J, Palade P, Batchelor AR, Dodds C, Kingman SW (2016) A tool for predicting heating uniformity in industrial radio frequency processing. Food Bioprocess Tech 9:1865–1873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-016-1762-6
Fiore A, Di Monaco R, Cavella S, Visconti A, Karneili O, Bernhardt S, Fogliano V (2013) Chemical profile and sensory properties of different foods cooked by a new radiofrequency oven. Food Chem 139:515–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.01.028
Fortune JA, Wu B, Klibanov AM (2010) Radio frequency radiation causes no nonthermal damage in enzymes and living cells. Biotechnol Prog 26:1772–1776
Friedman M (2003) Nutritional consequences of food processing. Forum Nutr 56:350–352
Gao M, Tang J, Wang Y, Powers J, Wang S (2010) Almond quality as influenced by radio frequency heat treatments for disinfestation. Postharvest Biol Technol 58:225–231
Geveke DJ, Bigley ABW, Brunkhorst CD (2017) Pasteurization of shell eggs using radio frequency heating. J Food Eng 193:53–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2016.08.009
Guo CF, Zhang ZN, Chen JJ, Fu HF, Subbiah J, Chen XW, Wang YY (2017) Effects of radio frequency heating treatment on structure changes of soy protein isolate for protein modification. Food Bioprocess Tech 10:1574–1583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-017-1923-2
Guo Q, Piyasena P, Mittal GS, Si W, Gong J (2006) Efficacy of radio frequency cooking in the reduction of Escherichia coli and shelf stability of ground beef. Food Microbiol 23:112–118
Guo WC, Zhu XH, Liu Y, Zhuang H (2010) Sugar and water contents of honey with dielectric property sensing. J Food Eng 97:275–281
Hansen JD, Drake SR, Watkins MA, Heidt ML, Anderson PA, Tang J (2006) Radio frequency pulse application for heating uniformity in postharvest codling moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) control of fresh apples (Malus domestica Borkh.). J Food Qual 29:492–504
Hippel ARV (1966) Dielectric materials and applications—student edition engineering
Hou L, Hou J, Li Z, Johnson JA, Wang S (2015) Validation of radio frequency treatments as alternative non-chemical methods for disinfesting chestnuts. J Stored Prod Res 63:75–79
Hou L, Johnson JA, Wang S (2016) Radio frequency heating for postharvest control of pests in agricultural products: a review. Postharvest Biol Technol 113:106–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.11.011
Hou L, Ling B, Wang S (2014) Development of thermal treatment protocol for disinfesting chestnuts using radio frequency energy. Postharvest Biol Technol 98:65–71
Huang Z, Marra F, Subbiah J, Wang S (2016) Computer simulation for improving radio frequency (RF) heating uniformity of food products: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1253000
Ikediala JN, Hansen JD, Tang J, Drake SR, Wang S (2002) Development of a saline water immersion technique with RF energy as a postharvest treatment against codling moth in cherries. Postharvest Biol Technol 24:209–221
Isaacs S et al (2005) An international outbreak of salmonellosis associated with raw almonds contaminated with a rare phage type of Salmonella enteritidis. J Food Prot 68:191–198
Jacob J, Chia LHL, Boey FYC (1995) Thermal and non-thermal interaction of microwave radiation with materials. J Mater Sci 30:5321–5327
Jiang H, Liu Z, Wang S (2017) Microwave processing: effects and impacts on food components. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1319322
Jiao S, Zhong Y, Deng Y (2016) Hot air-assisted radio frequency heating effects on wheat and corn seeds: quality change and fungi inhibition. J Stored Prod Res 69:265–271
Kou X, Li R, Hou L, Zhang L, Wang S (2018) Identifying possible non-thermal effects of radio frequency energy on inactivating food microorganisms. Int J Food Microbiol 269:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.01.025
Larena I, Torres R, de Cal A, Liñán M, Melgarejo P, Domenichini P, Bellini A, Mandrin JF, Lichou J, de Eribe XO, Usall J (2005) Biological control of postharvest brown rot (Monilinia spp.) of peaches by field applications of Epicoccum nigrum. Biol Control 32:305–310
Li R, Kou X, Cheng T, Zheng A, Wang S (2017) Verification of radio frequency pasteurization process for in-shell almonds. J Food Eng 192:103–110
Liu Q, Zhang M, Xu B, Fang Z, Zheng D (2015) Effect of radio frequency heating on the sterilization and product quality of vacuum packaged Caixin. Food Bioprod Process 95:47–54
Llave Y, Liu S, Fukuoka M, Sakai N (2015) Computer simulation of radiofrequency defrosting of frozen foods. J Food Eng 152:32–42
Lopez A, Baganis NA (2010) Effect of radio-frequency energy at 60 MHz on food enzyme activity. J Food Sci 36:911–914
Luechapattanaporn K, Wang Y, Wang J, Tang J, Hallberg LM, Dunne CP (2006) Sterilization of scrambled eggs in military polymeric trays by radio frequency energy. J Food Sci 70:E288–E294. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2005.tb07185.x
Lyng JG, Cronin DA, Brunton NP, Li W, Gu X (2007) An examination of factors affecting radio frequency heating of an encased meat emulsion. Meat Sci 75:470–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2006.07.022
Lyng JG, Zhang L, Brunton NP (2005) A survey of the dielectric properties of meats and ingredients used in meat product manufacture. Meat Sci 69:589–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2004.09.011
Lyu X, Peng X, Wang S, Yang B, Wang X, Yang H, Xiao Y, Baloch AB, Xia X (2018) Quality and consumer acceptance of radio frequency and traditional heat pasteurised kiwi puree during storage. International Journal of Food Science & Technology 53:209–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.13575
Manzocco L, Anese M, Nicoli MC (2008) Radiofrequency inactivation of oxidative food enzymes in model systems and apple derivatives. Food Res Int 41:1044–1049
Marchand C, Meunier T (1990) Recent developments in industrial radio-frequency technology. J Microw Power Electromagn Energy 25:39–46
Min Z, Hao J, Ruixin L, Silva MA, Rocha SCS (2010) Recent developments in microwave-assisted drying of vegetables, fruits, and aquatic products—drying kinetics and quality considerations. Dry Technol 28:1307–1316
Mitchell L (2016) The wave of the future. http://www.radiofrequency.com/pdfs/rf_pasteurization.pdf. Accessed 6 Jan 2016
Nagaraj G, Purohit A, Harrison MA, Singh RK, Hung Y, Mohan A (2016) Radiofrequency pasteurization of inoculated ground beef homogenate. Food Control 59:59–67
Okamoto A, Suzuki A (2002) Effects of high hydrostatic pressure-thawing on pork meat. Prog Biotechnol 19:571–576
Palazoğlu TK, Miran W (2017) Experimental comparison of microwave and radio frequency tempering of frozen block of shrimp. Innov Food Sci Emerg 41:292–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2017.04.005
Pircon LJ, Loquercio P, Doty DM (1953) High-frequency cooking, high-frequency heating as a unit operation in meat processing. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry 1:844–847
Piyasena P, Dussault C, Koutchma T, Ramaswamy HS, Awuah GB (2003) Radio frequency heating of foods: principles, applications and related properties—a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 43:587–606. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408690390251129
Ranjan S, Dasgupta N, Walia N, Chand CT, Ramalingam C (2017) Microwave blanching: an emerging trend in food engineering and its effects on Capsicum annuum L. J Food Process Eng 40(2):e12411. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12411
Risman P (1991) Terminology and notation of microwave power and electromagnetic energy. J Microw Power 26:243–250
Saadi S et al (2014) Evaluating efficiency of radio waves for microbial removal in water samples. J Adv Environ Health Res 2(3):157–164
Sanders HR (1966) Dielectric thawing of meat and meat products. Int J Food Sci Technol 1:183–192
Schustergajzago I, Kiszter AK, Tothmarkus M, Barath A, Markusbednarik Z, Czukor B (2006) The effect of radio frequency heat treatment on nutritional and colloid-chemical properties of different white mustard (Sinapis alba L.) varieties. Innov Food Sci Emerg 7:74–79
Shazman A, Mizrahi S, Cogan U, Shimoni E (2007) Examining for possible non-thermal effects during heating in a microwave oven. Food Chem 103:444–453
Sisquella M, Casals C, Picouet P, Vinas I, Torres R, Usall J (2013) Immersion of fruit in water to improve radio frequency treatment to control brown rot in stone fruit. Postharvest Biol Technol 80:31–36
Sisquella M, Vinas I, Picouet P, Torres R, Usall J (2014) Effect of host and Monilinia spp. variables on the efficacy of radio frequency treatment on peaches. Postharvest Biol Technol 87:6–12
Soghomonyan D, Trchounian K, Trchounian A (2016) Millimeter waves or extremely high frequency electromagnetic fields in the environment: what are their effects on bacteria? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:4761–4771
Sosa-Morales ME, Tiwari G, Wang S, Tang J, Garcia HS, Lopez-Malo A (2009) Dielectric heating as a potential post-harvest treatment of disinfesting mangoes, part II: development of RF-based protocols and quality evaluation of treated fruits. Biosyst Eng 103:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2009.02.014
Ştefănoiu G-A, Tănase EE, Miteluţ AC, Popa ME (2016) Unconventional treatments of food: microwave vs. radiofrequency. Agric Agric Sci Procedia 10:503–510
Tang J, Ikediala JN, Wang S, Hansen JD, Cavalieri RP (2000) High-temperature-short-time thermal quarantine methods. Postharvest Biol Tec 21:129–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(00)00171-X
Tiwari G, Wang S, Birla SL, Tang J (2008) Effect of water-assisted radio frequency heat treatment on the quality of 'Fuyu' persimmons. Biosyst Eng 100:227–234
Uemura K, Kanafusa S, Takahashi C, Kobayashi I (2017) Development of a radio frequency heating system for sterilization of vacuum-packed fish in water. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 81:762–767. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2017.1280660
Uyar R, Bedane TF, Erdogdu F, Palazoglu TK, Farag KW, Marra F (2015) Radio-frequency thawing of food products—a computational study. J Food Eng 146:163–171
Uyar R, Erdogdu F, Marra F (2014) Effect of load volume on power absorption and temperature evolution during radio-frequency heating of meat cubes: a computational study. Food Bioprod Process 92:243–251
Vishwanathan KH, Giwari GK, Hebbar HU (2013) Infrared assisted dry-blanching and hybrid drying of carrot. Food Bioprod Process 91:89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2012.11.004
Wang S, Ikediala JN, Tang J, Hansen JD, Mitcham EJ, Mao R, Swanson BG (2001a) Radio frequency treatments to control codling moth in in-shell walnuts. Postharvest Biol Technol 22:29–38
Wang S, Monzon M, Johnson JA, Mitcham EJ, Tang J (2007) Industrial-scale radio frequency treatments for insect control in walnuts: I: heating uniformity and energy efficiency. Postharvest Biol Technol 45:240–246
Wang S, Tang J, Cavalieri RP (2001b) Modeling fruit internal heating rates for hot air and hot water treatments. Postharvest Biol Technol 22:257–270
Wang S, Tang J, Johnson JA, Mitcham E, Hansen JD, Hallman G, Drake SR, Wang Y (2003) Dielectric properties of fruits and insect pests as related to radio frequency and microwave treatments. Biosyst Eng 85:201–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1537-5110(03)00042-4
Wang S, Tiwari G, Jiao S, Johnson JA, Tang J (2010) Developing postharvest disinfestation treatments for legumes using radio frequency energy. Biosyst Eng 105:341–349
Wang Y, Tang J, Barbara R, Kong F, Wang S (2008) Dielectric properties of salmon fillets as a function of temperature and composition. J Food Eng 87:236–246
Wang YY, Li YR, Wang SJ, Li Z, Gao MX, Tang JM (2011) Review of dielectric drying of foods and agricultural products. Int J Agric Biol Eng 4:1–19
Xu J, Zhang M, Adhikari B (2017a) Comparative study on the effect of radio frequency and high-pressure pasteurization on the texture, water distribution, and rheological properties of Nostoc sphaeroides. J Appl Phycol 30:1041–1048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1325-x
Xu J, Zhang M, An Y, Roknul A, Adhikari B (2017b) Effects of radio frequency and high pressure steam sterilization on the color and flavor of prepared Nostoc sphaeroides. J Sci Food Agric 98:1719–1724. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8644
Xu J, Zhang M, Bhandari B, Kachele R (2017c) ZnO nanoparticles combined radio frequency heating: a novel method to control microorganism and improve product quality of prepared carrots. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 44:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2017.07.025
Yang J, Tang JM, Wang SJ, Koral T (2014) Influence of dielectric properties on the heating rate in free-running oscillator radio frequency systems. J Food Eng 120:197–203
Zhang L, Lyng JG, Brunton NP (2004) Effect of radio frequency cooking on the texture, colour and sensory properties of a large diameter comminuted meat product. Meat Sci 68:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2004.03.011
Zhang M, Chen H, Mujumdar AS, Zhong Q, Sun J (2015) Recent developments in high-quality drying with energy-saving characteristic for fresh foods. Dry Technol 33:1590–1600. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2015.1012267
Zhang M, Jiang H, Lim R (2010) Recent developments in microwave-assisted drying of vegetables, fruits, and aquatic products—drying kinetics and quality considerations. Dry Technol 28:1307–1316
Zhang Z, Guo C, Gao T, Fu H, Chen Q, Wang Y (2017) Pilot-scale radio frequency blanching of potato cuboids: heating uniformity. Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture 98:312–320. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8473
Zhao Y, Flugstad B, Kolbe E, Park JW, Wells JH (2010) Using capacitive (radio frequency) dielectric heating in food processing and preservation—a review. J Food Process Eng 23:25–55
Zhao Y, Zhao W, Yang R, Singh Sidhu J, Kong F (2017) Radio frequency heating to inactivate microorganisms in broccoli powder. Food Quality and Safety 1:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1093/fqs/fyx005
Zheng A, Zhang L, Wang S (2017) Verification of radio frequency pasteurization treatment for controlling Aspergillus parasiticus on corn grains. Int J Food Microbiol 249:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.02.017
Zhu H, Li D, Li S, Wang S (2017) A novel method to improve heating uniformity in mid-high moisture potato starch with radio frequency assisted treatment. J Food Eng 206:23–36
Zhu X, Guo W, Jia Y, Kang F (2014) Dielectric properties of raw milk as functions of protein content and temperature. Food Bioprocess Tech 8:670–680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1440-5
Funding
We acknowledge the financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (Contract No. 2017YFD0400901), Jiangsu Province (China) Agricultural Innovation Project (Contract No. CX(17)2017), National First-class Discipline Program of Food Science and Technology (No. JUFSTR20180205), and Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory Project of Advanced Food Manufacturing Equipment and Technology (No. FMZ201803); all of which enabled us to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, C., Mujumdar, A.S. & Zhang, M. New Development in Radio Frequency Heating for Fresh Food Processing: a Review. Food Eng Rev 11, 29–43 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-018-9184-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-018-9184-z