Abstract
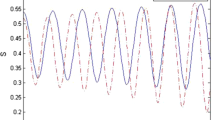
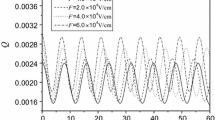
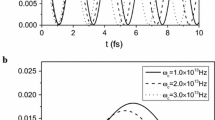
In this work, an electron which is strongly coupled to the strong electron–phonon (e–p) in RbCl quantum pseudodot qubit is considered. First, we employ the Pekar variational method and obtain the eigenenergies and eigenfunctions of the ground and the first excited states of the system. Then, we have employed three different entropies such as Tsallis, Landsberg–Vedral, and Escort for the system subjected to an applied electric field. In this regard, we have studied the effect of polaronic radius, electric field, e–p coupling strength, and non-extensive parameter. It is found that the entropies oscillate with passing time. The entropies increase with enhancing electric field, e–p coupling strength and decrease with polaronic radius. The results show that the missing information in the RbCl pseudodot qubit can be controlled by changing the system parameters. According to the results, it is deduced that the entropy is an important quantity to display the total storage or missing information in a qubit.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
S H Chen J. Low. Temp. Phys.170 108 (2013)
R Khordad, B Mirhosseini and H Bahramiyan Opt. Quant. Electron.48 122 (2016)
R Khordad and H R Rastegar Sedehi Superlatt. Microstruct.101 559 (2017)
L Q Feng and J L Xiao Opt. Quant. Electron.48 459 (2016)
E Togan, Y Chu, A S Trifonov, L Jiang, J Maze, L Childress, M V G Dutt, A S S \( \phi \) rensen, R Hemmer, A S Zibrov and M D Lukin Nature466 730 (2010)
R Roloff, T Eissfeller, P Vogl New J. Phys.12 093012 (2010)
M A Nielsen and I L Chang Computation and Quantum Information (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p 38 (2000)
M Mosca Quantum Algorithms Computational Complexity (New York: Springer) p 83 (2012)
G Passante, O Moussa, D A Trottier and R Laamme Phys. Rev. A84 044302 (2011)
C Weedbrook, S Pirandola, R Garcia-Patron, N J Cerf, T C Ralph, J H Shapiro and S Lloyd Rev. Mod. Phys.84 621 (2012)
G Feng, G Xu and G Long Phys. Rev. Lett.110 190501 (2013)
P Schindler, J T Barreiro, T Monz, V Nebendahl, D Nigg, M Chwalla, M Hennrich and R Blatt Science332 1059 (2011)
Y Sun, Z H Ding and J L Xiao J. Electron. Mater.45 3576 (2016)
J Gorman, D G Hasko and D A Williams Phys. Rev. Lett.95 090502 (2005)
J L Xiao, Int. J. Theor. Phys.55 (2016) 4918.
R Khordad and H R R Sedehi Indian J. Phys.91 825 (2017)
H Bahramiyan, R Khordad and H R R Sedehi Indian J. Phys.92 941 (2018)
J L Xiao, Chin. Phys. B. 26 (2017) 027104.
Y J Chen and J L Xiao Acta Phys. Sinica57 6758 (2008)
J L Xiao Mod. Phys. Lett. B29 1550098 (2015)
S M Ikhdair and M Hamzavi Physica B407 4198 (2012)
J L Xiao Quantum Inf. Process.12 3707 (2013)
X J Ma, B Qi and J L Xiao J. Low Temp. Phys.180 315 (2015)
R Khordad and A Ghanbari Opt. Quant. Electron.49 76 (2017)
R Khordad Solid State Sciences12 1253 (2010)
S I Pekar and M F Deigen Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz.18 481 (1948)
S I Pekar Untersuchungen uber die Elektronen-theorie der Kristalle (Berlin: Akademie Verlag) p 44 (1954)
L D Landau and S I Pekar Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz.18 419 (1948)
C E Shannon Bell Syst Tech J,27 379 (1948)
C Beck Contemp. Phys.50 495 (2009).
P Peretto An Introduction to the Modeling of Neural Networks (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) p 89 (1992)
C Tsallis J. Stat. Phys.52 479 (1988)
J F Bercher Phys. Lett. A375 2969 (2011)
J T Devreese Polarons in ionic crystals and polar semiconductors (Amsterdam: North-Holland) p 76 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sedehi, H.R.R., Khordad, R. Study of RbCl quantum pseudodot qubits by using of non-extensive entropies. Indian J Phys 94, 605–611 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01482-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-019-01482-y