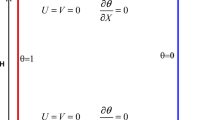Abstract
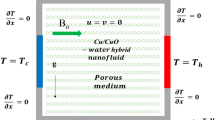
In this study, MHD conjugate free convection of a porous cavity having a curved shape conductive partition is numerically analyzed by using the Galerkin weighted residual finite element method. The numerical simulation is performed for different values of pertinent parameters: Rayleigh number (between \(10^4\) and \(10^6\)), Hartmann number (between 0 and 60), Darcy number (between \(5 \times 10^{-4}\) and 0.05), porosity of the medium (between 0.25 and 0.75), curvature of the partition (minor axis radius of the horizontal ellipse, between 0.01H and 0.3H) and conductivity ratio (between 0.05 and 50). It was observed that the heat transfer rate enhances locally and in average for higher values of Rayleigh number, Darcy number, porosity of the medium and conductivity ratio, whereas the impact is opposite for higher values of Hartmann number. The amount of average Nusselt number reduction is obtained as \(22\%\) when Hartmann number is changed from 0 to 60 at Rayleigh number of \(10^5\). Curvature and conductivity of the curved partition affect the variation in fluid flow and heat transfer characteristics. Maximum of \(7\%\) variation in the average Nusselt number is achieved when the curvature of the conductive partition is varied but the effects of thermal conductivity ratio on heat transfer rate are higher. Long Short-Term Memory Networks are used for estimation of the velocity and temperatures in the computational domain for various values of pertinent input parameters variation in the system which includes conjugate heat transfer mechanism in a porous enclosure with complex-shaped conductive partition under the effects of magnetic field.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c :
-
Elliptic curvature radius (m)
- Da :
-
Darcy number
- Gr :
-
Grashof number
- h :
-
Local heat transfer coefficient (W \(\hbox {m}^{-2}\) K\(^{-1}\))
- Ha :
-
Hartmann number
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m\(^{-1}\) K\(^{-1}\))
- Kr:
-
Conductivity ratio
- H :
-
Cavity height (m)
- n :
-
Unit normal vector
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- R :
-
Residual
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- u, v :
-
x–y velocity components (m s\(^{-1}\))
- W :
-
Weight function
- \(\alpha\) :
-
Thermal diffusivity (\(\hbox {m}^2\) s\(^{-1}\))
- \(\beta\) :
-
Expansion coefficient (K\(^{-1}\))
- \(\gamma\) :
-
Magnetic inclination angle
- \(\epsilon\) :
-
Porosity of the medium
- \(\nu\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity (\(\hbox {m}^2\) s\(^{-1}\))
- \(\theta\) :
-
Non-dimensional temperature
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density of the fluid (kg \(\hbox {m}^{-3}\))
- c:
-
Cold
- h:
-
Hot
- m:
-
Average
- p:
-
Solid partition
References
Mahmoud MA, Ben-Nakhi AE. Neural networks analysis of free laminar convection heat transfer in a partitioned enclosure. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2007;12:1265–76.
Yucel N, Ozdem AH. Natural convection in partially divided square enclosures. Heat Mass Transf. 2003;40:167–75.
Khalifa AJN, Khudheyer AF. Natural convection in partitioned enclosures: experimental study on 14 different configurations. Energy Convers Manag. 2001;42:653–61.
Varol Y, Oztop HF, Koca A. Effects of inclination angle on conduction—natural convection in divided enclosures filled with different fluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2010;37:182–91.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Corrugated conductive partition effects on MHD free convection of CNT-water nanofluid in a cavity. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2019;129:265–77.
Al-Rashed A, Kolsi L, Oztop HF, Aydi A, Malekshah EH, et al. 3D magneto-convective heat transfer in CNT-nanofluid filled cavity under partially active magnetic field. Phys E Low-Dimens Syst Nanostruct. 2018;99:294–303.
Pekmen B, Sezgin MT. MHD flow and heat transfer in a lid-driven porous enclosure. Comput Fluids. 2014;89:191–9.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Numerical study of MHD mixed convection in a nanofluid filled lid driven square enclosure with a rotating cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;78:741–54.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Effect of a rotating cylinder in forced convection of ferrofluid over a backward facing step. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;71:142–8.
Hsiao KL. To promote radiation electrical MHD activation energy thermal extrusion manufacturing system efficiency by using Carreau-Nanofluid with parameters control method. Energy. 2017;130:486–99.
Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD. Ferrohydrodynamic and magnetohydrodynamic effects on ferrofluid flow and convective heat transfer. Energy. 2014;75:400–10.
Hajialigol N, Fattahi A, Ahmadi MH, Qomi ME, Kakoli E. MHD mixed convection and entropy generation in a 3-D microchannel using Al2O3 water nanofluid. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2015;46:30–42.
Hsiao KL. Stagnation electrical MHD nanofluid mixed convection with slip boundary on a stretching sheet. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;98:850–61.
Abbassi H, Nassrallah SB. MHD flow and heat transfer in a backward-facing step. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2007;34:231–7.
Sarris IE, Zikos GK, Grecos AP, Vlachos NS. On the limits of validity of the low magnetic Reynolds number approximation in MHD natural-convection heat transfer. Numer Heat Transf Part B. 2006;50:158–80.
Hsiao KL. Micropolar nanofluid flow with MHD and viscous dissipation effects towards a stretching sheet with multimedia feature. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2017;112:983–90.
Hossain MS, Alim MA. MHD free convection within trapezoidal cavity with non-uniformly heated bottom wall. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;69:327–36.
Oztop HF, Al-Salem K, Pop I. MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with corner heater. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54:494–3504.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. MHD mixed convection of nanofluid filled partially heated triangular enclosure with a rotating adiabatic cylinder. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng. 2014;45:2150–62.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Modeling and optimization of MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven trapezoidal cavity filled with alumina-water nanofluid: Effects of electrical conductivity models. Int J Mech Sci. 2018;136:264–78.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF, Chamkha AJ. MHD mixed convection and entropy generation of nanofluid filled lid driven cavity under the influence of inclined magnetic fields imposed to its upper and lower diagonal triangular domains. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;406:266–81.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Influence of inclination angle of magnetic field on mixed convection of nanofluid flow over a backward facing step and entropy generation. Adv Powder Technol. 2015;26:1663–75.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. MHD Pulsating forced convection of nanofluid over parallel plates with blocks in a channel. Int J Mech Sci. 2019;157:726–40.
Selimefendigil F, Oztop HF. Fluid–solid interaction of elastic-step type corrugation effects on the mixed convection of nanofluid in a vented cavity with magnetic field. Int J Mech Sci. 2019;152:185–97.
Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ. Conjugate natural convection in a differentially heated composite enclosure filled with a nanofluid. J Porous Media. 2015;18:699–716.
Sun Q, Pop I. Free convection in a triangle cavity filled with a porous medium saturated with nanofluids with flush mounted heater on the wall. Int J Therm Sci. 2011;50:2141–53.
Sheremet MA, Trifonova TA. Unsteady conjugate natural convection in a vertical cylinder containing a horizontal porous layer: Darcy model and Brinkman-extended Darcy model. Transp Porous Media. 2014;101:437–63.
Selimefendigil F, Ismael MA, Chamkha AJ. Mixed convection in superposed nanofluid and porous layers in square enclosure with inner rotating cylinder. Int J Mech Sci. 2017;124:95–108.
Guedda M, Ouahsine A. Similarity solutions of MHD flows in a saturated porous medium. Eur J Mech B Fluids. 2012;33:87–94.
Makinde O, Aziz A. MHD mixed convection from a vertical plate embedded in a porous medium with a convective boundary condition. Int J Therm Sci. 2010;49:1813–20.
Khan M, Fetecau C, Haya T. MHD transient flows in a channel of rectangular cross-section with porous medium. Phys Lett A. 2007;369:44–54.
Chamkha AJ, Selimefendigil F. MHD free convection and entropy generation in a corrugated cavity filled with a porous medium saturated with nanofluids. Entropy. 2018;20:846.
Aleshkova IA, Sheremet MA. Unsteady conjugate natural convection in a square enclosure filled with a porous medium. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2010;53:5308–20.
Sivaraj C, Sheremet MA. MHD natural convection in an inclined square porous cavity with a heat conducting solid block. J Magn Magn Mater. 2017;426:351–60.
Rudraiah N, Barron RM, Venkatachalappa M, Subbaraya CK. Effect of a magnetic field on free convection in a rectangular enclosure. Int J Eng Sci. 1995;33:1075–84.
Ghasemi B, Aminossadati SM, Raisi A. Magnetic field effect on natural convection in a nanofluid-filled square enclosure. Int J Therm Sci. 2011;50:1748–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selimefendigil, F., Akbulut, Y., Sengur, A. et al. MHD conjugate natural convection in a porous cavity involving a curved conductive partition and estimations by using Long Short-Term Memory Networks. J Therm Anal Calorim 140, 1457–1468 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08865-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08865-7