Abstract
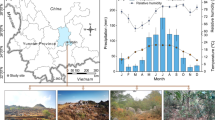
This study aims to investigate the diversity of mangrove species and their soil erosion mitigation performance in Hung Hoa Mangrove Forest, Vinh City, Vietnam. Under high rainfall climatic condition, the mangrove plants were found to reduce soil erosion due to storm runoff during dry season. The soil organic matter in the covered and uncovered part by species of the mangrove forest was 141.1 ± 37.6 g/kg and 95.2 ± 19.2 g/kg, respectively. The percentage of clay and silt in the mangrove forest, covered and uncovered by mangrove species were found to be 55.7 ± 2.4% and 45.5 ± 2.2%, respectively. The increase in distance from 10,045 to 14,378 m was correlated to the decrease in soil salinity from 5.9 ± 0.8 to 3.8 ± 0.5 ppt (r2 = 0.546; P < 0.05). A total of 11 mangrove species were detected in the mangrove forest. The number of species ascribed to dicotyledons, monocotyledons and pteridophytes in the mangrove forest community were 17, 12 and 3, respectively. Based on the result obtained from this field study, it was observed that the mangrove forest plays an important role to provide growth and reproduction habitat for the local flora and protect the land from the effects of high precipitation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anh DT, Hoang LP, Bui MD, Rutschmann P (2018) Simulating future flows and salinity intrusion using combined one and two dimensional hydrodynamic modelling—the case of Hau River, Vietnamese Mekong Delta. Water 10:897 (1–21)
Bako AN, Darboux F, James F, Josserand C, Lucas C (2016) Pressure and shear stress caused by raindrop impact at the soil surface: scaling laws depending on the water depth. Earth Surf Process Landf 41:1199–1210
Basyuni M, Baba S, Kinjo Y, Oku H (2012) Differential enzymatic defense mechanisms in leaves and roots of two true mangrove species under long-term salt stress. Aquat Bot 97:17–23
Belhassan K (2011) Relationship between river flow, rainfall and groundwater pumpage in Mikkes Basin (Morocco). Iran J Earth Sci 3:134–152
Biswas A, Biswas A (2014) Comprehensive approaches in rehabilitating salt affected soils: a review on Indian perspective. Open Trans Geosci 1:13–24
Cao L, Zhang Y, Lu H, Yuan J, Zhu Y, Liang Y (2015) Grass hedge effects on controlling soil loss from concentrated flow: a case study in the red soil region of China. Soil Tillage Res 148:97–105
Chau NL, Chu LM (2017) Fern cover and the importance of plant traits in reducing erosion on steep soil slopes. CATENA 151:98–106
Dolgopolova EN (2013) The conditions for tidal bore formation and its effect on the transport of saline water at river mouths. Water Resour 40:16–30
Fan P, Ouyang Z, Nguyen DD, Nguyen TTH , Park H , Chen J (2019) Urbanization, economic development, environmental and social changes in transitional economies: Vietnam after Doimoi. Landsc Urban Plan 187:145–155
Farooqui A, Ranjana Y, Joshi Y (2016) Low Na/K ratio in the leaves of mangroves mitigates salinity stress in estuarine ecosystem. Trop Plant Res 3:78–86
Feng Y, Sun T, Zhu MS, Qi M, Yang W, Shao DD (2018) Salt marsh vegetation distribution patterns along groundwater table and salinity gradients in Yellow River Estuary under the influence of land reclamation. Ecol Indic 92:82–90
Jayatissa LP, Wickramasinghe WAADL, Dahdouh-Guebas F, Huxham M (2008) Interspecific variations in responses of mangrove seedlings to two contrasting salinities. Int Rev Hydrobiol 93:700–710
Jennerjahn TC, Venugopalan I (2002) Relevance of mangroves for the production and deposition of organic matter along tropical continental margins. Sci Nat 89:23–30
Jones K, Hanna E (2004) Design and implementation of an ecological engineering approach to coastal restoration at Loyola Beach, Kleberg County, Texas. Ecol Eng 22:249–261
Kantharajan G, Pandey PK, Krishnan P, Ragavan P, Jeevamani JJJ, Purvaja R, Ramesh R (2018) Vegetative structure and species composition of mangroves along the Mumbai Coast, Maharashtra, India. Reg Stud Mar Sci 19:1–8
Kodikara KAS, Jayatissa LP, Huxham M, Dahdouhguebas F, Koedam N (2017) The effects of salinity on growth and survival of mangrove seedlings changes with age. Acta Bot Bras 32:37–46
Kumar T, Ghose M (2006) Mycorrhizal status (VAM) of some mangroves growing in saline and non-saline. J Mycopathol Res 44:311–320
Kusumaningtyas MA, Hutahaean AA, Fischer HW, Pérez-Mayo M, Ransby D, Jennerjahn TC (2019) Variability in the organic carbon stocks, sources, and accumulation rates of Indonesian mangrove ecosystems. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 218:310–323
Li Q, Xi M, Wang Q, Kong F, Li Y (2017) Characterization of soil salinization in typical estuarine area of the Jiaozhou Bay, China. Phys Chem Earth 103:51–61
Li J, Tfwala SS, Chen S (2018) Effects of vegetation density and arrangement on sediment budget in a sediment-laden flow. Water 10:1412 (1–13)
Maren DSV, Hoekstra P, Hoitink AJF (2004) Tidal flow asymmetry in the diurnal regime: bed-load transport and morphologic changes around the Red River Delta. Ocean Dyn 54:424–434
Mckee M, White JR, Putnam-Duhon LA (2016) Simulated storm surge effects on freshwater coastal wetland soil pore water salinity and extractable ammonium levels: implications for marsh recovery after storm surge. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 181:338–344
Nehru P, Balasubramanian P (2018) Mangrove species diversity and composition in the successional habitats of Nicobar Islands, India: a post-tsunami and subsidence scenario. For Ecol Manag 427:70–77
Nelson DW, Sommers LE, Sparks DL, Page AL, Helmke PA, Loeppert RH, Soltanpour PN, Tabatabai MA, Johnston CT, Sumner ME (1996) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods of soil analysis: Part 3—chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America Book Series. Crop Science Society of America (CSSA), Madison, pp 961–1010
Praveen P, Lokesh SL, Ganashruthy MK (2013) Characteristics of tree canopy affecting through fall and interception of rainfall in a stand of silver oak (Grevilia robusta). Int J Agric Biol Eng 6:98–100
Quartel S, Kroon A, Augustinus PGEF, Santen PV, Tri NH (2007) Wave attenuation in coastal mangroves in the Red River Delta, Vietnam. J Asian Earth Sci 29:576–584
Rushdi T, Mahmoud AA (2015) Hydrochemistry, evolution, and origin of brines in supratidal saline pans, south Jeddah, Red Sea Coast, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 8:8835–8851
Satyanarayana B, Idris IF, Mohamad KA, Husain ML, Shazili NAM, Dahdouh-Guebas F (2010) Mangrove species distribution and abundance in relation to local environmental settings: a case-study at Tumpat, Kelantan Delta, East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Bot Mar 53:79–88
Schweinsbergmickan MSZ, Müller T (2010) Impact of effective microorganisms and other biofertilizers on soil microbial characteristics, organic-matter decomposition, and plant growth. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 172:704–712
Tagour RMH, Elhamed GMA, Elmetwally IM (2010) Response of rice and associated weeds to bioregulator (biohorm) spray and weed management in salinity soil. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 18:123–134
Tang VT, Fu D, Binh TN, Rene ER, Sang TTT, Singh RP (2018) An investigation on performance and structure of ecological revetment in a sub-tropical area: a case study on Cuatien River, Vinh City, Vietnam. Water 10:636 (1–18)
Twiford AD (2018) Parasitic plants. Curr Biol 28:857–859
Vuong NM, Ichikawa Y, Ishidaira H (2016) Performance assessment of rainwater harvesting considering rainfall variations in Asian tropical monsoon climates. Hydrol Res Lett 10:27–33
Wakushima S, Kuraishi S, Sakurai N (1994) Soil salinity and pH in Japanese mangrove forests and growth of cultivated mangrove plants in different soil conditions. J Plant Res 107:39–46
Wei W, Chen L, Fu B, Huang Z, Wu D, Gu L (2007) The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area. J Hydrol 335:247–258
Yadav S, Irfan M, Ahmad A, Haya S (2011) Causes of salinity and plant manifestations to salt stress: a review. J Environ Biol 32:667–685
Zhang L, Gao G, Tang X, Shao K, Bayartu S, Dai J (2013) Bacterial community changes along a salinity gradient in a Chinese wetland. Can J Microbiol 59:611–619
Ziadat FM, Taimeh AY (2013) Effect of rainfall intensity, slope, land use and antecedent soil moisture on soil erosion in an arid environment. Land Degrad Dev 24:582–590
Acknowledgements
The current study was supported by the Green Processing, Bioremediation and Alternative Energies Research Group Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. The authors thank the group of BS, MS students and employees from the Laboratory of Vinh Medical University, Construction Testing Center-Vilas 178 (Vinh City) and Vinh University for their analytical and instrumentation support. The authors also thank IHE Delft (The Netherlands) and IUCN-Mangrove for Future Program for providing infrastructural and staff time support to collaborate with researchers from Ton Duc Thang University (Vietnam).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Tang, T., Rene, E.R., Binh, T.N. et al. Mangroves diversity and erosion mitigation performance in a low salinity soil area: case study of Vinh City, Vietnam. Wetlands Ecol Manage 28, 163–176 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-019-09704-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-019-09704-0