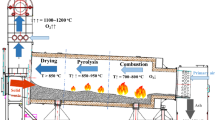
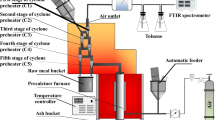
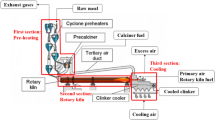
Abstract
Hazardous waste output in the world is increasing every year. To achieve higher efficiency and lower pollution, the incineration technology for hazardous waste needs to be studied further. This study mainly reviews the research progress in incineration, slagging, and pollutant emission in the rotary kiln in China and abroad in the last 10 years, and conducts a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of the research. Considering that there are many variables involved in the incineration process, the incineration law cannot be validated in a limited timeframe by experiments. Researchers often use computer simulations to predict and verify the incineration process through experiments and to provide reference opinions for commercial operations. Through the analysis of the research progress in rotary kilns, it is observed that the basic research in rotary kilns is becoming mature. The latest research trend in rotary kilns is interdisciplinary and mixed research. From a new perspective, further research should be focused on a comparative analysis of the rotary kiln and the cement kiln, full life cycle assessment of the impact factors of rotary kiln on the environment, the impact of the factory treatment process on the workers’ health, etc. The research direction of rotary kiln in China and abroad for the future has been predicted reasonably.

































Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
27 August 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-021-00078-9
References
National Hazardous Waste List. The Bulletin of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. 2016;39–40.
Statistics NBO. Chinese statistical yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press; 2016 (in Chinese).
Visvanathan C. Hazardous waste disposal. Resour Conserv Recycl. 1996;16:201–12.
Zhu J, Jiang X, Liu G, Yan J, Chi Y. Discussion on the technology of waste disposal in rotary kiln. Environ Eng. 2004;5:57–61.
Yang Y, Pijnenborg MJA, Reuter MA, Verwoerd J. Analysis of transport phenomena in a rotary-kiln hazardous waste incinerator. Prog Comput Fluid Dyn. 2007;7:25–39.
Lester TW, Cundy VA, Sterling AM, Montestruc AN, Jakway AL, Lu C, Leger CB, Pershing DW, Lighty JS, Silcox GD, Owens WD. Rotary kiln incineration—comparison and scaling of field-scale and pilot-scale contaminant evolution rates from sorbent beds. Environ Sci Technol. 1991;25:1142–52.
Lemieux PM, Pershing DW. Design and construction of a rotary kiln simulator for use in studying the incineration of hazardous-waste. Rev Sci Instrum. 1989;60:2768–77.
Liu G, Chi Y, Jiang X, Zhu J, Yan J, Cen F. Mass transfer of simulative hazardous waste particles in rotary kiln. J Eng Thermophys. 2005;2:343–6 (in Chinese).
Carroll GJ, Thurnau RC, Fournier DJ. Mercury emissions from a hazardous-waste incinerator equipped with a state-of-the-art wet scrubber. J Air Waste Manag Accoc. 1995;45:730–6.
Ottoboni AP, De Souza I, Menon GJ, Da Silva RJ. Efficiency of destruction of waste used in the co-incineration in the rotary kilns. Energ Convers Manag. 1998;39:1899–909.
Tan PF, Vix P. Modeling and optimization of rotary kiln treating EAF dust. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing. 2005;12:308–12.
Mikulcic H, von Berg E, Vujanovic M, Duic N. Numerical study of co-firing pulverized coal and biomass inside a cement calciner. Waste Manag Res. 2014;32:661–9.
M. Qiu, B. Xu, L. Chen, J. Qin. A brief discussion on the incineration technology of hazardous waste rotary kiln (in Chinese). Jiangxi Chem Ind. 2016;51–53.
J. Jia, L. Zhao. Research on control parameters and adjustment methods of rotary kiln incineration system of hazardous waste (in Chinese). Environ Dev. 2014;25–27.
Ma P, Ma Z, Yan J, Chi Y, Ni M, Cen K. Industrial hazardous waste treatment featuring a rotary kiln and grate furnace incinerator: a case study in China. Waste Manag Res. 2011;29:1108–12.
Huang H, Buekens A. Chemical kinetic modeling of de novo synthesis of PCDD/F in municipal waste incinerators. Chemosphere. 2001;44:1505–10.
Kaiser S, Weigl K, Spiess-Knafl K, Aichernig C, Friedl A. Modeling a dry-scrubbing flue gas cleaning process. Chem Eng Process. 2000;39:425–32.
Zhang S. Engineering design of disposing hazardous waste by rotary kiln systems. Metall Equip. 2010;2:58–62 (in Chinese).
Zhang L, Zhang Y. Theory and practice on incineration and disposal of hazardous wastes (in Chinese). China Environ Prot Ind. 2010;11:36–8.
Zhang D, Yang H, Gao M. Engineering situation of rotary kiln incineration system on hazardous wastes. China Environ Prot Ind. 2010;10:56–8 (in Chinese).
Zhang S. Engineering application of disposing hazardous waste by rotary kiln. Ind Furn. 2010;2:26–9 (in Chinese).
S. Zhang. Optimization design of hazardous waste incineration system of rotary kiln (in Chinese). China Environ Prot Ind. 2015;59–63.
Liu J, An C. Study on applying computer control system to prevent hazardous waste rotary kiln incineration from slagging. Energy Eng. 2010;67:58–62 (in Chinese).
X. Jiang, Z. Fei, S. Lu, C. Li, C. An, Y. Chi, J. Yan, K. Yu, J. Pan, Z. Shi. Incineration characteristics of multi-incineration system of rotary fluidizing and ash-cooling for hazardous wastes (in Chinese). Chin J Environ Eng. 2010;909–914.
J. Qian, X. Jiang, F. Wang, Y. Zhang, X. Shen. Study on the melting characteristics of slag from the incinerator of hazardous wastes containing fluorine and chlorine (in Chinese). Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae. 2011;2499–2505.
C. Li. Studies and application on thermal disposal and slagging characteristics for typical hazardous waste in two-stage incineration system with rotary kiln (in Chinese). Zhe Jiang University. 2011. pp 208.
Qian J, Jiang X, Wang F, Chi Y, Yan J. Effect of fluorine and chlorine on slag melting characteristics: experimental study and simulation by neural networks. Thermochim Acta. 2011;526:29–34.
Ndiaye LG, Caillat S, Chinnayya A, Gambier D, Baudoin B. Application of the dynamic model of Saeman to an industrial rotary kiln incinerator: numerical and experimental results. Waste Manag. 2010;30:1188–95.
Bujak J. Determination of the optimal area of waste incineration in a rotary kiln using a simulation model. Waste Manag. 2015;42:148–58.
Bujak J. Experimental study of the energy efficiency of an incinerator for medical waste. Appl Energy. 2009;86:2386–93.
Barr P. Heat transfer processes in rotary kilns. Vancouver: The University of British Columbia; 1986. p. 299.
Elattar HF, Stanev R, Specht E, Fouda A. CFD simulation of confined non-premixed jet flames in rotary kilns for gaseous fuels. Comput Fluids. 2014;102:62–73.
Meier W, Barlow RS, Chen YL, Chen JY. Raman/Rayleigh/LIF measurements in a turbulent CH4/H2/N2 jet diffusion flame: experimental techniques and turbulence–chemistry interaction. Combust Flame. 2000;123:326–43.
Kim HK, Kim Y, Lee SM, Ahn KY. Studies on combustion characteristics and flame length of turbulent oxy—fuel flames. Energy Fuel. 2007;21:1459–67.
Lombardi F, Lategano E, Cordiner S, Torretta V. Waste incineration in rotary kilns: a new simulation combustion tool to support design and technical change. Waste Manag Res. 2013;31:739–50.
H. Liu, K. Yu, J. Li, Y. Nie. Environment risk assessment of hazardous waste incineration (in Chinese). Res Environ Sci. 2005;48–52.
Zhou M, Li C, Jiang X, Lu Y, Li X. Study on flue gas complying with standard in hazardous wastes incineration disposal. China Environ Prot Ind. 2011;1:30–3 (in Chinese).
Zhou M, Wang H, Zhou B, An C, Wang L, Su Z. The development of integrated feeding system for multi-formation hazardous wastes. Energy Eng. 2009;5:25–9 (in Chinese).
Yue Q, Fan Y, Gen L, Zheng H, Wang J. Process design on the treatment of flue gas from hazardous waste incineration. Environ Sanit Eng. 2012;33:28–30 (in Chinese).
Block C, Van Caneghem J, Van Brecht A, Wauters G, Vandecasteele C. Incineration of hazardous waste: a sustainable process. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2015;6:137–45.
Yuan XY, Lou SL, Wu YJ, Li XW. The disposal method and application of hazardous waste in Wuhan. LancasteR: Destech Publications Inc.; 2016. p. 172–5.
Bujak J, Sitarz P. Reduction of NOx and CO emissions through the optimization of incineration parameters in a rotary kiln. Environ Prot Eng. 2016;42:85–100.
Li M, Wang C, Cen K, Ni M, Li X. PCDD/F emissions during startup and shutdown of a hazardous waste incinerator. Chemosphere. 2017;181:645–54.
Weber R, Sakurai T, Ueno S, Nishino J. Correlation of PCDD/PCDF and CO values in a MSW incinerator—indication of memory effects in the high temperature/cooling section. Chemosphere. 2002;49:127–34.
Da Silva CE, Hoppe AE, Ravanello MM, Mello N. Medical wastes management in the south of Brazil. Waste Manag. 2005;25:600–5.
H. Guo. Process control parameters optimization of medical waste incineration engineering by rotary kiln (in Chinese). Chin J Environ Eng. 2012;2072–2076.
Lu Q. Formation of dioxin in a rotary kiln medical waste incineration line. Chin J Environ Eng. 2013;2:743–6 (in Chinese).
Lu S, Wu H, Li X, Yan J. Correlation between rotary speed of a medical wastes incinerator rotary kiln and dioxin emission in sediments. J Combust Sci Technol. 2011;1:11–6 (in Chinese).
Chen J, Chen T, Wang Q, Wang C, Guo Y, Lu Y, Li X. PCDD/Fs emission levels of hazardous and medical waste incineration in China. Acta Sci Circum. 2014;34:973–9 (in Chinese).
Bujak J. Thermal treatment of medical waste in a rotary kiln. J Environ Manag. 2015;162:139–47.
Yang Y, Reuter MA, Voncken JH, Verwoerd J. Understanding of hazardous waste incineration through computational fluid-dynamics simulation. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2002;37:693–705.
Huber F, Blasenbauer D, Mallow O, Lederer J, Winter F, Fellner J. Thermal co-treatment of combustible hazardous waste and waste incineration fly ash in a rotary kiln. Waste Manag. 2016;58:181–90.
Li W, Huang Q, Lu S, Wu H, Li X, Yan J. Life cycle assessment of the environmental impacts of typical industrial hazardous waste incineration in eastern China. Aerosol Air Qual Res. 2015;15:242–51.
Vermeulen I, Van Caneghem J, Block C, Dewulf W, Vandecasteele C. Environmental impact of incineration of calorific industrial waste: rotary kiln vs. cement kiln. Waste Manag. 2012;32:1853–63.
Villalba Weinberg A, Varona C, Chaucherie X, Goeuriot D, Poirier J. Extending refractory lifetime in rotary kilns for hazardous waste incineration. Ceram Int. 2016;42:17626–34.
Lin C, Huang H, Hsiao W. Mass and number size distributions of emitted particulates at five important operation units in a hazardous industrial waste incineration plant. J Occup Environ Hyg. 2016;13:325–38.
Van Caneghem J, Block C, Van Brecht A, Wauters G, Vandecasteele C. Mass balance for POPs in hazardous and municipal solid waste incinerators. Chemosphere. 2010;78:701–8.
Krot OP, Rovenskyi OI. Modeling of Installations with a rotary kiln for thermal decontamination of wastes. Probl Reg Energ. 2018;1(36):44–57.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant nos. 2018YFF0215001, 2018YFC1901302, 2017YFC0703100), the Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 51621005), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 51676172), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant no. 2018FZA4010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, X., Li, Y. & Yan, J. Hazardous waste incineration in a rotary kiln: a review. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 1, 3–37 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-019-00001-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-019-00001-3