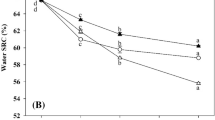
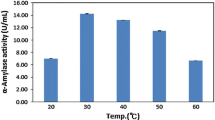
Abstract
The rice flours were hydrolyzed using α-amylase (A), α-amylase and xylanase (AX), and α-amylase, xylanase and β-amylase (AXB). The effects of different enzymatic rice flour hydrolysates (ERH) on the quality of the fermented rice cake (FRC) were determined at 25 °C for 4 days. ERH had higher porosity, water absorption index, water solubility index and lower viscosity than the control. Moisture content of FRC center decreased significantly after 4 days. Specific volumes of fresh A-, AX- and AXB-FRC were higher than the control. Color of fresh A-FRC was closer to that of the control. AXB-FRC had lower hardness and firming rate than other samples during storage. After 4 days of storage, FRC with ERH had lower endotherm enthalpy and more uniform and clearer pore structure than the control. Therefore, the ERH with single or mixed enzymes could improve the structure of FRC, and extend its shelf-life.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adedeji AA, Ngadi M. Porosity determination of deep-fat-fried coatings using pycnometer (Fried batter porosity determination by pycnometer). Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 46: 1266-1275 (2011)
Ananingsih VK, Gao J, Zhou W. Impact of green tea extract and fungal alpha-amylase on dough proofing and steaming. Food Bioprocess Technol. 6: 3400-3411 (2013)
Ariffin F, Baharom MA, Kaur B, Murad M. The physicochemical properties and sensory evaluation of bread made with a composite flour from wheat and tempoyak (fermented durian). Am. J. Appl. Sci. 12: 775-784 (2015)
Baik MY, Chinachoti P. Moisture redistribution and phase transitions during bread staling. Cereal Chem. 77: 484-488 (2000)
Barrera GN, Tadini CC, León AE, Ribotta PD. Use of alpha-amylase and amyloglucosidase combinations to minimize the bread quality problems caused by high levels of damaged starch. J. Food Sci. Technol. 53: 3675-3684 (2016)
Benavent-Gil Y, Rosell CM. Comparison of porous starches obtained from different enzyme types and levels. Carbohydr. Polym. 157: 533-540 (2017)
Błaszczak W, Sadowska J, Rosell CM, Fornal J. Structural changes in the wheat dough and bread with the addition of alpha-amylases. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 219: 348-354 (2004)
Courtin C, Delcour JA. Arabinoxylans and endoxylanases in wheat flour bread-making. J. Cereal Sci. 35: 225-243 (2002)
Dura A, Błaszczak W, Rosell CM. Functionality of porous starch obtained by amylase or amyloglucosidase treatments. Carbohydr. Polym. 101: 837-845 (2014)
Eugenia Steffolani M, Ribotta PD, Pérez GT, León AE. Combinations of glucose oxidase, α-amylase and xylanase affect dough properties and bread quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 47: 525-534 (2012)
Ghoshal G, Shivhare U, Banerjee U. Effect of xylanase on quality attributes of whole-wheat bread. J. Food Qual. 36: 172-180 (2013)
Goesaert H, Leman P, Bijttebier A, Delcour JA. Antifirming effects of starch degrading enzymes in bread crumb. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57: 2346-2355 (2009)
Gujral HS, Haros M, Rosell CM. Starch hydrolyzing enzymes for retarding the staling of rice bread. Cereal Chem. 80: 750-754 (2003)
Heyman B, De Vos WH, Van der Meeren P, Dewettinck K. Gums tuning the rheological properties of modified maize starch pastes: differences between guar and xanthan. Food Hydrocoll. 39: 85-94 (2014)
Hickman BE, Janaswamy S, Yao Y. Properties of starch subjected to partial gelatinization and β-amylolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57: 666-674 (2008)
Hidalgo A, Brandolini A. Evaluation of heat damage, sugars, amylases and colour in breads from einkorn, durum and bread wheat flours. J. Cereal Sci. 54: 90-97 (2011)
Hug-Iten S, Escher F, Conde-Petit B. Staling of bread: role of amylose and amylopectin and influence of starch-degrading enzymes. Cereal Chem. 80: 654-661 (2003)
Jang S, Shin WK, Kim Y. Texture of steamed rice cake prepared via soy residue and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose supplementation. Cereal Chem. 96: 57-65 (2019)
Jiang Z, Li X, Yang S, Li L, Tan S. Improvement of the breadmaking quality of wheat flour by the hyperthermophilic xylanase B from Thermotoga maritima. Food Res. Int. 38: 37-43 (2005)
Kaltsa O, Georgopoulos T, Yanniotis S, Mandala L. Effect of enzyme blends and dough strengthening emulsifier on extending the shelf life of sandwich bread applying response surface methodology. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 3: 149-160 (2013)
Kim HY, Park MJ, Woo SI. Development of functional Jeungpyun with dietary fiber and shelf-life studies. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 8: 58-64 (1999)
Kunamneni A, Singh S. Response surface optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of maize starch for higher glucose production. Biochem. Eng. J. 27: 179-190 (2005)
Lim SB, Tingirikari J, Kwon YW, Li L, Kim GE, Han NS. Polyphasic microbial analysis of traditional Korean Jeung-pyun sourdough fermented with makgeolli. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 27: 226-233 (2017)
Matsushita K, Santiago DM, Noda T, Tsuboi K, Kawakami S, Yamauchi H. The bread making qualities of bread dough supplemented with whole wheat flour and treated with enzymes. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 23: 403-410 (2017)
Mokrzycki W, Tatol M. Colour difference ∆E—a survey. MG. & V. 20: 383-411 (2011)
Nguyen DHD, Tran PL, Ha HS, Lee JS, Hong WS, Le QT, Oh BC, Park SH. Presence of β-amylase in ramie leaf and its anti-staling effect on rice cake. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 24: 37-40 (2015)
Oladele A, Aina J. Chemical composition and functional properties of flour produced from two varieties of tigernut (Cyperus esculentus). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 6: 2473-2476 (2007)
Ragaee S, Abdel-Aal E-SM. Pasting properties of starch and protein in selected cereals and quality of their food products. Food Chem. 95: 9-18 (2006)
Renzetti S, Arendt E. Effect of protease treatment on the baking quality of brown rice bread: from textural and rheological properties to biochemistry and microstructure. J. Cereal Sci. 50: 22-28 (2009)
Rocha TdS, Carneiro APdA, Franco CML. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on some physicochemical properties of root and tuber granular starches. Food Sci. Technol. 30: 544-551 (2010)
Shibuya N, Iwasaki T. Effect of cell wall degrading enzymes on the cooking properties of milled rice and the texture of cooked rice. Nippon Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaishi 31: 656-660 (1984)
Sokolova V, Ludwig AK, Hornung S, Rotan O, Horn PA, Epple M, Giebel B. Characterisation of exosomes derived from human cells by nanoparticle tracking analysis and scanning electron microscopy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 87: 146-150 (2011)
Song J, Park H. Effect of starch degradation enzymes on the retrogradation of a Korean rice cakes. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 32: 1262-1269 (2003)
Stojceska V, Ainsworth P, Plunkett A, İbanoğlu E, İbanoğlu Ş. Cauliflower by-products as a new source of dietary fibre, antioxidants and proteins in cereal based ready-to-eat expanded snacks. J. Food Eng. 87: 554-563 (2008)
Wang Y-Y, Norajit K, Ryu G-H. Influence of extruded hemp-rice flour addition on the physical properties of wheat bread. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 16: 62-66 (2011)
Yeboah-Awudzi M, Lutterodt HE, Kyereh E, Reyes V, Sathivel S, Manful J, King JM. Effect of bambara groundnut supplementation on the physicochemical properties of rice flour and crackers. J. Food Sci. Technol. 55: 3556-3563 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by High Value-added Food Technology Development Program funded by Korean Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (117067-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, LW., Kim, S.M. Effects of different carbohydrases on the physicochemical properties of rice flour, and the quality characteristics of fermented rice cake. Food Sci Biotechnol 29, 503–512 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00693-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00693-7