Abstract
Carbonate concretions have been recorded in many recent and ancient marine sediments around the world. The Middle Miocene marl of the Tenes area, situated in the northeast of the Lower Chelif Basin in NW-Algeria, contains such carbonate concretions but with a variety of different structures and morphologies. Three different basic types are distinguished: nodular (spheroidal, ellipsoidal, disc, and irregular), stratiform, and tubular concretions, the last locally have a central conduit. The close association between carbonate concretions and synsedimentary deformation structures (synsedimentary faults, slumps) and normal faults, pronounced in the Ounsour Anhas outcrop, indicates synsedimentary instability related to upward fluid movement. The concretions were formed by precipitation of micritic carbonate within the host marl at shallow burial depth, probably in the active microbial methanogenesis zone. Strongly varying δ13C values (− 9.82 to + 5.85‰ PDB) are interpreted as the result of the balance between 13C-enriched (residual CO2 from methanogenesis) and 13C-depleted (microbial organic matter decomposition) CO2 added to the pore solutions. δ18O values (− 2.39 to + 1.71‰ PDB) indicate that carbonate concretion growth occurred during early diagenesis conditions, from marine-derived pore-water.

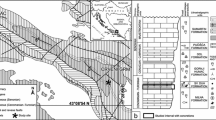
Modified from Brives (1913)













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams AE, MacKenzie WS (1998) A Colour Atlas of Carbonate Sediments Under the Microscope. Manson publishing, London, p 180
Aiello IW, Garrison RE, Moore JC, Kastner M, Stokes DS (2001) Anatomy and origin of carbonate structures in a Miocene cold-seep field. Geology 29:1111–1114
Aloisi G, Pierre C, Rouchy J, Faugères J (2002) Isotopic evidence of methane-related diagenesis in the mud volcanic sediments of the Barbados Accretionary Prism. Cont Shelf Res 22:2355–2372
Belkebir L, Bessedik M, Ameur-Chehbeur A, Anglada R (1996) Le Miocène des bassins nord-occidentaux d’Algérie: biostratigraphie et eustatisme in: Géologie de l’Afrique et de l’Atlantique Sud: Actes Colloques Angers 1994. Edition Elf Aquitaine (Pau) 16:553–561
Berner RA (1984) Sedimentary pyrite formation: an update. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:605–615
Bessedik M, Belkebir L, Mansour B (2002) Le Miocène supérieur du bassin du Bas Chélif: attribution biostratigraphique à partir des foraminifères planctoniques. Mém Ser géol Algérie 11:187–194
Bohrmann G, Greinert J, Suess E, Torres M (1998) Authigenic carbonates from the Cascadia subduction zone and their relation to gas hydrate stability. Geology 26:647–650
Bojanowski MJ (2007) Oligocene cold-seep carbonates from the Carpathians and their inferred relation to gas hydrates. Facies 53:347–360
Brives A (1897) Les terrains tertiaires du Bassin du Bas Chélif et du Dahra. Thèse Science, N°21, Lyon, Alger, 126
Brives A (1913) Carte géologique au 1/50 000 de Ténès - Cap Ténès. Ser Géol Algérie
Campbell KA (2006) Hydrocarbon seep and hydrothermal vent paleoenvironments and palaeontology: past developments and future research directions. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 232:362–407
Campbell KA, Farmer JD, Des Marais D (2002) Ancient hydrocarbon seeps from the Mesozoic convergent margin of California: carbonate geochemistry, fluids and palaeoenvironments. Geofluids 2:63–94
Campbell KA, Francis DA, Collins M, Gregory MR, Nelson CS, Greinert J, Aharon P (2008) Hydrocarbon seep–carbonates of a Miocene forearc (East Coast Basin), North Island, New Zealand. Sediment Geol 204:83–105
Campbell KA, Nelson CS, Alfaro AC, Boyd S, Greinert J, Nyman SL, Grosjean E, Logan GA, Gregory MR, Cooke S et al (2010) Geological imprint of methane seepage on the seabed and biota of the convergent Hikurangi Margin, New Zealand: box core and grab carbonate results. Mar Geol 272:285–306
Cassan G (1968) Foraminifères planctoniques du stratotype du Cartennien (Ténès) Algérie. Committee Mediterranean Neogene Stratigraphy. In: Proc. IV Session, Bologne, 1967, Giornale Geol (2), XXXV, fasc. II p. 377–386
Clari P, Cavagna S, Martire L, Hunziker J (2004) A Miocene mud volcano and its plumbing system: a chaotic complex revisited (Monferrato, MW Italy). J Sediment Res 74:662–676
Claypool GE, Kaplan IR (1974) The origin and distribution of methane in marine sediments. In: Kaplan IR (ed) Natural gases in marine sediments. Plenum, New York, pp 99–139
Claypool GE, Threlkeld CN (1983) Anoxic diagenesis and methane generation in sediments of the Blake Outer Ridge. Deep Sea Drilling Project Site 533, Leg 76. In: Sheridan RE, Gradstein FM (eds) Init Repts Deep Sea Drilling Proj 76. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, pp 391–402
Conti S, Fontana D (2002) Sediment instability related to fluid venting in Miocene authigenic carbonate deposits of the northern Apennines (Italy). Int J Earth Sci 91:1030–1040
Conti S, Fontana D, Gubertini A, Sighinolfi G, Tateo F, Fioroni C, Fregni P (2004) A multidisciplinary study of middle Miocene seep–carbonates from the northern Apennine foredeep (Italy). Sediment Geol 169:1–19
De Boever E, Swennen R, Dimitrov L (2006) Lower Eocene carbonate cemented chimneys (Varna, NE Bulgaria): formation mechanisms and the (a)biological mediation of chimney growth? Sediment Geol 185:159–173
De Boever E, Birgel D, Thiel V, Muchez P, Peckmann J, Dimitrov L, Swennen R (2009) The formation of giant tubular concretions triggered by anaerobic oxidation of methane as revealed by archaeal molecular fossils (Lower Eocene, Varna, Bulgaria). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 280:23–36
Dela Pierre F, Martire L, Natalicchio M, Clari P, Petrea C (2010) Authigenic carbonates in Upper Miocene sediments of the Tertiary Piedmont Basin (NW Italy): Vestiges of an ancient gas hydrate stability zone? Geol Soc Am Bull 122:994–1010
Delteil J (1974) Tectonique de la chaîne alpine en Algérie d’après l’étude du Tell oriental (Mont de la Mina, Beni Chougrane, Dahra). Thèse de Doctorat d’État, université de Nice, France, p 294
Dìaz-del-Rìo V, Somoza L, Martìnez-Frìas J, Mata MP, Delgado A, Hernán-dez-Molina FJ, Lunar R, Martìn-Rubì JA, Maestro A, Fernández-Puga C, León R, Llave E, Medialdea T, Vázquez JT (2003) Vast fields of hydrocarbon-derived carbonate chimneys related to the accretionary wedge/olistostrome of the Gulf of Cádiz. Mar Geol 195:177–200
Fenet B (1975) Recherches sur l’alpinisation de la bordure septentrionale du Bouclier africain à partir de l’étude d’un élément de l’orogène nord-maghrébin: les monts du Djebel Tessala et les massifs du littoral de l’oranais. Thèse de Doctorat d’État, université de Nice, France, p 301
Feng D, Chen DF, Qi L, Roberts H (2008) Petrographic and geochemical characterization of seep carbonate from Alaminos Canyon, Gulf of Mexico. Chin Sci Bull 53:1716–1724
Ferry S, Pellenard P, Collin PY, Thierry J, Marchand D, Deconinck J-F, Robin C, Carpentier C, Durlet C, Curial A (2007) Synthesis of recent stratigraphic data on Bathonian to Oxfordian deposits of the eastern Paris Basin. Mém Soc géol Fr 178:37–57
Flügel E (2010) Microfacies of carbonate rocks: analysis, interpretation and implications, vol 2. Springer, Berlin
Gaillard C, Rio M, Rolin Y, Roux M (1992) Fossil chemosynthetic communities related to vents or seeps in sedimentary basins: the pseudobioherms of southeastern France compared to other world examples. Palaios 7:451–465
Glangeaud L (1932) Etude géologique de la région littorale de la province d’Alger. Bull Ser Carte géol Algérie, p 617
Glangeaud L (1952) Histoire géologique de la province d’Alger. Publication du XIXe Congrès géologique international, Alger, Monographie Régionale, série 1, no. 25
Greinert J, Bohrmann G, Suess E (2001) Gas hydrate-associated carbonates and methane venting at Hydrate Ridge: classification, distribution, and origin of authigenic lithologies. In: Parnell CK, Dillon KP (eds) Natural gas hydrates: occurrence, distribution and detection. Geophysical Monograph 124: 99–113
Hatem E, Tribovillard N, Averbuch O, Vidier D, Sansjofre P, Birgel D, Guillot F (2014) Oyster patch reefs as indicators of fossil hydrocarbon seeps induced by synsedimentary faults. Mar Pet Geol 55:176–185
Irwin H, Curtis C, Coleman M (1977) Isotopic evidence for source of diagenetic carbonates formed during burial of organic-rich sediments. Nature 269:209–213
Lédesert B, Buret C, Chanier F, Fèrriere J, Recourt P (2003) Tubular structures of northern Wairarapa (New Zealand) as possible examples of ancient fluid expulsion in an accretionary prism: evidence from field and petrographical observations. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 216:95–107
Lepvrier C, Magné J (1975) Le Néogène « postnappes » du Tell septentrional à l’Ouest d’Alger. Bull Soc géol France 4:612–619
Liang H, Chen X, Wang C, Zhao D, Weissert H (2016) Methane-derived authigenic carbonates of mid-Cretaceous age in southern Tibet: types of carbonate concretions, carbon sources, and formation processes. J Asian Earth Sci 115:153–169
Lin Z, Sun X, Lu Y, Gong J, Teichert BMA, Peckmann J (2016) Stable isotope patterns of coexisting pyrite and gypsum indicating variable methane flow at a seep site of the Shenhu area, South China Sea. J Asian Earth Sci 123:213–223
Loyd SJ, Sample J, Tripati RE, Defliese WF, Brooks K, Hovland M, Torres M, Marlow J, Hancock LG, Martin R, Lyons T, Tripati AE (2016) Methane seep carbonates yield clumped isotope signatures out of equilibrium with formation temperatures. NatCommun 7:12274
Massaad M (1974) Framboidal pyrite in concretions. Miner Deposita 9:87–89
Merinero R, Lunar R, Martìnez-Frìas J, Somoza L, Dìaz-del-Rìo V (2008) Iron oxyhydroxide and sulphide mineralization in hydrocarbon seep-related carbonate submarine chimneys, Gulf of Cadiz (SW Iberian Peninsula). Mar Pet Geol 25:706–713
Naehr TH, Eichhubl P, Orphan VJ, Hovland M, Paull CK, Ussler IIIW, Lorenson TD, Greene HG (2007) Authigenic carbonate formation at hydrocarbon seeps in continental margin sediments: a comparative study. Deep-Sea Res II 54:1268–1291
Nehza O, Woo KS, Chun JH, Bahk JJ, Kim JK, Hyun S (2012) Methane hydrate-derived carbonate concretions in East Sea. Geo Sci J 16:25–34
Nelson CS, Smith AM (1996) Stable oxygen and carbon isotope compositional fields for skeletal and diagenetic components in New Zealand Cenozoic nontropical carbonate sediments and limestone: a synthesis and review. N Z J Geol Geophys 39:93–107
Nelson CS, Nyman SL, Campbell KA, Rowland JR (2017) Influence of faulting on the distribution and development of cold seep-related dolomitic conduit concretions at East Cape, New Zealand. N Z J Geol Geophys 60(4):478–496
Neurdin-Trescartes J (1992) Le remplissage sédimentaire du basin néogène du Chélif, modèle de référence de basins intramontagneux. Thèse de Doctorat d’État, Université de Pau et pays de l’Adour, France, p 605
Nyman SL, Nelson CS, Campbell KA (2010) Miocene tubular concretions in East Coast Basin, New Zealand: analogue for the subsurface plumbing of cold seeps. Mar Geol 272:319–336
Oppo D, Capozzi R, Picotti V, Ponza A (2015) A genetic model of hydrocarbon-derived carbonate chimneys in shelfal fine-grained sediments: the Enza River field, Northern Apennines (Italy). Mar Pet Geol 3:555–565
Oppo D, Viola I, Capozzi R (2017) Fluid sources and stable isotope signatures in authigenic carbonates from the Northern Apennines, Italy. Mar Pet Geol 86:606–619
Orpin AR (1997) Dolomite chimneys as possible evidence of coastal fluid expulsion, uppermost Otago continental slope, southern New Zealand. Mar Geol 138:51–67
Peckmann J, Thiel V (2004) Carbon cycling at ancient methane-seeps. Chem Geol 205:443–467
Peckmann J, Thiel V, Michaelis W, Clari P, Gaillard C, Martire L, Reitner J (1999) Cold seep deposits of Beauvoisin (Oxfordian; southeastern France) and Marmorito (Miocene; northern Italy): microbially induced authigenic carbonates. Int J Earth Sci 88:60–75
Peckmann J, Reimer A, Luth C, Hansen BT, Heinicke C, Hoefs J, Reitner J (2001) Methane-derived carbonate and authigenic pyrite from the northwestern Black Sea. Mar Geol 177:129–150
Perrodon A (1957) Etude géologique des basins néogènes sublittoraux de l’Algérie occidentale. Bull Ser Carte géol Algérie 12:328p
Pierre C, Rouchy JM (2004) Isotopic compositions of diagenetic dolomites in the Tortonian marls of the western Mediterranean margins: evidence of past gas hydrate formation and dissociation. Chem Geol 205:469–484
Pierre C, Rouchy JM, Blanc-Valleron MM (2002) Gas hydrate dissociation in the Lorca Basin (SE Spain) during the Mediterranean Messinian salinity crisis. Sediment Geol 147:247–252
Pierre C, Blanc-Valleron MM, Caquineau S, März C, Ravelo AC, Takahashi K, Alvarez-Zarikian C (2014) Mineralogical, geochemical and isotopic characterization of authigenic carbonates from the methane-bearing sediments of the Bering Sea continental margin (IODP expedition 323, sites U1343-1345). Deep Sea Res II Topical Studies in Oceanography 125–126:133–144
Pierre C, Rouchy JM, Blanc-Valleron MM, Etoubleau J, Fouquet Y (2015) Methanogenesis and clay minerals diagenesis during the formation of dolomite nodules from the Tortonian marls of southern Spain. Mar Pet Geol 66:606–615
Raiswell R, Fisher QJ (2000) Mudrock-hosted carbonate concretions: a review of growth mechanisms and their influence on chemical and isotopic composition. J Geol Soc London 157:239–251
Roberts AP, Jiang WT, Florindo F, HorngChS Laj C (2005) Assessing the timing of greigite formation and the reliability of the Upper Olduvai polarity transition record from the Crostolo River, Italy. Geophys Res Letters 32:1–4
Roberts HH, Feng D, Joye SB (2010) Cold-seep carbonates of the middle and lower continental slope, northern Gulf of Mexico. Deep-Sea Res II 57:2040–2054
SN Repal (1952) Le basin néogène du Chélif. Publication du XIXe Congrès géologique international d’Alger, Alger 16 (1èresérie):1–56
Stakes DS, Orange D, Paduan JB, Salamy KA, Maher N (1999) Cold-seeps and authigenic carbonate formation in Monterey Bay, California. Mar Geol 159:93–109
Viola I, Oppo D, Franchi F, Capozzi R, Dinelli E, Liverani B, Taviani M (2015) Mineralogy, geochemistry and petrography of methane-derived authigenic carbonates from Enza River, Northern Apennines (Italy). Mar Pet Geol 66:566–581
Viola I, Capozzi R, Bernasconi SM, Rickli J (2017) Carbon, oxygen and strontium isotopic constraints on fluid sources, temperatures and biogeochemical processes during the formation of seep carbonates—Secchia River site, Northern Apennines. Sediment Geol 357:1–15
Wallmann K, Aloisi G, Haeckel M, Obzhirov A, Pavlova G, Tishchenko P (2006) Kinetics of organic matter degradation, microbial methane generation, and gas hydrate formation in anoxic marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:3905–3927
Wallmann K, Aloisi G, Haeckel M, Tishchenko P, Pavlova G, Greinert J, Kutterolf S, Eisenhauer A (2008) Silicate weathering in anoxic marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:3067–3090
Wehrmann LM, Risgaard-Petersen N, Schrum HN, Walsh EA, Huh Y, Ikehara M, Pierre C, D’Hondt S, Ferdelman TG, Ravelo AC, Takahashi K, Alvarez-Zarikian C, The Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Expedition 323 Scientific Party (2011) Coupled organic and inorganic carbon cycling in the deep subseafloor sediment of the northeast Bering Sea Slope (IODP Exp. 323). Chem Geol 284:251–261
Westphal H, Lavi J, Munnecke A (2015) Diagenesis makes the impossible come true: intersecting beds in calcareous turbidites. Facies 61:3
Whiticar M (1999) Carbon and hydrogen isotope systematics of bacterial formation and oxidation of methane. Chem Geol 161:291–314
Whiticar MJ, Faber E, Schoell M (1986) Biogenic methane formation in marine and freshwater environments: CO2 reduction versus acetate fermentation-Isotope evidence. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 50:693–709
Woo KS, Khim BK (2006) Stable oxygen and carbon isotopes of carbonate concretions of the Miocene Yeonil Group in the Pohang Basin, Korea: types of concretions and formation conditions. Sediment Geol 183:15–30
Acknowledgements
This study is a part of the PhD thesis of A. Nemra, funded by the Algerian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research. The authors wish to thank Radouane Sadji (Oran, Algeria) for his help during the field work, John Noel Hooker (Penn State University, United States) for helpful discussions, and Birgit Leipner-Mata for preparation of thin-sections. We are also grateful to Mattia Pizzati (Parma, Italy) and an anonymous reviewer for their very constructive comments that helped us to improve the manuscript. A special thank goes to the editor-in-Chief Maurice Tucker (Bristol) for his great help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nemra, A., Ouali Mehadji, A., Munnecke, A. et al. Carbonate concretions in Miocene mudrocks in NW Algeria: types, geochemistry, and origins. Facies 65, 17 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-019-0559-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-019-0559-2