Abstract
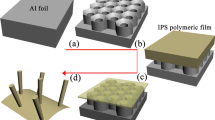
As narrow as 50 nm metal nanowire array patterns were successfully fabricated by nanoimprint lithography (NIL) using thermally curable monomer based resin. Compared to conventional hot embossing lithography, which has used thermoplastic polymers such as PMMA as an imprint resin and thus process temperature and pressure are over 180°C and 50 bar, respectively, thermally curable monomer based resin enabled imprint process at relatively lower temperature (120°C) and pressure (20 bar). Due to the highly fluidic nature of monomer based liquid phase resin, residual layer was not observed after imprinting. Imprinted resist pattern was then treated with oxygen plasma for 5 seconds and 5 nm of Ti layer and 15 nm of Au layer was deposited by e-beam evaporation. The imprinted resist pattern was lifted-off by dipping into an organic solvent, such as acetone. As the result, as narrow as 50 nm Au nanowire array pattern with area of 30 mm × 40 mm was fabricated on a Si substrate. 30 mm × 40 mm of nanowire pattern area was not limited by nanoimprint process, but the laser interference lithography process, which was used to fabricated the master template for imprinting.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
A. Murray, M. Scheinfen, M. Isaacson, and I. Adesida, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 3, 367 (1985).
A. M. Hawryluk and L. G. Seppala, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 6, 2162 (1988).
W. Hinsberg, F. A. Houle, J. Hoffnagle, M. Sanchez, G. Wallraff, and M. Morrison, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 16, 3689 (1998).
S. Y. Chou, P. R Krauss, and P. J. Renstrom, Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 3114 (1995).
M. D. Austin, W. Zhang, H. Ge, D. Wasserman, S. A. Lyon and S. Y. Chou, Nanotechnol. 16, 1058 (2005).
H. Lee, S. Hong, K. Yang, and K. Choi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 143112 (2006).
P. Carlberg, M. Graczyk, E.-L. Sarwe, I. Maximov, M. Beck, and L. Montelius, Microelectron. Eng. 67–68, 203 (2003).
B. Heidari, I. Maximov, and L. Montelius, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 18, 3557 (2000).
S. Y. Chou and P. R. Krauss, Microelectron. Eng. 35, 237 (1997).
K. D. Lee, S. W. Ahn, S. H. Kim, S. H. Lee, J. D. Park, P. W. Yoon, D. H. Kim, and S. S. Lee, Current Appl. Phys. 6, 149 (2006).
G. Y. Jung, S. Ganapathiappan, D. D. A. Ohlberg, D. L. Olynick, Y. Chen, W. M. Tong, R. S. Williams, Nano Lett. 4, 1225 (2004).
S.-H. Hong, B.-J. Bae, K.-S. Han, E.-J. Hong, H. Lee, and K.-W. Choi, Electron. Mater. Lett. 5, 39 (2009).
K.-Y. Yang, J.-W. Kim, K.-J. Byeon, and H. Lee, Microelectron. Eng. 84, 1552 (2007).
H. Lee and G.-Y. Jung, Microelectron. Eng. 77, 168 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, SH., Bae, BJ., Yang, KY. et al. Fabrication of sub-50 nm Au nanowires using thermally curing nanoimprint lithography. Electron. Mater. Lett. 5, 139–143 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3365/eml.2009.12.139
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3365/eml.2009.12.139