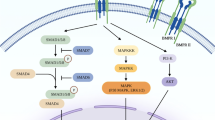
Abstract
Epithelial tissues provide tissue barriers and specialize in organs and glands. When epithelial homeostasis is physiologically or pathologically stimulated, epithelial cells produce mesenchymal cells through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, forming new tissues, promoting the cure of diseases or leading to illness. A variety of cytokines are involved in the regulation of epithelial cell differentiation. Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), especially the bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) has a variety of biological functions and plays a prominent role in the regulation of epithelial cell differentiation. BMP4 is an important regulatory factor of a series of life activities in vertebrates, which is also related to cell proliferation, differentiation and mobility, it also has relation with tumor development. This paper mainly reviews the mechanism of BMP4’s regulation on epithelial tissues, as well as its effect on the growth, differentiation, benign lesions and malignant lesions of epithelial tissues, and expounds the function of BMP4 in epithelial tissues, to provide theoretical support for the research on reducing epithelial diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMPs:
-
bone morphogenetic proteins
- BMP4:
-
bone morphogenetic protein 4
- BMPRI, BMPRII:
-
BMP type I and II receptors
- Smad:
-
drosophila mothers against decapentaplegic protein
- r-smads:
-
receptor-regulated Smads
- coSmads:
-
common partner Smads
- P38 MAPK:
-
P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
- ERK1/2:
-
extracellular regulated protein kinase 1/2
- JNK:
-
c-Jun amino terminal kinase
- PI3-K:
-
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase
- PKB:
-
serine/threonine kinase B
- AT1s:
-
type I alveolar cells
- AT2s:
-
type II alveolar cells
- Sulf1:
-
sulfatase sulf-1
- OC1:
-
cochlear tissues and a sensory epithelial cell line
- NR2B gene:
-
aspartic acid receptor subunit gene
- Foxn1:
-
forkhead transcription factor 1
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor
- IFN-γ:
-
interferon-γ
- IL-8:
-
active interleukin 8
- BE:
-
Barrett’s esophagus
- KLF4:
-
kruppel-like factor
- COPD:
-
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- ID3:
-
inhibitor of differentiation 3
- M1:
-
classical activation of macrophages
- M2:
-
selective activation of macrophages
- ID2:
-
differentiation inhibitor 2
References
Auersperg N, Wong AS, Choi KC, Kang SK, Leung PC (2001) Ovarian surface epithelium: biology, endocrinology, and pathology. Endocr. Rev. 22:255–288. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv.22.2.0422
Bleuming SA et al (2006) Altered bone morphogenetic protein signalling in the helicobacter pylori-infected stomach. J. Pathol. 209:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.1976
Bohnenpoll T, Feraric S, Nattkemper M, Weiss AC, Rudat C, Meuser M, Trowe MO, Kispert A (2017a) Diversification of Cell Lineages in Ureter Development. J Am Soc Nephrol 28:1792–1801. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2016080849
Bohnenpoll T et al (2017b) A SHH-FOXF1-BMP4 signaling axis regulating growth and differentiation of epithelial and mesenchymal tissues in ureter development. PLoS Genet. 13:e1006951. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006951
Buresh-Stiemke RA, Malinowski RL, Keil KP, Vezina CM, Oosterhof A, Van Kuppevelt TH, Marker PC (2012) Distinct expression patterns of Sulf1 and Hs6st1 spatially regulate heparan sulfate sulfation during prostate development. Developmental dynamics: an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists 241:2005–2013. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.23886
Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR (2004) Bone morphogenetic proteins growth factors (Chur, Switzerland) 22:233-241 https://doi.org/10.1080/08977190412331279890
Chen J, Zheng Y, Xiong H, Ou Y (2014) NMDA receptors are involved in the regulation of BMP4-mediated survival in rat cochlear epithelial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 566:275–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2014.02.067
Cho KW et al (2006) Molecular interactions between Tbx3 and Bmp4 and a model for dorsoventral positioning of mammary gland development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103:16788–16793. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0604645103
Chung MI BM, Barkauskas CE, Kobayashi Y, Hogan BLM. (2018) Niche-mediated BMP/SMAD signaling regulates lung alveolar stem cell proliferation and differentiation Biologists Ltd 145
Coffman LG, Choi YJ, McLean K, Allen BL, di Magliano MP, Buckanovich RJ (2016) Human carcinoma-associated mesenchymal stem cells promote ovarian cancer chemotherapy resistance via a BMP4/HH signaling loop. Oncotarget 7:6916–6932. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6870
Cunha GR (1985) Mesenchymal-epithelial interactions during androgen-induced development of the prostate. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 171:15–24
Fiaturi NRJ, Nielsen HC, Castellot JJ Jr (2018) CCN5 in alveolar epithelial proliferation and differentiation during neonatal lung oxygen injury. J Cell Commun Signal 12:217–229
Haraguchi R, Matsumaru D, Nakagata N, Miyagawa S, Suzuki K, Kitazawa S, Yamada G (2012) The hedgehog signal induced modulation of bone morphogenetic protein signaling: an essential signaling relay for urinary tract morphogenesis. PLoS One 7:e42245. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042245
He F et al (2010) Modulation of BMP signaling by noggin is required for the maintenance of palatal epithelial integrity during palatogenesis. Dev. Biol. 347:109–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.08.014
Hilliard SA, Yu L, Gu S, Zhang Z, Chen YP (2005) Regional regulation of palatal growth and patterning along the anterior-posterior axis in mice. J. Anat. 207:655–667. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00474.x
Hoffman MP, Kidder BL, Steinberg ZL, Lakhani S, Ho S, Kleinman HK, Larsen M (2002) Gene expression profiles of mouse submandibular gland development: FGFR1 regulates branching morphogenesis in vitro through BMP- and FGF-dependent mechanisms. Development (Cambridge, England) 129:5767–5778
Honda H (2017) The world of epithelial sheets. Develop. Growth Differ. 59:306–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/dgd.12350
Huber GA, Priest SM, Geisbuhler TP (2018) Cardioprotective Effect of Hydroxysafflor Yellow A via the Cardiac Permeability Transition Pore. Planta Med. 84:507–518. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-122501
Jia S, Zhou J, Gao Y, Baek JA, Martin JF, Lan Y, Jiang R (2013) Roles of Bmp4 during tooth morphogenesis and sequential tooth formation. Development (Cambridge, England) 140:423–432. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.081927
Kahata K, Dadras MS, Moustakas A (2018) TGF-beta Family Signaling in Epithelial Differentiation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol.:10. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a022194
Keil KP, Altmann HM, Abler LL, Hernandez LL, Vezina CM (2015) Histone acetylation regulates prostate ductal morphogenesis through a bone morphogenetic protein-dependent mechanism. Developmental dynamics : an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists 244:1404–1414. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.24321
Khedoe PP et al (2013) The effect of PPE-induced emphysema and chronic LPS-induced pulmonary inflammation on atherosclerosis development in APOE*3-LEIDEN mice. PLoS One 8:e80196. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080196
Kim JS, Crooks H, Dracheva T, Nishanian TG, Singh B, Jen J, Waldman T (2002) Oncogenic beta-catenin is required for bone morphogenetic protein 4 expression in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:2744–2748
Kleinschmit A, Koyama T, Dejima K, Hayashi Y, Kamimura K, Nakato H (2010) Drosophila heparan sulfate 6-O endosulfatase regulates wingless morphogen gradient formation. Dev. Biol. 345:204–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.07.006
Li Q, Zhang S, Sui Y, Fu X, Li Y, Wei S (2019) Sequential stimulation with different concentrations of BMP4 promotes the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into dental epithelium with potential for tooth formation. Stem Cell Res Ther 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1378-7
Li X et al (2013) BMP4 increases canonical transient receptor potential protein expression by activating p38 MAPK and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 49:212–220. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2012-0051OC
Li Z et al (2014) Bone morphogenetic protein 4 inhibits liposaccharide-induced inflammation in the airway. Eur. J. Immunol. 44:3283–3294. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201344287
Liu Y et al (2017) The BMP4-Smad signaling pathway regulates hyperandrogenism development in a female mouse model. J. Biol. Chem. 292:11740–11750. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.781369
Ma J et al (2017) BMP4 enhances hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation by promoting cell cycle progression via ID2/CDKN1B signaling. Mol. Carcinog. 56:2279–2289. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22681
Marker PC, Donjacour AA, Dahiya R, Cunha GR (2003) Hormonal, cellular, and molecular control of prostatic development. Dev. Biol. 253:165–174
Martinez VG et al (2017) BMP4 induces M2 macrophage polarization and favors tumor progression in bladder. Cancer clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 23:7388–7399. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-17-1004
Miao N et al (2019) Loss of Fam20c causes defects in the acinar and duct structure of salivary glands in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 43:2103–2117. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2019.4126
Mills CG, Lawrence ML, Munro DAD, Elhendawi M, Mullins JJ, Davies JA (2017) Asymmetric BMP4 signalling improves the realism of kidney organoids. Sci. Rep. 7:14824. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14809-8
Miyazawa K, Miyazono K (2017) Regulation of TGF-beta Family Signaling by Inhibitory Smads. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol.:9. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a022095
Mysorekar IU, Isaacson-Schmid M, Walker JN, Mills JC, Hultgren SJ (2009) Bone morphogenetic protein 4 signaling regulates epithelial renewal in the urinary tract in response to uropathogenic infection. Cell Host Microbe 5:463–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2009.04.005
Neves H, Dupin E, Parreira L, Le Douarin NM (2012) Modulation of Bmp4 signalling in the epithelial-mesenchymal interactions that take place in early thymus and parathyroid development in avian embryos. Dev. Biol. 361:208–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.10.022
Obonyo M, Guiney DG, Harwood J, Fierer J, Cole SP (2002) Role of gamma interferon in Helicobacter pylori induction of inflammatory mediators during murine infection. Infect. Immun. 70:3295–3299
Owens P et al (2012) Disruption of bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2 (BMPR2) in mammary tumors promotes metastases through cell autonomous and paracrine mediators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 109:2814–2819. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1101139108
Pokrywczynska M, Rasmus M, Jundzill A, Balcerczyk D, Adamowicz J, Warda K, Buchholz L, Drewa T (2019) Mesenchymal stromal cells modulate the molecular pattern of healing process in tissue-engineered urinary bladder: the microarray data. Stem Cell Res Ther 10:–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1266-1
Rahman MS, Akhtar N, Jamil HM, Banik RS, Asaduzzaman SM (2015) TGF-β/BMP signaling and other molecular events: regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone formation. Bone Research 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/boneres.2015.5
Rock JR, Randell SH, Hogan BL (2010) Airway basal stem cells: a perspective on their roles in epithelial homeostasis and remodeling. Dis. Model. Mech. 3:545–556. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.006031
Seppo Valnio IK, Adrian Jowett, Irma Thesleff (1993) Identification of BMP-4 as a Signal Mediating Secondary Induction between Epithelial and Mesenchymal Tissues during Early Tooth Development Cell 75
Shaykhiev R, Zuo WL, Chao I, Fukui T, Witover B, Brekman A, Crystal RG (2013) EGF shifts human airway basal cell fate toward a smoking-associated airway epithelial phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110:12102–12107. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1303058110
Shepherd TG, Nachtigal MW (2003) Identification of a putative autocrine bone morphogenetic protein-signaling pathway in human ovarian surface epithelium and ovarian cancer cells. Endocrinology 144:3306–3314. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2003-0185
Shepherd TG, Theriault BL, Nachtigal MW (2008) Autocrine BMP4 signalling regulates ID3 proto-oncogene expression in human ovarian cancer cells. Gene 414:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2008.02.015
Shin K et al (2014) Hedgehog signaling restrains bladder cancer progression by eliciting stromal production of urothelial differentiation factors. Cancer Cell 26:521–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2014.09.001
Shirai YT, Ehata S, Yashiro M, Yanagihara K, Hirakawa K, Miyazono K (2011) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -4 play tumor suppressive roles in human diffuse-type gastric carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 179:2920–2930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.08.022
Soza-Ried C, Bleul CC, Schorpp M, Boehm T (2008) maintenance of thymic epithelial phenotype requires extrinsic signals in mouse and zebrafish journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 181:5272–5277
Su D et al. (2009) BMP4-Smad signaling pathway mediates Adriamycin-induced premature senescence in lung Cancer cells*S the journal of biological chemistry 284:12153-12164 https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M807930200
Swann JB, Krauth B, Happe C, Boehm T (2017) Cooperative interaction of BMP signalling and Foxn1 gene dosage determines the size of the functionally active thymic epithelial compartment. Sci. Rep. 7:8492. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09213-1
Swarup N, Nayak MT, Chowdhary Z, Mehendiratta M, Khatana S, Choi SJ, Sagolsem C (2018) evaluation and Immunolocalization of BMP4 and FGF8 in Odontogenic cyst and tumors analytical cellular pathology (Amsterdam) 2018 https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1204549
Taddei A et al (2014) Cyclooxygenase-2 and inflammation mediators have a crucial role in reflux-related esophageal histological changes and Barrett's esophagus. Dig. Dis. Sci. 59:949–957. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2975-4
Takabayashi H et al (2014) Anti-inflammatory activity of bone morphogenetic protein signaling pathways in stomachs of mice. Gastroenterology 147:396–406.e397. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.04.015
Theriault BL, Shepherd TG, Mujoomdar ML, Nachtigal MW (2007) BMP4 induces EMT and rho GTPase activation in human ovarian cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 28:1153–1162. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgm015
Wang C, Ross WT, Mysorekar IU (2017) Urothelial generation and regeneration in development, injury, and cancer. Developmental dynamics: an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists 246:336–343. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.24487
Wertheimer T et al (2018) Production of BMP4 by endothelial cells is crucial for endogenous thymic regeneration. Science immunology 3. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.aal2736
Yan W et al (2016) BMP4 promotes a phenotype change of an esophageal squamous epithelium via up-regulation of KLF4. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 101:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2016.09.007
Zaki MA et al (2011) Prognostic implication of types of tumor-associated macrophages in Hodgkin lymphoma. Virchows Archiv: an international journal of pathology 459:361–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-011-1140-8
Zhang C, Niu C, Yang K, Shaker A (2018) Human esophageal myofibroblast secretion of bone morphogenetic proteins and GREMLIN1 and paracrine regulation of squamous epithelial growth. Sci. Rep. 8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30799-7
Zhang L et al (2012) BMP4 administration induces differentiation of CD133+ hepatic cancer stem cells, blocking their contributions to hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 72:4276–4285. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-12-1013
Zhang Y et al. (2015) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling modulates corneal epithelium stratification via inhibition of Bmp4 during mouse development development (Cambridge, England) 142:3383-3393 https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.125393
Zheng Y, Rayner M, Feng L, Hu X, Zheng X, Bearth E, Lin J (2008) EGF Mediates Survival of Rat Cochlear Sensory Cells via an NF-kappaB Dependent Mechanism In Vitro. The open neuroscience journal 2:9–15. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874082000802010009
Zhu XJ, Liu Y, Dai ZM, Zhang X, Yang X, Li Y, Qiu M, Fu J, Hsu W, Chen Y, Zhang Z (2014) BMP-FGF signaling axis mediates Wnt-induced epidermal stratification in developing mammalian skin. PLoS Genet. 10:e1004687. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004687
Zieske JD (2004) Corneal development associated with eyelid opening. The international journal of developmental biology 48:903–911. https://doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.041860jz
Zuo WL et al (2019) Exaggerated BMP4 Signalling alters human airway basal progenitor cell differentiation to cigarette smoking-related phenotypes. Eur. Respir. J. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.02553-2017
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Outstanding Young Teacher Training Program of Jilin University[419080520314]; the Science and Technology Department [20180101146JC]; the Science and Technology Project of Jilin Traditional Chinese Medicine[2019134]; and the International Cooperation Project of Jilin Provincial Science and Technology Department in the charge of Zhang Yan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed. We further confirm that the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all of us.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, S., Wang, S., He, Y. et al. Regulation of bone morphogenetic protein 4 on epithelial tissue. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 14, 283–292 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-019-00537-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-019-00537-3