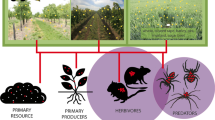
Abstract
Conventional agriculture is based on a high level of chemical inputs such as pesticides and fertilisers, leading to serious environmental impacts, health risks and loss of biodiversity in agrosystems. The reduction of pesticide use is a priority for intensively sprayed agricultural systems such as orchards. The preservation and promotion of biodiversity within orchards and their boundaries is therefore an issue to explore. Indeed, orchard systems contain high plant diversity and perennial multi-strata designs that provide wealthy resources and habitats to living communities such as beneficial organisms. Orchards thus offer favourable areas to maintain food-webs within the agrosystem, provided that favourable situations are not altered by cultural practices such as applying an excess of pesticides. Here, we analysed literature on the effects of the manipulation of plant diversity and habitats on the control of pests by arthropod and bird communities in apple, pear and peach orchards. Many investigations focus on the role of plant management to enhance biodiversity in orchards but only 22 research reports presenting 30 case studies were dedicated to the study of the ecosystem service provided by plant diversity for orchard pest control. The underlying mechanisms were seldom demonstrated, and the tested grass covers and tree assemblages aimed at favouring either the beneficial complex or only some beneficial species to control one or a few pests. The effect of plant management on pest control was mostly positive (16 cases) or null (9), but also negative in some cases (5). This finding reveals the difficulties of identifying selected plants or plant assemblages for the control of key pests. We conclude that further research is needed to identify the processes involved on different scales for biological control. Orchard systems should be re-designed to optimise ecosystem services provided by biodiversity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agerberg J. (2007) Impact des pratiques agricoles et du paysage sur l’avifaune des vergers de pommiers du Sud-Est de la France, Mémoire INRA Avignon — AgroParisTec, 57 p. + annexes.
Alston D. (1994) Effect of apple orchard floor vegetation on density and dispersal of phytophagous and predaceous mites in Utah, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 50, 73–84.
Altieri M.A. (1995) Agroecology: the science of sustainable agriculture, Westview Process, Boulder, USA
Altieri M.A., Schmidt L.L. (1985) Cover crop manipulation in Northern California orchards and vineyards: effects on arthropods communities, Biol. Agric. Hortic. 3, 1–24.
Altieri M.A., Schmidt L.L. (1986) The dynamics of colonizing arthropod communities at the interface of abandoned, organic and commercial apple orchards and adjacent woodland habitats, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 16, 29–43.
Andow D.A. (1991) Polycultures and pest populations, Annu. Rev. Entomol. 36, 561–586.
Andreev R., Olszak R., Kutinkova H. (2006) Harmful and beneficial entomofauna in apple orchards grown under different management systems, Bull. IOBC/wprs 29, 13–19.
Aubertot J.N., Barbier J.M., Carpentier A., Gril J.J., Guichard L., Lucas P., Savary S., Savini I., Voltz M. (2005) Pesticides, agriculture et environnement, Réduire l’utilisation des pesticides et limiter leurs impacts environnementaux, Expertise scientifique collective, synthèse du rapport, INRA & Cemagref, France, 64 p.
Audemard H. (1992) Population dynamics in codling moth, in: Van der Geest L.P.S., Evenhuis H.H. (Eds.), Tortricid pests: their biology, natural enemies and control, Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp. 329–338.
Balázs K., Jenser G., Bujáki G. (1996) Eight years’ experiences of IPM in Hungarian apple orchards, Bull. IOBC/wprs 19, 95–101.
Baldi I., Mohammed-Brahim B., Brochard P., Dartigues J.-F., Salamon R. (1998) Long-term effects of pesticides on health: review of current epidemiologic knowledge, Rev. Epidemiol. Sante 46, 134–142.
Barbosa P. (1999) Conservation Biological Control, Academic Press, San Diego, USA, 396 p.
Barthelet B. (1982) Étude faunistique d’une haie brise-vent composite, Mémoire de l’École Nationale des Ingénieurs des Travaux Horticoles, Angers, 101 p.
Baudry O., Bourgery C., Guyot G., Rieux R. (2000) Les haies composites réservoirs d’auxiliaires, Ctifl, Paris, 116 p.
Bengtsson J., Ahnström J., Weibull A.C. (2005) The effects of organic agriculture on biodiversity and abundance: a meta-analysis, J. Appl. Ecol. 42, 261–269.
Benton T.G., Vickery J.A., Wilson J.D. (2003) Farmland biodiversity: is habitat heterogeneity the key? Trends Ecol. Evol. 18, 182–188.
Berrie A., Cross J. (2006) Development of an integrated pest and disease management system for apples to produce fruit free from pesticide residues — aspects of disease control, Bull. IOBC/wprs 29, 129–138.
Bishop C.A., Collins B., Mineau P., Burgess N.M., Read W.F., Risley C. (2000) Reproduction of cavity-nesting birds in pesticide-sprayed apple orchards in southern Ontario, Canada, 1988–1994, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 19, 588–599.
Bogya S., Markó V. (1999) Effect of pest management systems on ground-dwelling spider assemblages in an apple orchard in Hungary, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 73, 7–18.
Bogya S., Markó V., Szinetár Cs. (1999) Comparison of pome fruit orchard inhabiting spider assemblages at different geographical scales, Agr. Forest Entomol. 1, 261–269.
Boivin T., Chadoeuf J., Bouvier J.-C., Beslay D., Sauphanor B. (2005) Modelling the interactions between phenology and insecticide resistance genes in the codling moth Cydia pomonella, Pest Manag. Sci. 61, 53–67.
Boller E.F., Häni F., Poehling H.M. (2004) Ecological infrastructures: ideabook on functional biodiversity at the farm level, Landwirtschaftliche Beratungszentrale Lindau, Lindau, Suisse.
Bouvier J.C. (2004) Exposition et réponse de l’avifaune aux pratiques phytosanitaires en vergers: Possibilités de traduction en termes de bioindication et de transfert vers la profession agricole, Mémoire d’Ingénieur Diplômé par l’État, spécialité Agriculture, ENSA Montpellier, 62 p. + annexes.
Bouvier J.C., Toubon J.F., Boivin T., Sauphanor B. (2005) Effects of apple orchard management strategies on the great tit (Parus major) in Southeastern France, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 24, 2846–2852.
Brown M.W. (1993) Resilience of the natural arthropod community on apple to external disturbance, Ecol. Entomol. 18, 169–183.
Brown M.W. (1998) Diversification of orchard ecosystems to augment populations of biological control fauna, in: Brunnhofer V., Soldan T. (Eds.), Proc. 6th European Congress of Entomology (Book of Abstracts), Ceské Budejovice, August 23–29 1998, Institute of Entomology, Academy of the Czech republic and University of South Bohemia, pp. 623–624.
Brown M.W. (2001a) Functional biodiversity and agro-ecosystems management: 2. role in integrated fruit production, Bull. IOBC/wprs 24, 5–11.
Brown M.W. (2001b) Flowering ground cover plants for pest management in peach and apple orchards, Bull. IOBC/wprs 24, 379–382.
Brown M.W., Adler C.R.L. (1989) Community structure of phytophagous arthropods on apple, Environ. Entomol. 18, 600–607.
Brown M.W., Welker W.V. (1992) Development of the phytophagous arthropod community on apple as affected by orchard management, Environ. Entomol. 31, 485–492.
Brown M.W., Glenn D.M. (1999) Ground cover plants and selective insecticides as pest management tools in apple orchards, J. Econ. Entomol. 92, 899–905.
Brown M.W., Schmitt J.J. (2001) Seasonal and diurnal dynamics of beneficial insect populations in apple orchards under different management intensity, Biol. Control 30, 415–424.
Brown M.W., Schmitt J.J., Abraham B.J. (2003) Seasonal and diurnal dynamics of spiders (Araneae) in West Virginia orchards and the effect of orchard management on spider communities, Environ. Entomol. 32, 830–839.
Brown M.W., Mathews C.R., Krawczyk G. (2008) Analyzing the results of biodiversity experiments: enhancing parasitism of tufted apple budmoth, in: Proc. 7th IOBC International Conference on Integrated Fruit Production (Book of Abstracts), Avignon, October 28–30 2008, p. 6.
Bugg R.L., Waddington C. (1994) Using cover crops to manage arthropod pests of orchards: a review, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 50, 11–28.
Burgio G., Ferrari R., Boriani L., Pozzati M., van Lenteren J. (2006) The role of ecological infrastructures on Coccinellidae (Coleopera) and other predators in weedy field margins within northern Italy agroecosystems, Bull. Insect. 59, 59–67.
Campo L. (1992) La faune auxiliaire des haies composites: inventaire sur quatre sites du sud de la France, Mémoire de l’Institut Polytechnique, Toulouse, 64 p.
Carraretto L. (1992) Les haies composites: intérêt dans la protection intégrée, Mémoire d’ingénieur de l’École Supérieure d’Agriculture de Purpan, 89 p.
Chamberlain D.E., Fuller R.J., Bunce R.G.H., Duckworth J.C., Shrubb M. (2000) Patterns of change in the abundance of farmland birds in relation to the timing of recent intensification of agriculture in England and Wales, J. Appl. Ecol. 37, 771–788.
Chaubet B. (1993) Diversité écologique, aménagement des agroécosystèmes et favorisation des ennemis des cultures: cas des aphidiphages, Courr. Cell. Environ. INRA 18, 45–63.
Clergue B., Amiaud B., Pervanchon F., Lasserre-Joulin F., Plantureux S. (2005) Biodiversity: function and assessment in agricultural areas. A review, Agron. Sustain. Dev. 25, 1–15.
Codron J.M., Jacquet F., Habib R., Sauphanor B. (2003) Bilan et perspectives environnementales de la filière arboriculture fruitière, in: Quae (Ed.), Les Dossiers de l’Environnement de l’INRA 23: Agriculture, territoire, environnement dans les politiques européennes, pp. 31–67.
Coli W.M., Ciurlino R.A., Hosmer T. (1994) Effect of understory and border vegetation composition on phytophagous and predatory mites in Massachussetts commercial apple orchard, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 50, 49–60.
Commission Européenne (2008) http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/protection/pesticides/legislation_fr.htm consulté le 10/03/2009.
Cortesero A.M., Stapel J.O., Lewis W.J. (2000) Understanding and manipulating plant attributes to enhance biological control, Biol. Control 17, 35–49.
Croft B.A. (1982) Management of apple orchard weeds to improve biological control of spider mites, Abstracts Meet, Weed Sci. Soc. Am. 257, 134.
Debras J.-F. (2001) Optimisation du choix des essences d’une haie composite pour lutter contre le psylle du poirier Cacopsylla pyri L., Mémoire d’Ingénieur Diplômé par l’État, ENSA Montpellier, 80 p. + annexes.
Debras J.-F. (2007) Rôles fonctionnels des haies dans la régulation des ravageurs: Le cas du psylle Cacopsylla pyri L. dans les vergers du sud-est de la France, Thèse de doctorat de l’Université d’Avignon, Sciences de la vie, 239 p.
Debras J.-F., Cousin M., Rieux R. (2002) Mesure de la ressemblance de la faune utile du poirier avec celle de 43 espèces végétales pour optimiser la composition de haies réservoirs d’auxiliaires, Fruits 57, 55–65.
Debras J.-F., Torre F., Rieux R., Kreiter S., Garcin M.S., Van Helden M., Buisson E., Dutoit T. (2006) Discrimination between agricultural management and the hedge effect in pear orchards (south-eastern France), Ann. Appl. Biol. 149, 347–355.
Debras J.-F., Dussaud A., Rieux R., Dutoit T. (2007) Recherche prospective sur le rôle “source” des haies en production fruitière intégrée. Le cas des perce-oreilles: Forficula auricularia L. et Forficula pubescens Gené, C.R. Acad. Sci. Fr. 330, 664–673.
Debras J.-F., Senoussi R., Rieux R., Buisson E., Dutoit T. (2008) Spatial distribution of an arthropod community in a pear orchard (southern France), Identification of a hedge effect, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 127, 166–176.
Defrance H., Marboutie G., Atger P. (1987) Expérimentation d’une haie brise-vent composite, PHM Rev. Hortic. 280, 25–29.
Deguine J.-P., Ferron P. (2004) Protection des cultures et développement durable, bilan et perspectives, Courrier Cell. Env. INRA 52, 57–65.
Delmas Y. (1995) Peuplements d’Arthropodes d’un verger de pêchers, des haies de bordure et de la strate herbacée de l’inter-rang, Mémoire de l’École Nationale des Ingénieurs des Travaux de l’Horticulture et du Paysage, Angers, 56 p.
Doles J.L., Zimmerman R.J., Moore J.C. (2001) Soil microarthropod community structure and dynamics in organic and conventionally managed apple orchards in Western Colorado, USA, Appl. Soil Ecol. 18, 83–96.
Epstein D.L., Zack R.S., Brunner J.F., Gut L., Brown J.J. (2000) Effects of broad-spectrum insecticides on epigeal arthropod biodiversity in Pacific Northwest apple orchards, Environ. Entomol. 29, 340–348.
Eurostat (2002) The use of plant protection products in the European Union, Data 1992–1999, Eurostat report 2002.
Fazekas J., Kadar F., Lovei G.L. (1992) Comparison of ground beetle assemblages (Coleoptera: Carabidae) of an abandoned apple orchard and the bordering forest, Acta Phytopathol. Entomol. Hung. 27, 233–238.
Finke D.L., Denno R.F. (2006) Spatial refuge from intraguild predation: implications for prey suppression and trophic cascades, Oecologia 149, 265–275.
Fitz Gerald J.D., Solomon M.G. (2004) Can flowering plants enhance numbers of beneficial arthropods in UK apple and pear orchards? Biocontrol Sci. Techn. 14, 291–300.
Flexner J.L., Westigard P.H., Gonzalves P., Hilton R. (1991) The effect of groundcover and herbicide treatment on twospotted spider mite density and dispersal in southern Oregon pear orchards, Entomol. Exp. Appl. 60, 111–123.
Fluetsch K.M., Sparling D.W. (1994) Avian nesting success and diversity in conventionally and organically Managed orchards, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 13, 2118–2124.
Forman R.T.T., Baudry J. (1984) Hedgerows and hedgerow networks in Landscape Ecology, Environ. Manag. 8, 495–510.
Furness R.W., Greenwood J.J.D. (1993) Birds as monitors of environmental change, Chapman and Hall, London, 288 p.
Fye R.E. (1980) Weed sources of Lygus bugs in the Yakima valley and Columbia basin in Washington, J. Econ. Entomol. 73, 469–473.
Fye R.E. (1983) Cover crop manipulation for building pear psylla (Homoptera: Psyllidae) predator populations in pear orchards, J. Econ. Entomol. 76, 306–310.
Garnier M. (1994) Milieux naturels servant à la compensation écologique, Document environnement n∘17, OFEFP, Berne, 35 p.
Gauthier J. (1993) Haies composites et strate herbacée: incidences sur les populations d’arthropodes d’un verger de pêchers conduit en protection intégrée dans la moyenne vallée du Rhône, Mémoire de l’École Nationale des Ingénieurs des Travaux de l’Horticulture et du Paysage, Angers, 58 p.
Genghini M., Gellini S., Gustin M. (2006) Organic and integrated agriculture: the effects on bird communities in orchard farms in northern Italy, Biodivers. Conserv. 15, 3077–3094.
Gingras D., Boivin G. (2002) Effect of plant structure, host density and foraging duration on host finding by Trichogramma evanescens (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae), Environ. Entomol. 31, 1153–1157.
Greaves M.P., Marshall E.J.P. (1987) Field margins: definitions and statistics, in: Way J.M., Greig-Smith P.W. (Eds.), Field margins: definitions and statistics, British Crop Protection Council, Farnham, UK, pp. 3–10.
Green R.E., Osborne P.E., Sears E.J. (1994) The distribution of passerine birds in hedgerows during the breeding season in relation to characteristics of the hedgerow and adjacent farmland, J. Appl. Ecol. 31, 677–692.
Grison P., Biliotti E. (1953) La signification des “stations-refuges” pour la faune entomologique, C.R. Acad. agric. Fr. 39, 106–109.
Gruys P. (1982) Hits and misses. The ecological approach to pest control in orchards, Entomol. Exp. Appl. 31, 70–87.
Gut L.J., Westigard P.H., Liss W.J. (1988) Arthropod colonization and community development on young pear trees in Southern Oregon, Melandaria 46, 1–13.
Hall R.W., Ehler L.E. (1979) Rate of establishment of natural enemies in classical biological control, Bull. Entomol. Soc. Am. 25, 280–282.
Harwood R.W.J., Wratten S.D., Nowakoski M. (1992) The effect of managed fields margin on hoverfly (Diptera: Syrphidae) distribution and within fields abundance, in: Brighton Crop Protection Conference — Pests and Diseases. British Crop Protection Council, Hampshire, UK, pp. 1033–1037.
Hérard F. (1986) Annotated list of the entomophagous complex associated with pear psylla, Psylla pyri (L.) (Hom.: Psyllidae) in France, Agronomie 6, 1–34.
Herzog F., Dreier S., Hofer G., Marfurt C., Schupbach B., Spiess M., Walter T. (2005) Effect of ecological compensation areas on floristic and breeding bird diversity in Swiss agricultural landscapes, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 108, 189–204.
Hole D.G., Perkins A.J., Wilson J.D., Alexander I.H., Grice P.V., Evans A.D. (2005) Does organic farming benefit biodiversity? Biol. Conserv. 122, 113–130.
Horton D.R., Broers D.A., Lewis R.R., Granatstein D., Richard S.Z., Unruh T.R., Moldenke A.R., Brown J.J. (2002) Effects of mowing frequency on densities of natural enemies in three Pacific Northwest pear orchards, Entomol. Exp. Appl. 106, 135–145.
IDF Institut pour le Développement Forestier (1981) Réalisation pratique des haies brise-vent et bandes boisées, IDF, Paris, 129 p.
Irvin N.A., Scarratt S.L., Wratten S.D., Frampton C.M., Chapman R.B., Tylianakis J.M. (2006) The effects of floral understoreys on parasitism of leafrollers (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) on apples in New Zealand, Agr. Forest Entomol. 8, 25–34.
Jeanneret P. (2000) Interchanges of a common pest guild between orchards and surrounding ecoystems: a multivariate analysis of landscape influence, in: Ekbom B., Irwin M.E., Robert Y. (Eds.), Interchanges of insects between agricultural and surrounding landscapes, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp. 85–107.
Jenser G., Balázs K., Erdélyi Cs., Haltrich A., Kádár F., Kozár F., Markó V., Rácz V., Samu F. (1999) Changes in arthropod population composition in IPM apple orchards under continental climatic conditions in Hungary, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 73, 141–154.
Jones G.A., Sieving K.E., Jacobson S.K. (2005a) Avian diversity and functional insectivory on North-Central Florida farmlands, Conserv. Biol. 19, 1234–1245.
Jones G.A., Sieving K.E., Jacobson S.K., Avery M.L., Meagher R.L. (2005b) Parasitized and non-parasitized prey selectivity by an insectivorous bird, Crop Prot. 24, 185–189.
Jonsen I.D., Fahrig L. (1997) Responses of generalist and specialist insect herbivores to landscape spatial structure, Landscape Ecol. 12, 185–197.
Kozár F. (1992) Organization of arthropod communities in agroecosystems, Acta Phytopathol. Entomol. Hung. 27, 365–373.
Kozár F., Brown M.W., Lightner G. (1994) Spatial distribution of homopteran pests and beneficial insects in an orchard and its connection with ecological plant protection, J. Appl. Entomol. 117, 519–529.
Krebs J.R., Wilson J.D., Bradbury R.B., Siriwardena G.M. (1999) The second silent spring? Nature 400, 611–612.
Labrie G., Prince C., Bergeron J.M. (2003) Abundance and developmental stability of Pterostichus melanarius (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in organic and integrated pest management orchards of Quebec, Canada, Environ. Entomol. 32, 123–132.
Lacas J.-G., Voltz M., Gouy V., Carluer N., Gril J.-J. (2005) Using grassed strips to limit pesticide transfer to surface water: a review, Agron. Sustain. Dev. 25, 253–266.
Landis D.A., Wratten S.D., Gurr G.M. (2000) Habitat management to conserve natural enemies of arthropod pests in agriculture, Annu. Rev. Entomol. 45, 175–201.
Langellotto G.A., Denno R.F. (2004) Responses of invertebrate natural enemies to complex-structured habitats: a meta-analytical synthesis, Oecologia 139, 1–10.
Lawton J.H. (1983) Plant architecture and the diversity of phytophagous insects, Ann. Rev. Entomol. 28, 23–39.
Leius K. (1967) Influence of wild flowers on parasitism of tent caterpillar and codling moth, Can. Entomol. 99, 444–446.
Le Roux X., Barbault R., Baudry J., Burel F., Doussan I., Garnier E., Herzog F., Lavorel S., Lifran R., Roger-Estrade J., Sarthou J.-P., Trommetter M. (2008) Agriculture et biodiversité. Valoriser les synergies. Expertise scientifique collective, synthèse du rapport, INRA (France).
Lewis T. (1969) The diversity of the insect fauna in a hedgerow and neighbouring fields, J. Appl. Ecol. 6, 453–458.
Liss W.J., Gut L.J., Westigard P.H., Warren C.E. (1986) Perspectives on arthropod community structure, organization, and development in agricultural crops, Annu. Rev. Entomol. 31, 455–478.
Longcore T. (2003) Terrestrial arthropods as indicators of ecological restoration success in coastal sage scrub (California, USA), Restor. Ecol. 11, 397–409.
Lys J.A., Nentwig W. (1994) Improvement of the overwintering sites for Carabidae, Staphylinidae and Araneae by strip-management in a cereal field, Pedobiologia 38, 238–242.
Mathews C.R., Bottrell D.G., Brown M.W. (2004) Habitat manipulation of the apple orchard floor to increase ground-dwelling predators and predation of Cydia pomonella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), Biol. Control 30, 265–273.
Maudsley M.J. (2000) A review of the ecology and conservation of hedgerow invertebrates in Britain, J. Environ. Manage. 60, 65–76.
McClure M.S., Andreadis T.G., Lacy G.H. (1982) Manipulating orchard ground cover to reduce invasion by leafhopper vectors of peach X-disease, J. Econ. Entomol. 75, 64–68.
Meagher R.L., Meyer J.R. (1990a) Influence of ground cover and herbicide treatments on Tetranychus urticae populations in peach orchards, Exp. Appl. Acarol. 9, 149–158.
Meagher R.L., Meyer J.R. (1990b) Effect of ground cover management on certain abiotic and biotic interactions in peach orchard ecosystems, Crop Prot. 9, 65–72.
Meyer J.R., Zehr E.I., Meagher R.L. Jr., Salvo S.K. (1992) Survival and growth of peach trees and pest populations in orchard plots managed with experimental ground covers, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 41, 353–363.
Miliczky E.R., Horton D.R. (2005) Densities of beneficial arthropods within pear and apple orchards affected by distance from adjacent native habitat and association of natural enemies with extra-orchard host plants, Biol. Control 33, 249–259.
Miliczky E.R., Calkins C.O., Horton D.R. (2000) Spider abundance and diversity in apple orchards under three insect pest management programmes in Washington State, USA, Agr. Forest Entomol. 2, 203–215.
Miñarro A., Dapena T. (2003) Effects of groundcover management on ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in an apple orchard, Appl. Soil Ecol. 23, 111–117.
Moles R.T., Breen J. (1995) Long-term change within lowland farmland bird communities in relation to field boundary attributes, Biology Environment — Proc. R. Ir. Acad. 95, 203–215.
Mols C.M.M., van Noordwijk A.J., Visser M.E. (2005) Assessing the reduction of caterpillar numbers by great tits Parus major breeding in apple orchards, ARDEA 93, 259–269.
Monteiro L.B., Dor C., Franck P., Lavigne C., Sauphanor B. (2008) Pest management practices and environmental factors affect natural regulation of the codling moth, in: Proc. 7th IOBC International Conference on Integrated Fruit Production (Book of Abstracts), Avignon, October 28–30, 2008, p. 99.
Neumann U. (1993) How to achieve better results with the mating disruption technique, Bull. IOBC/wprs 16, 93–98.
Noss R.F. (1990) Indicators for monitoring biodiversity: a hierarchical approach, Conserv. Biol. 4, 355–364.
Nyrop J.P., Minns J.C., Herring C.P. (1994) Influence of ground cover on dynamics of Amblyseius fallacis Garman (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) in New York apple orchards, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 50, 61–72.
OILB Organisation Internationale de Lutte Biologique (1977) Vers la production agricole intégrée par la lutte intégrée, Bull. IOBC/wprs 4, 1–163.
Ormerod S.J., Watkinson A.R. (2000) Editors’ Introduction: Birds and agriculture, J. Appl. Ecol. 37, 699–705.
Paoletti M.G., Boscolo P., Sommaggio D. (1998) Beneficial insects in fields surrounded by hedgerows in North Eastern Italy, Biol. Agric. Hortic. 15, 311–323.
Parfait G., Jarry M. (1987) Diversité végétale et impact des insectes phytophages: une revue bibliographique des méthodes appliquées au cas des cultures associées, Acta Oecol., Oecol. Gen. 8, 365–378.
Parish T., Lakhani K.H., Sparks T.H. (1994) Modelling the relationship between bird population variables and hedgerow and the other field margin attributes: species richness of winter, summer and breeding birds, J. Appl. Ecol. 31, 764–775.
Pearsall I.A., Walde S.J. (1995) A Comparison of Epigaeic Coleoptera Assemblages in Organic, Conventional, and Abandoned Orchards in Nova-Scotia, Canada, Can. Entomol. 127, 641–658.
Pekár S. (1999) Effect of IPM practices and conventional spraying on spider population dynamics in an apple orchard, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 73, 155–166.
Pekár S. (2003) Change in the community of epigeal spiders and harvestmen (Araneae, Opiliones) with the age of an apple orchard, Plant Soil Environ. 49, 81–88.
Pfammatter W., Vuignier R. (1998) Amélioration de la lutte biologique dans les cultures fruitières au moyen de bandes de plantes sauvages, in: 1er Colloque transnational sur les luttes biologique, intégrée et raisonnée, Lille, January 21–23, 1998, Région Nord-Pas-de-Calais, Lille, France, pp. 71–72.
PIRRP (2006) Plan Interministériel de Réduction des Risques liés aux Pesticides 2006–2009, Ministère de l’Environnement, de l’Énergie, du Développement durable et de l’Aménagement du territoire, http://www.ecologie.gouv.fr/Planinterministeriel-de-reduction. html, consulté le 10/03/2009.
Pollard K.A., Holland J.M. (2006) Arthropods within the woody element of hedgerows and their distribution pattern, Agr. Forest Entomol. 8, 203–211.
Powell G.V.N. (1984) Reproduction of an atricial songbird, the redwinged blackbird, in field treated with organophosphate insecticide fenthion, J. Appl. Ecol. 21, 83–95.
Price P.W., Bouton C.E., Gross P., McPheron B.A., Thompson J.N., Weis A.E. (1980) Interactions among three trophic levels: influence of plants on interactions between insect herbivores and natural enemies, Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 11, 41–65.
Prokopy R.J. (1994) Integration in orchard pest and habitat management, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 50, 1–10.
Prokopy R.J., Mason J.L., Christie M., Wright S.E. (1996) Arthropod pest and natural enemy abundance under second-level versus first-level integrated pest management practices in apple orchards: a 4-year study, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 57, 35–47.
Rands M.R.W. (1986) Effect of hedgerow characteristics on partridge breeding densities, J. Appl. Ecol. 23, 479–487.
Reboulet J.N. (1996) Bandes boisées ou enherbées: incidence sur les ravageurs et les auxiliaires des cultures voisines, Adalia 33, 22–24.
Reyes M., Franck P., Olivares J., Margaritopoulos J., Knight A., Sauphanor B. (2008) Worldwide variability of insecticide resistance mechanisms in the codling moth, Cydia pomonella L. (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae), Bull. Entomol. Res., doi:10.1017/S0007485308006366.
Ricci B., Franck P., Toubon J.-F., Bouvier J.-C., Sauphanor B., Lavigne C. (2009) The influence of landscape on insect pest dynamics: a case study in southeastern France, Landscape Ecol. 24, 337–349.
Rieux R. (1994) Et si l’on pouvait aménager l’environnement végétal des cultures pour manipuler les auxiliaires? Fruit Belge 447, 9–16.
Rieux R., Simon S., Defrance H. (1999) Role of hedgerows and ground cover management on arthropod populations in pear orchards, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 73, 129–140.
Risch S.J., Andow D., Altieri M.A. (1983) Agroecosystem diversity and pest control: data, tentative conclusions, and new research directions, Environ. Entomol. 12, 625–629.
Robertson G.M., Eknert B., Ihse M. (1990) Habitat analysis from infrared aerial photographs and the conservation of birds in Swedish agricultural landscape, Am. Bio. 19, 195–203.
Rodet G. (1985) Incidence des zones refuge sur la dynamique de l’entomofaune d’un verger de pêchers, Mémoire de DEA, Université de Paris XI, Paris VI et Museum, 66 p.
Rosenzweig M.L. (1995) Species diversity in space and time, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Rösler S. (2003) Natur- und Sozialverträglichkeit des Integrierten Obstbaus, Ph.D. thesis University of Kassel, Germany, 430 p.
Russell E.P. (1989) Enemies hypothesis: a review of the effect of vegetational diversity on predatory insects and parasitoids, Environ. Entomol. 18, 590–599.
Sanz J.J. (2001) Experimentally increased insectivorous bird density results in a reduction of caterpillar density and leaf damage to Pyrenean oak, Ecol. Res. 16, 387–394.
Sarthou J.P. (1995) Haies composites et protection biologique: l’entomofaune associée aux essences ligneuses, in: Corroyer N., Garapon D., Arnal A. (Eds.), Mise en place et développement de haies composites en arboriculture biologique, Groupe de Recherche en Agriculture Biologique, Avignon, France, Annexe 2.
Sauphanor B. (2004) Réchauffement climatique et nuisibilité du carpocapse sur les pommiers, in: Lésel R. (Ed.), Effets du réchauffement climatique, Cahiers d’études et de recherches francophones / Agricultures 13.
Sauphanor B. (2009) Les phéromones d’insectes et la lutte par confusion sexuelle, in: Pintureau B., Grenier S., Mouret H., Sauge M.H., Sauphanor B., Sforza R., Tailliez P., Volkoff A.N. (Eds.), La lutte biologique, application aux arthropodes ravageurs et aux adventices, Ed. Ellipse, Coll. Technosup, Paris, pp. 52–73.
Sauphanor B., Audemard H. (1983) Analyse comparée des populations de Lépidoptères en en vergers de Pomacées par piégeage avec des phéromones de synthèse, Agronomie 3, 947–955.
Sauphanor B., Miniggio C., Faivre d’Arcier F. (1993) Effets à moyen terme des pesticides sur la faune auxiliaire en vergers de poiriers, J. Appl. Entomol. 116, 467–478.
Sauphanor B., Brosse V., Bouvier J.-C., Speich P., Micou A., Martinet C. (2000) Monitoring resistance to diflubenzuron and deltamethrin in French codling moth populations (Cydia pomonella), Pest. Manag. Sci. 56, 74–82.
Sauphanor B., Bouvier J.C., Boisneau C., Rieux R., Simon S., Capowiez Y., Toubon J.F. (2005) Impacts biologiques des systèmes de protection en vergers de pommiers, Phytoma Def. Veg. 581, 32–36.
Sauphanor B., Dirwimmer C. et al. (2009) Analyse comparative de différents systèmes en arboriculture fruitière, in: Ecophyto R&D: vers des systèmes de culture économes en produits phytosanitaires, Rapport d’Expertise Collective Inra, Inra Ed., Tome IV, 49 p.
Schoemans P. (1995) Intérêt des insectes et araignées présents sur des haies vis-à-vis de vergers de pommiers conduits en lutte intégrée, Fruit Belge 456, 117–123.
Shaltiel L., Coll M. (2004) Reduction of pear psylla damage by the predatory bug Anthocoris nemoralis (Heteroptera: Anthocoridae): the importance of orchard colonization time and neighbouring vegetation, Biocontrol Sci. Techn. 14, 811–821.
Simon S. (1999) Incidence de l’environnement végétal sur les populations d’arthropodes du verger de poiriers, Thèse de doctorat de l’Université de Montpellier 2, Biologie des populations et écologie, 438 p.
Simon S., Rieux R., Faivre d’Arcier F., Defrance H., Comte D. (1993) Aménagement de l’environnement végétal du verger de poiriers, in: ANPP Association Nationale de Protection des Plantes, 3e Conférence Internationale sur les Ravageurs en Agriculture, Montpellier, December 7–9 1993, ANPP, Paris, pp. 1009–1016.
Simon S., Defrance H., Rieux R., Reboulet J.N. (1998) Les bandes boisées, réservoirs d’arthropodes: incidence sur la protection des cultures, Gibier Faune Sauvage, Game Wildl. 15(HS1), 33–42.
Simon S., Sauphanor B., Lauri P.-E. (2007a) Control of fruit tree pests through manipulation of tree architecture, Pest Techn. 1, 33–37.
Simon S., Defrance H., Sauphanor B. (2007b) Effect of codling moth management on orchard arthropods, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 122, 340–348.
Simon S., Sauphanor B., Defrance H., Lauri P.E. (2009) Manipulation des habitats du verger biologique et de son environnement pour le contrôle des bio-agresseurs. Des éléments pour la modulation des relations arbre-ravageur-auxiliaires, Innov. Agron. 4, 125–134.
Skirvin D.J. (2004) Virtual plant models of predatory mite movement in complex plant canopies, Ecol. Model. 171, 301–313.
Solomon G. (1981) Windbreaks as a source of orchard pests and predators, in: Thresh J.M. (Ed.), Pests, pathogens and vegetation: the role of weeds and wild plants in the ecology of crop pests and diseases, Pitman Books Ltd., London, pp. 273–283.
Solomon M.G., Cross J.V., Fitz Gerald J.D., Campbell C.A.M., Jolly R.L., Olszak R.W., Niemczyk E., Vogt H. (2000) Biocontrol of pests of apples and pears in northern and central Europe — 3. Predators, Biocontrol Sci. Techn. 10, 91–128.
Spellman B., Brown M.W., Mathews C.R. (2006) Effect of floral and extrafloral resources on predation of Aphis spiraecola by Harmonia axyridis on apple, BioControl 51, 715–724.
Stary P. (1983) The perennial stinging nettle (Urtica dioica) as a reservoir of aphid parasitoïds (Hymenoptera, Aphidiidae), Acta Entomol. Bohemoslov. 81, 81–86.
Stephens M.J., France C.M., Wratten S.D., Frampton C. (1998) Enhancing biological control of leafrollers (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) by sowing buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) in an orchard, Biocontrol Sci. Techn. 8, 547–558.
Suckling D.M., Walker J.T.S., Wearing C.H. (1999) Ecological impact of three pest management systems in New Zealand apple orchards, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 73, 129–140.
Szentkiràlyi F., Kozár F. (1991) How many species are there in apple insect communities?: testing the resource diversity and intermediate disturbance hypotheses, Ecol. Entomol. 16, 491–503.
Tasin M., Demaria D., Ryne C., Cesano A., Galliano A., Anfora G., Ioriatti C., Alma A. (2008) Effect of anti-hail nets on Cydia pomonella behavior in apple orchards, Entomol. Exp. Appl. 129, 32–36.
Tscharntke T., Bommarco R., Clough Y., Crist T.O., Kleijn D., Rand T.A., Tylianakis J.M., Van Nouhuys S., Vidal S. (2007) Conservation biological Control and enemy diversity on a landscape scale, Biol. Control 43, 294–309.
Tuovinen T. (1994) Influence of surrounding trees and bushes on the phytoseiid mite fauna on apple orchard trees in Finland, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 50, 39–47.
Van Emden H.F., Williams G.F. (1974) Insect stability and diversity in agro-ecosystems, Annu. Rev. Entomol. 19, 455–475.
Van Helden M., Fargeas E., Fronzes M., Maurice O., Thibaud M., Gil F., Pain G. (2006) The influence of local and landscape characteristics on insect pest population levels in viticulture, Bull. IOBC/wprs 29, 145–148.
Vogt H., Weigel A. (1999) Is it possible to enhance the biological control of aphids in an apple orchard with flowering strips? Bull. IOBC/wprs 22, 39–46.
Vogt H., Weigel A., Wyss E. (1998) Aspects of indirect plant protection strategies in orchards: are flowering strips an adequate measure to control apple aphids? in: Brunnhofer V., Soldan T. (Eds.), Proc. 6th European Congress of Entomology (Book of Abstracts), Ceské Budejovice, August 23–29, 1998, Institute of Entomology, Academy of the Czech republic and University of South Bohemia, pp. 625–626.
Westigard P.H., Flexner L.J., Vanburskirk P., Gonzalves P., Hilton R. (1990) Dispersal pattern of the twospotted spider mite from orchard groundcover into pear, Bull. IOBC/wprs 13, 53–57.
Whalon M.E., Croft B.A. (1986) Immigration and colonization of portable apple trees by arthropod pests and their natural enemies, Crop Prot. 5, 376–384.
Wildbolz T. (1988) Integrated pest management in Swiss apple orchards: stability and risks, Entomol. Exp. Appl. 49, 71–74.
Witzgall P., Stelinsky L., Gut L., Thomson D. (2008) Codling moth management and chemical ecology, Annu. Rev. Entomol. 53, 503–522.
Wyss E. (1995) The effects of weed strips on aphids and aphidophagous predators in an apple orchard, Entomol. Exp. Appl. 75, 43–49.
Wyss E. (1996) The effects of artificial weed strips on diversity and abundance of the arthropod fauna in a Swiss experimental apple orchard, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 60, 47–59.
Wyss E., Niggli U., Nentwig W. (1995) The impact of spiders on aphid populations in a strip-managed apple orchard, J. Appl. Entomol. 119, 473–478.
Yan Y., Yu Y., Du X., Zhao B. (1997) Conservation and augmentation of natural enemies in pest management of Chinese apple orchards, Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 62, 253–260.
Zandstra B.H., Motooka P.S. (1978) Beneficial effects of weeds in pest management — a review, PANS 24, 333–338.
Zehnder G., Gurr G.M., Kühne S., Wade M.R., Wratten S.D., Wyss E. (2007) Arthropod pest management in organic crops, Ann. Rev. Entomol. 52, 57–80.
Zhang W., Ricketts T.H., Kremen C., Carney K., Swinton S.M. (2007) Ecosystem services and dis-services to agriculture, Ecol. Econ. 64, 253–260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Simon, S., Bouvier, JC., Debras, JF. et al. Biodiversity and pest management in orchard systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 30, 139–152 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1051/agro/2009013
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/agro/2009013