Abstract
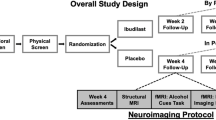
Methamphetamine (MA) triggers neuroinflammation and medications that counteract MA-induced neuroinflammation may reduce MA-induced neurodegeneration and improve neurocognition and treatment outcomes in MA use disorder. We performed a randomized, placebo-controlled trial to determine the safety and efficacy of ibudilast (IBUD), a phosphodiesterase inhibitor that reduces neuroinflammation, for the treatment of MA use disorder. Treatment-seeking volunteers with MA use disorder were randomly assigned to receive 12 weeks of IBUD 50 mg twice daily (N = 64) or placebo (N = 61) with medication management counseling. Participants visited the outpatient research clinic twice weekly to provide urine specimens for drug screens and undergo study assessments. The primary outcome was end of treatment MA-abstinence (EOTA) during weeks 11 and 12 of treatment. Serum IBUID levels were measured for IBUD participants during week 3 of treatment. There was no difference in EOTA for IBUD (14%) versus placebo (16%, p > 0.05). There was no correlation between serum IBUD levels and MA use during treatment and mean IBUD levels for participants with (mean = 51.3, SD = 20.3) and without (mean = 54.7, SD = 33.0, p = 0.70) EOTA. IBUD was well tolerated. IBUD did not facilitate MA abstinence in this outpatient trial. Whether targeting neuroinflammation, either with IBUD in other subgroups of MA users or clinical trial designs, or with other anti-inflammatory medications, is an effective strategy for treating MA use disorder is not clear.

The proportion of urine drug screens negative for methamphetamine (MA) during the two week lead-in period (weeks −2 and − 1) and the 12 week medication treatment period (weeks 1–12) for ibudilast versus placebo



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV-TR, fourth edition, text Revision. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Anderson AL, Reid MS, Li SH, Holmes T, Shemanski L, Slee A, Smith EV, Kahn R, Chiang N, Vocci F, Ciraulo D, Dackis C, Roache JD, Salloum IM, Somoza E, Urschel HC 3rd, Elkashef AM (2009) Modafinil for the treatment of cocaine dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend 104:133–139
Anderson AL, Li SH, Markova D, Holmes TH, Chiang N, Kahn R, Campbell J, Dickerson DL, Galloway GP, Haning W, Roache JD, Stock C, Elkashef AM (2015) Bupropion for the treatment of methamphetamine dependence in non-daily users: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Drug Alcohol Depend 150:170–174
Barkhof F, Hulst HE, Drulovic J, Uitdehaag BM, Matsuda K, Landin R (2010) Ibudilast in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a neuroprotectant? Neurology 74:1033–1040
Beardsley PM, Shelton KL, Hendrick E, Johnson KW (2010) The glial cell modulator and phosphodiesterase inhibitor, AV411 (ibudilast), attenuates prime- and stress-induced methamphetamine relapse. Eur J Pharmacol 637:102–108
Birath JB, Briones M, Amaya S, Shoptaw S, Swanson AN, Tsuang J, Furst B, Heinzerling K, Obermeit L, Maes L, McKay C, Wright MJ (2017) Ibudilast may improve attention during early abstinence from methamphetamine. Drug Alcohol Depend 178:386–390
Bisaga A, Aharonovich E, Garawi F, Levin FR, Rubin E, Raby WN, Vosburg SK, Nunes EV (2005) Utility of lead-in period in cocaine dependence pharmacotherapy trials. Drug Alcohol Depend 77:7–11
Bisaga A, Aharonovich E, Cheng WY, Levin FR, Mariani JJ, Raby WN, Nunes EV (2010) A placebo-controlled trial of memantine for cocaine dependence with high-value voucher incentives during a pre-randomization lead-in period. Drug Alcohol Depend 111:97–104
Brensilver M, Heinzerling KG, Shoptaw S (2013) Pharmacotherapy of amphetamine-type stimulant dependence: an update. Drug Alcohol Rev 32:449–460
Cho Y, Crichlow GV, Vermeire JJ, Leng L, Du X, Hodsdon ME, Bucala R, Cappello M, Gross M, Gaeta F, Johnson K, Lolis EJ (2010) Allosteric inhibition of macrophage migration inhibitory factor revealed by ibudilast. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:11313–11318
De Virgilio A, Greco A, Fabbrini G, Inghilleri M, Rizzo MI, Gallo A, Conte M, Rosato C, Ciniglio Appiani M, de Vincentiis M (2016) Parkinson's disease: autoimmunity and neuroinflammation. Autoimmun Rev 15:1005–1011
DeYoung DZ, Heinzerling KG, Swanson AN, Tsuang J, Furst BA, Yi Y, Wu YN, Moody DE, Andrenyak DM, Shoptaw SJ (2016) Safety of intravenous methamphetamine administration during Ibudilast treatment. J Clin Psychopharmacol 36:347–354
Fantegrossi WE, Ciullo JR, Wakabayashi KT, De La Garza R 2nd, Traynor JR, Woods JH (2008) A comparison of the physiological, behavioral, neurochemical and microglial effects of methamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine in the mouse. Neuroscience 151(2):533–543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.11.007
First MBSRL, Gibbon M, JBW W (2002) Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I Disorders, Research Version, Patient Edition. (SCID-I/P). Biometrics Research, New York
Flora G, Lee YW, Nath A, Maragos W, Hennig B, Toborek M (2002) Methamphetamine-induced TNF-alpha gene expression and activation of AP-1 in discrete regions of mouse brain: potential role of reactive oxygen intermediates and lipid peroxidation. Neuromolecular Med 2(1):71–85. https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:2:1:71
Fox RJ, Coffey CS, Conwit R, Cudkowicz ME, Gleason T, Goodman A, Klawiter EC, Matsuda K, McGovern M, Naismith RT, Ashokkumar A, Barnes J, Ecklund D, Klingner E, Koepp M, Long JD, Natarajan S, Thornell B, Yankey J, Bermel RA, Debbins JP, Huang X, Jagodnik P, Lowe MJ, Nakamura K, Narayanan S, Sakaie KE, Thoomukuntla B, Zhou X, Krieger S, Alvarez E, Apperson M, Bashir K, Cohen BA, Coyle PK, Delgado S, Dewitt LD, Flores A, Giesser BS, Goldman MD, Jubelt B, Lava N, Lynch SG, Moses H, Ontaneda D, Perumal JS, Racke M, Repovic P, Riley CS, Severson C, Shinnar S, Suski V, Weinstock-Guttman B, Yadav V, Zabeti A, NN102/SPRINT-MS Trial Investigators (2018) Phase 2 trial of Ibudilast in progressive multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 379:846–855
Gibson LC, Hastings SF, McPhee I, Clayton RA, Darroch CE, Mackenzie A, Mackenzie FL, Nagasawa M, Stevens PA, Mackenzie SJ (2006) The inhibitory profile of Ibudilast against the human phosphodiesterase enzyme family. Eur J Pharmacol 538:39–42
Heinzerling KG, Swanson AN, Kim S, Cederblom L, Moe A, Ling W, Shoptaw S (2010) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of modafinil for the treatment of methamphetamine dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend 109:20–29
Heinzerling KG, Swanson AN, Hall TM, Yi Y, Wu Y, Shoptaw SJ (2014) Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of bupropion in methamphetamine-dependent participants with less than daily methamphetamine use. Addiction 109:1878–1886
Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2009) Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8:382–397
Huckans M, Fuller BE, Chalker AL, Adams M, Loftis JM (2015) Plasma inflammatory factors are associated with anxiety, depression, and cognitive problems in adults with and without methamphetamine dependence: an exploratory protein Array study. Front Psych 6:178
Kohno M, Link J, Dennis LE, McCready H, Huckans M, Hoffman WF, Loftis JM (2019) Neuroinflammation in addiction: a review of neuroimaging studies and potential immunotherapies. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 179:34–42
Ladenheim B, Krasnova IN, Deng X, Oyler JM, Polettini A, Moran TH, Huestis MA, Cadet JL (2000) Methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity is attenuated in transgenic mice with a null mutation for interleukin-6. Mol Pharmacol 58(6):1247–1256. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.58.6.1247
Lee NK, Jenner L, Harney A, Cameron J (2018) Pharmacotherapy for amphetamine dependence: a systematic review. Drug Alcohol Depend 191:309–337
Ling W, Shoptaw S, Wesson D, Rawson RA, Compton M, Klett CJ (1997) Treatment effectiveness score as an outcome measure in clinical trials. NIDA Res Monogr 175:208–220
Loftis JM, Choi D, Hoffman W, Huckans MS (2011) Methamphetamine causes persistent immune dysregulation: a cross-species, translational report. Neurotox Res 20:59–68
Minghetti L, Ajmone-Cat MA, De Berardinis MA, De Simone R (2005) Microglial activation in chronic neurodegenerative diseases: roles of apoptotic neurons and chronic stimulation. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 48:251–256
Mizuno T, Kurotani T, Komatsu Y, Kawanokuchi J, Kato H, Mitsuma N, Suzumura A (2004) Neuroprotective role of phosphodiesterase inhibitor ibudilast on neuronal cell death induced by activated microglia. Neuropharmacology 46:404–411
Morley KC, Cornish JL, Faingold A, Wood K, Haber PS (2017) Pharmacotherapeutic agents in the treatment of methamphetamine dependence. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 26:563–578
Narita M, Suzuki M, Kuzumaki N, Miyatake M, Suzuki T (2008) Implication of activated astrocytes in the development of drug dependence: differences between methamphetamine and morphine. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1141:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1441.032
Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bedirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, Cummings JL, Chertkow H (2005) The Montreal cognitive assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc 53:695–699
Papageorgiou M, Raza A, Fraser S, Nurgali K, Apostolopoulos V (2019) Methamphetamine and its immune-modulating effects. Maturitas 121:13–21
Pettinati HM, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (U.S.) (2004) Medical management treatment manual : a clinical research guide for medically trained clinicians providing pharmacotherapy as part of the treatment for alcohol dependence. U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, Bethesda
Pettinati HM, Weiss RD, Dundon W, Miller WR, Donovan D, Ernst DB, Rounsaville BJ (2005) A structured approach to medical management: a psychosocial intervention to support pharmacotherapy in the treatment of alcohol dependence. J Stud Alcohol 15: 170–178; discussion 168–179
Rolan P, Hutchinson M, Johnson K (2009) Ibudilast: a review of its pharmacology, efficacy and safety in respiratory and neurological disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother 10:2897–2904
Schurer S, Klingel K, Sandri M, Majunke N, Besler C, Kandolf R, Lurz P, Luck M, Hertel P, Schuler G, Linke A, Mangner N (2017) Clinical characteristics, Histopathological features, and clinical outcome of methamphetamine-associated cardiomyopathy. JACC Heart Fail 5:435–445
Sekine Y, Ouchi Y, Sugihara G, Takei N, Yoshikawa E, Nakamura K, Iwata Y, Tsuchiya KJ, Suda S, Suzuki K, Kawai M, Takebayashi K, Yamamoto S, Matsuzaki H, Ueki T, Mori N, Gold MS, Cadet JL (2008) Methamphetamine causes microglial activation in the brains of human abusers. J Neurosci 28(22):5756–5761. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1179-08.2008
Shaerzadeh F, Streit WJ, Heysieattalab S, Khoshbouei H (2018) Methamphetamine neurotoxicity, microglia, and neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 15:341
Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Wegrzynowicz M, Lee E, Bowman AB, Aschner M (2011) Role of astrocytes in brain function and disease. Toxicol Pathol 39:115–123
Snider SE, Vunck SA, van den Oord EJ, Adkins DE, McClay JL, Beardsley PM (2012) The glial cell modulators, ibudilast and its amino analog, AV1013, attenuate methamphetamine locomotor activity and its sensitization in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 679:75–80
Snider SE, Hendrick ES, Beardsley PM (2013) Glial cell modulators attenuate methamphetamine self-administration in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 701:124–130
Sobell MB, Sobell LC, Klajner F, Pavan D, Basian E (1986) The reliability of a timeline method for assessing normal drinker college students’ recent drinking history: utility for alcohol research. Addict Behav 11:149–161
Soontornniyomkij V, Kesby JP, Morgan EE, Bischoff-Grethe A, Minassian A, Brown GG, Grant I (2016) Effects of HIV and methamphetamine on brain and behavior: evidence from human studies and animal models. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 11:495–510
Spitzer R, Williams J, Gibbbon M, First M (1995) The structured clinical interview for DSM-IV. American Psychiatric Press, Washington, DC
Stout RL, Wirtz PW, Carbonari JP, Del Boca FK (1994) Ensuring balanced distribution of prognostic factors in treatment outcome research. J Stud Alcohol supplement s12:70–75
Suzumura A, Ito A, Yoshikawa M, Sawada M (1999) Ibudilast suppresses TNFalpha production by glial cells functioning mainly as type III phosphodiesterase inhibitor in the CNS. Brain Res 837:203–212
Thomas DM, Kuhn DM (2005) Attenuated microglial activation mediates tolerance to the neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine. J Neurochem 92(4):790–797. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02906.x
Thomas DM, Francescutti-Verbeem DM, Kuhn DM (2008) The newly synthesized pool of dopamine determines the severity of methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurochem 105(3):605–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05155.x
Wakita H, Tomimoto H, Akiguchi I, Lin JX, Ihara M, Ohtani R, Shibata M (2003) Ibudilast, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, protects against white matter damage under chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat. Brain Res 992:53–59
Worley MJ, Swanson AN, Heinzerling KG, Roche DJ, Shoptaw S (2016) Ibudilast attenuates subjective effects of methamphetamine in a placebo-controlled inpatient study. Drug Alcohol Depend 162:245–250
Yang X, Wang Y, Li Q, Zhong Y, Chen L, Du Y, He J, Liao L, Xiong K, Yi CX, Yan J (2018) The main molecular mechanisms underlying methamphetamine- induced neurotoxicity and implications for pharmacological treatment. Front Mol Neurosci 11:186
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (DA035054). Study medication and matching placebo was provided by MediciNova, Inc.
Funding
This study was funded by NIH grant number DA035054.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Heinzerling has received study medication from MediciNova and DeNovo, has been a scientific advisor for Alkermes and Indivior, and is a founder of BDH Pharma, LLC. Dr. Briones is a founder of BDH Pharma, LLC. Dr. Shoptaw has received study medication from Gilead. No other authors declare potential conflicts.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinzerling, K.G., Briones, M., Thames, A.D. et al. Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Targeting Neuroinflammation with Ibudilast to Treat Methamphetamine Use Disorder. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 15, 238–248 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-019-09883-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-019-09883-w