Abstract
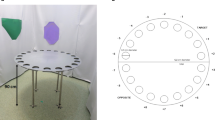
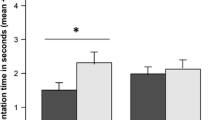
Spatial learning and memory skills are imperative for the survival and fitness of subterranean rodents because of the harsh underground niche in which they live that necessitates the avoidance of higher energy expenditures or probable conflicts with conspecifics or predators. Our study aims to assess the spatial learning and working memory performance of a subterranean rodent species, plateau zokors (Eospalax baileyi), compared to that of the surface-dwelling plateau pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) and laboratory rats (Rattus norvegicus) which spend a considerable time of their lives above ground. Animals were tested with a spatial delayed alternation task in a T-maze for six consecutive days. Plateau zokors showed less efficient learning and working memory capacity in the T-maze compared to plateau pikas and laboratory rats, which maintained accurate and consistent increased spatial learning rates and working memory performances. The three species did not show bias towards a certain arm of the maze. Additionally, clear sex-specific differences were observed in the laboratory rats regarding spatial learning and working memory functions, while in pikas and zokors, no sex-specific variations were detected. The latency to accomplish the task was significantly lower in rats than in pikas and zokors, but no sex-specific differences were detected in all the species. The inferior performance of plateau zokors, compared to pikas and rats, in the T-maze might imply that although the functional significance of working memory may overlap in diverse taxonomic groups, the adaptive value thereof may differ considerably across taxa on account of the divergence in environmental stability, domestication, habitat structure, behavioural needs and the available sensory cues between species.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso P, López-Solà C, Real E, Segalàs C, Menchón JM (2015) Animal models of obsessive–compulsive disorder: utility and limitations. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 11:1939–1955
Birkett LP, Newton-Fisher NE (2011) How abnormal is the behaviour of captive, zoo-living chimpanzees? PLoS One 6(6):e20101
Bogacz R, Brown E, Moehlis J, Holmes P, Cohen JD (2006) The physics of optimal decision making: a formal analysis of models of performance in two-alternative forced-choice tasks. Psychol Rev 113(4):700–765
Brust V, Guenther A (2015) Domestication effects on behavioural traits and learning performance: comparing wild cavies to Guinea pigs. Anim Cogn 18(1):99–109
Burda H, Marhold S, Westenberger T, Wiltschko R, Wiltschko W (1990) Magnetic compass orientation in the subterranean rodentCryptomys hottentotus (Bathyergidae). Experientia 46(5):528–530
Carman HM, Mactutus CF (2002) Proximal versus distal Cue utilization in spatial navigation: the role of visual acuity? Neurobiol Learn Mem 78(2):332–346
Costanzo MS, Bennett NC, Lutermann H (2009) Spatial learning and memory in African mole-rats: the role of sociality and sex. Physiol Behav 96(1):128–134
Crish CM, Crish SD, Comer C (2016) Tactile sensing in the naked mole rat. In: Prescott T, Ahissar E, Izhikevich E (eds) Scholarpedia of touch. Atlantis Press, Paris, pp 95–101
Deacon RMJ, Rawlins JNP (2006) T-maze alternation in the rodent. Nat Protoc 1:7
Deutschlander ME, Freake MJ, Borland SC, Phillips JB, Madden RC, Anderson LE, Wilson BW (2003) Learned magnetic compass orientation by the Siberian hamster, Phodopus sungorus. Anim Behav 65(4):779–786
Dudchenko PA (2004) An overview of the tasks used to test working memory in rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28(7):699–709
Elizalde N, Gil-Bea FJ, Ramirez MJ, Aisa B, Lasheras B, Del Rio J, Tordera RM (2008) Long-lasting behavioral effects and recognition memory deficit induced by chronic mild stress in mice: effect of antidepressant treatment. Psychopharmacology 199(1):1–14
Gaulin SJC, Fitzgerald RW (1989) Sexual selection for spatial-learning ability. Anim Behav 37(Part 2):322–331
Gross AN, Richter SH, Engel AKJ, Würbel H (2012) Cage-induced stereotypies, perseveration and the effects of environmental enrichment in laboratory mice. Behav Brain Res 234(1):61–68
Harris AP, D’Eath RB, Healy SD (2009) Environmental enrichment enhances spatial cognition in rats by reducing thigmotaxis (wall hugging) during testing. Anim Behav 77(6):1459–1464
Hébert M, Bulla J, Vivien D, Agin V (2017) Are distal and proximal visual cues equally important during spatial learning in mice? A pilot study of overshadowing in the spatial domain. Front Behav Neurosci 11:109
Hegab IM, Wei W (2014) Neuroendocrine changes upon exposure to predator odors. Physiol Behav 131:149–155
Hegab IM, Jin Y, Ye M et al (2014a) Defensive responses of Brandt’s voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii) to stored cat feces. Physiol Behav 123:193–199
Hegab IM, Shang G, Ye M et al (2014b) Defensive responses of Brandt’s voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii) to chronic predatory stress. Physiol Behav 126:1–7
Hegab IM, Wang A, Yin B et al (2014c) behavioral and neuroendocrine response of Brandt’s voles, Lasiopodomys brandtii, to odors of different species. Eur J Wildl Res 60(2):331–340
Hegab IM, Kong S, Yang S, Mohamaden WI, Wei W (2015) The ethological relevance of predator odors to induce changes in prey species. Acta Ethol 18(1):1–9
Hegab IM, Tan Y, Wang C, Yao B, Wang H, Ji W, Su J (2018a) Examining object recognition and object-in-place memory in plateau zokors, Eospalax baileyi. Behav Process 146:34–41
Hegab IM, Qian Z, Pu Q, Wang Z, Yukun K, Cai Z et al (2018b) Gender difference in unconditioned and conditioned predator fear responses in Smith’s zokors (Eospalax smithii). Glob Ecol Conserv 16:e00503
Hines M, Fane BA, Pasterski VL, Mathews GA, Conway GS, Brook C (2003) Spatial abilities following prenatal androgen abnormality: targeting and mental rotations performance in individuals with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Psychoneuroendocrino 28(8):1010–1026
Jonasson Z (2005) Meta-analysis of sex differences in rodent models of learning and memory: a review of behavioral and biological data. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28(8):811–825
Kaiser S, Hennessy MB, Sachser N (2015) Domestication affects the structure, development and stability of biobehavioural profiles. Front Zool 12(1):S19
Kimchi T, Terkel J (2001a) Magnetic compass orientation in the blind mole rat Spalax ehrenbergi. J Exp Biol 204(4):751–758
Kimchi T, Terkel J (2001b) Spatial learning and memory in the blind mole-rat in comparison with the laboratory rat and Levant vole. Anim Behav 61(1):171–180
Kimchi T, Terkel J (2004) Comparison of the role of somatosensory stimuli in maze learning in a blind subterranean rodent and a sighted surface-dwelling rodent. Behav Brain Res 153(2):389–395
Kontis D, Boulougouris V, Papakosta VM, Kalogerakou S, Papadopoulos S, Poulopoulou C, Papadimitriou GN, Tsaltas E (2008) Dopaminergic and serotonergic modulation of persistent behaviour in the reinforced spatial alternation model of obsessive–compulsive disorder. Psychopharmacology 200(4):597–610
Kruska DCT, Steffen K (2013) Comparative allometric investigations on the skulls of wild cavies (Cavia aperea) versus domesticated Guinea pigs (C. aperea f. porcellus) with comments on the domestication of this species. Mamm Biol 78(3):178–186
Künzl C, Kaiser S, Meier E, Sachser N (2003) Is a wild mammal kept and reared in captivity still a wild animal. Horm Behav 43(1):187–196
Lewis M, Kim S-J (2009) The pathophysiology of restricted repetitive behavior. J Neurodev Disord 1(2):114–132
Lopez J, de Vasconcelos AP, Cassel J-C (2008) Environmental cue saliency influences the vividness of a remote spatial memory in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90(1):285–289
Luna F, Antinuchi CD (2003) Daily movements and maximum speed in Ctenomys talarum (Rodentia: Ctenomyidae) in artificial enclosures. J Mammal 84(1):272–277
Madison DM, McShea WJ (1987) Seasonal changes in reproductive tolerance, spacing, and social organization in Meadow Voles: a microtine model. Am Zool 27(3):899–908
Mastrangelo ME, Schleich CE, Zenuto RR (2010) Spatial learning abilities in males and females of the subterranean rodent Ctenomys talarum. Ethol Ecol Evol 22(1):101–108
Moritz RE, Burda H, Begall S, Němec P (2007) Magnetic compass: a useful tool underground. In: Begall S, Burda H, Schleich CE (eds) Subterranean rodents: news from underground. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 161–174
Norris RW, Zhou K, Zhou C, Yang G, William Kilpatrick C, Honeycutt RL (2004) The phylogenetic position of the zokors (Myospalacinae) and comments on the families of muroids (Rodentia). Mol Phylogenet Evol 31(3):972–978
Olton DS, Paras BC (1979) Spatial memory and hippocampal function. Neuropsychologia 17(6):669–682
Oosthuizen MK, Scheibler A-G, Charles Bennett N, Amrein I (2013) Effects of laboratory housing on exploratory behaviour, novelty discrimination and spatial reference memory in a subterranean, solitary rodent, the cape mole-rat (Georychus capensis). PLoS One 8(9):e75863
Phillips JB, Youmans PW, Muheim R, Sloan KA, Landler L, Painter MS, Anderson CR (2013) Rapid learning of magnetic compass direction by C57BL/6 mice in a 4-armed ‘plus’ water maze. PLoS One 8(8):e73112
Piet AT, El Hady A, Brody CD (2018) Rats adopt the optimal timescale for evidence integration in a dynamic environment. Nat Commun 9(1):4265–4265
Qu J, Russell JC, Ji W, Yang M, Chen Q, Li W, Zhang Y (2017) Five-year population dynamics of plateau pikas (Ochotona curzoniae) on the east of Tibetan plateau. Eur J Wildl Res 63(3):51
Sandstrom NJ, Kim JH, Wasserman MA (2006) Testosterone modulates performance on a spatial working memory task in male rats. Horm Behav 50(1):18–26
Schaefers ATU, Winter Y (2011) Rapid task acquisition of spatial-delayed alternation in an automated T-maze by mice. Behav Brain Res 225(1):56–62
Schleich CE (2010) Ontogeny of spatial working memory in the subterranean rodent ctenomys talarum. Dev Psychobiol 52(6):592–597
Shams I, Avivi A, Nevo E (2005) Oxygen and carbon dioxide fluctuations in burrows of subterranean blind mole rats indicate tolerance to hypoxic–hypercapnic stresses. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 142(3):376–382
Shao Y, Li J-X, Ge R-L, Zhong L, Irwin DM, Murphy RW, Zhang Y-P (2015) Genetic adaptations of the plateau zokor in high-elevation burrows. Sci Rep 5:17262
Sipos E, Kurunczi A, Kasza Á, Horváth J, Felszeghy K, Laroche S, Toldi J, Párducz Á, Penke B, Penke Z (2007) β-Amyloid pathology in the entorhinal cortex of rats induces memory deficits: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 147(1):28–36
Smith AT, Gao WX (1991) Social relationships of adult black-lipped Pikas (Ochotona curzoniae). J Mammal 72(2):231–247
Stuermer IW, Wetzel W (2006) Early experience and domestication affect auditory discrimination learning, open field behaviour and brain size in wild Mongolian gerbils and domesticated laboratory gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus forma domestica). Behav Brain Res 173(1):11–21
Su J, Hegab Ibrahim M, Ji W et al (2018) Function-related drivers of skull morphometric variation and sexual size dimorphism in a subterranean rodent, plateau Zokor (Eospalax baileyi). Ecol Evol 8(9):4631–4643
du Toit L, Bennett NC, Nickless A, Whiting MJ (2012) Influence of spatial environment on maze learning in an African mole-rat. Anim Cogn 15(5):797–806
Wegner RE, Begall S, Burda H (2006) Light perception in ‘blind’ subterranean Zambian mole-rats. Anim Behav 72(5):1021–1024
Williams JL, Baker SL, Gress JE, Givens B (1998) Effects of predator-induced stress and age on working memory in rats. Psychol Rec 48(3):355–372
Wolff JO (1989) Social behavior. In: Kirkland GL, Layne JN (eds) Advances in the study of Peromyscus (Rodentia). Texas Tech University Press, Lubbock, Tex., USA
Yin B, Fan H, Li S et al (2011) Behavioral response of Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus) to odors of different mammalian species. J Pest Sci 84(3):265
Yin B, Gu C, Lu Y et al (2017) Repeated exposure to cat urine induces complex behavioral, hormonal, and c-fos mRNA responses in Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus). Die Naturwissenschaften 104(7–8):64
Yoon T, Okada J, Jung MW, Kim JJ (2008) Prefrontal cortex and hippocampus subserve different components of working memory in rats. Learn Mem 15(3):97–105
Zhang Y (2007) The biology and ecology of plateau Zokors (Eospalax fontanierii). In: Begall S, Burda H, Schleich CE (eds) Subterranean rodents: news from underground. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 237–249
Zhang Y, Fan N, Zhou W (1993) Study on the population ecology of the plateau zokors. Chinese Journal of Vector Biology and Control 4:359–361
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Liu J (2003) Burrowing rodents as ecosystem engineers: the ecology and management of plateau zokors Myospalax fontanierii in alpine meadow ecosystems on the Tibetan plateau. Mammal Rev 33(3–4):284–294
Zipser B, Schleking A, Kaiser S, Sachser N (2014) Effects of domestication on biobehavioural profiles: a comparison of domestic Guinea pigs and wild cavies from early to late adolescence. Front Zool 11(1):30–30
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Shangli Shi (Dean of School of Grassland Sciences, Gansu Agricultural University) and the Department of Hygiene, Zoonoses and Animal Behavior and Management, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Suez Canal University, for their moral and career support. The authors would like also to thank the two anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions that inevitably improved the status of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for this work was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Funds of Gansu Agricultural University (supporting funds for youth mentor, GAU-QDFC-2018-02), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 31460566 and 31760706), Gansu Provincial Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (no. 1606RJDA314), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (nos. 2015M572614 and 2016T90958, “Fuxi Talent” Plan of Gansu Agricultural University (Gaufx-02J03), Key Laboratory of Grassland Ecosystem (Gansu Agricultural University), Ministry of Education (2017-GSAU-CYJ-03) and Talented Young Scientists fellowship (TYSP) of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Experimental procedures were approved by the animal ethics committee of Gansu Agricultural University (GSAU-CYAE01) and permission from the local authorities was required for capturing wild plateau zokors and pikas.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hegab, I.M., Tan, Y., Kang, Y. et al. Assessing spatial learning and working memory in plateau zokors in comparison with plateau pikas and laboratory rats. acta ethol 22, 163–173 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10211-019-00320-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10211-019-00320-y