Abstract
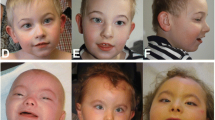
Microdeletions encompassing 14q11.2 locus, involving SUPT16H and CHD8, were shown to cause developmental delay, intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders and macrocephaly. Variations leading to CHD8 haploinsufficiency or loss of function were also shown to lead to a similar phenotype. Recently, a 14q11.2 microduplication syndrome, encompassing CHD8 and SUPT16H, has been described, highlighting the importance of a tight control of at least CHD8 gene-dosage for a normal development. There have been only a few reports of 14q11.2 microduplications. Patients showed variable neurodevelopmental issues of variable severity. Breakpoints of the microduplications were non-recurrent, making interpretation of the CNV and determination of their clinical relevance difficult. Here, we report on two patients with 14q11.2 microduplication encompassing CHD8 and SUPT16H, one of whom had normal intelligence. Review of previous reports describing patients with comparable microduplications allowed for a more precise delineation of the condition and widening of the phenotypic spectrum.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coe BP, Witherspoon K, Rosenfeld JA, van Bon B, Vulto-van Silfhout A, Bosco P, Friend KL, Baker C, Buono S, Vissers LE, Schuurs-Hoeijmakers JH, Hoischen A, Pfundt R, Krumm N, Carvill GL, Li D, Amaral D, Brown N, Lockhart PJ, Scheffer IE, Alberti A, Shaw M, Pettinato R, Tervo R, de Leeuw N, Reijnders MR, Torchia BS, Peeters H, O'Roak BJ, Fichera M, Hehir-Kwa JY, Shendure J, Mefford HC, Haan E, Gécz J, de Vries BB, Romano C, Eichler EE (2014) Refining analyses of copy number variation identifies specific genes associated with developmental delay. Nat Genet 46:1063–1071. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3092
Van Den Bossche MJ, Johnstone M, Strazisar M et al (2012) Rare copy number variants in neuropsychiatric disorders: specific phenotype or not? Am J Med Genet Part B Neuropsychiatr Genet Off Publ Int Soc Psychiatr Genet 159B:812–822. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.32088
Breckpot J, Vercruyssen M, Weyts E et al (2016) Copy number variation analysis in adults with catatonia confirms haploinsufficiency of SHANK3 as a predisposing factor. Eur J Med Genet 59:436–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2016.08.003
Zahir F, Firth HV, Baross A, Delaney AD, Eydoux P, Gibson WT, Langlois S, Martin H, Willatt L, Marra MA, Friedman JM (2007) Novel deletions of 14q11.2 associated with developmental delay, cognitive impairment and similar minor anomalies in three children. J Med Genet 44:556–561. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.2007.050823
Neale BM, Kou Y, Liu L et al (2012) Patterns and rates of exonic de novo mutations in autism spectrum disorders. Nature 485:242–245. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11011
Smyk M, Poluha A, Jaszczuk I et al (2016) Novel 14q11.2 microduplication including the CHD8 and SUPT16H genes associated with developmental delay. Am J Med Genet A 170A:1325–1329. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.37579
McLaren W, Gil L, Hunt SE, Riat HS, Ritchie GR, Thormann A, Flicek P, Cunningham F (2016) The Ensembl variant effect predictor. Genome Biol 17:122. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-0974-4
D’Angelo CS, Varela MC, de Castro CI et al (2014) Investigation of selected genomic deletions and duplications in a cohort of 338 patients presenting with syndromic obesity by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification using synthetic probes. Mol Cytogenet 7:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-014-0075-6
Vuillaume M-L, Naudion S, Banneau G et al (2014) New candidate loci identified by array-CGH in a cohort of 100 children presenting with syndromic obesity. Am J Med Genet A 164:1965–1975. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.36587
Brunetti-Pierri N, Paciorkowski AR, Ciccone R, Della Mina E, Bonaglia MC, Borgatti R, Schaaf CP, Sutton VR, Xia Z, Jelluma N, Ruivenkamp C, Bertrand M, de Ravel TJ, Jayakar P, Belli S, Rocchetti K, Pantaleoni C, D'Arrigo S, Hughes J, Cheung SW, Zuffardi O, Stankiewicz P (2011) Duplications of FOXG1 in 14q12 are associated with developmental epilepsy, mental retardation, and severe speech impairment. Eur J Hum Genet EJHG 19:102–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2010.142
Terrone G, Cappuccio G, Genesio R et al (2014) A case of 14q11.2 microdeletion with autistic features, severe obesity and facial dysmorphisms suggestive of wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 164A:190–193. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.36200
Drabova J, Seemanova E, Hancarova M, Pourova R, Horacek M, Jancuskova T, Pekova S, Novotna D, Sedlacek Z (2015) Long term follow-up in a patient with a de novo microdeletion of 14q11.2 involving CHD8. Am J Med Genet A 167A:837–841. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.36957
Merner N, Forgeot d’Arc B, Bell SC et al (2016) A de novo frameshift mutation in chromodomain helicase DNA-binding domain 8 (CHD8): a case report and literature review. Am J Med Genet A 170A:1225–1235. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.37566
O’Roak BJ, Vives L, Girirajan S et al (2012) Sporadic autism exomes reveal a highly interconnected protein network of de novo mutations. Nature 485:246–250. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10989
Manning BJ, Yusufzai T (2017) The ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling enzymes CHD6, CHD7, and CHD8 exhibit distinct nucleosome binding and remodeling activities. J Biol Chem 292:11927–11936. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.779470
Nishiyama M, Skoultchi AI, Nakayama KI (2012) Histone H1 recruitment by CHD8 is essential for suppression of the Wnt-β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 32:501–512. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.06409-11
Griesi-Oliveira K, Sunaga DY, Alvizi L et al (2013) Stem cells as a good tool to investigate dysregulated biological systems in autism spectrum disorders. Autism Res Off J Int Soc Autism Res 6:354–361. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.1296
Gompers AL, Su-Feher L, Ellegood J, Copping NA, Riyadh MA, Stradleigh TW, Pride MC, Schaffler MD, Wade AA, Catta-Preta R, Zdilar I, Louis S, Kaushik G, Mannion BJ, Plajzer-Frick I, Afzal V, Visel A, Pennacchio LA, Dickel DE, Lerch JP, Crawley JN, Zarbalis KS, Silverman JL, Nord AS (2017) Germline Chd8 haploinsufficiency alters brain development in mouse. Nat Neurosci 20:1062–1073. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4592
Belotserkovskaya R, Oh S, Bondarenko VA, Orphanides G, Studitsky VM, Reinberg D (2003) FACT facilitates transcription-dependent nucleosome alteration. Science 301:1090–1093. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1085703
Deciphering Developmental Disorders Study (2015) Large-scale discovery of novel genetic causes of developmental disorders. Nature 519:223–228. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14135
Deciphering Developmental Disorders Study (2017) Prevalence and architecture of de novo mutations in developmental disorders. Nature 542:433–438. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21062
Lelieveld SH, Reijnders MRF, Pfundt R et al (2016) Meta-analysis of 2,104 trios provides support for 10 new genes for intellectual disability. Nat Neurosci 19:1194–1196. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4352
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the following: Alexis Leurent, Heidi Tampere, Delphine Ceraso and Karine Baroli for technical support; European Reference Network ERN-ITHACA; Pr Nigel Quayle for manuscript editing. Also, we thank patients and families who contributed to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PNG 556 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smol, T., Thuillier, C., Boudry-Labis, E. et al. Neurodevelopmental phenotype associated with CHD8-SUPT16H duplication. Neurogenetics 21, 67–72 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-019-00599-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-019-00599-w