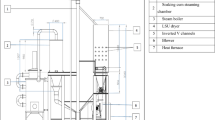
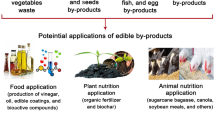
Abstract
Rice, being cultivated and consumed on all continents, has great social and economic importance. Among the forms of grain processing, parboiling stands out because of its numerous physical and nutritional benefits. However, there are few literature researches devoted to the survey of these data. Given the relevance of parboiling and parboiled rice to the world population, this work provides a critical and systematic review of the parboiling process, including thermodynamic properties, environmental and social impacts, as well as relevant information on parboiled rice, considering its consumption and health benefits. Additionally, a pioneering review is presented on new technologies applied to the process, and mathematical modeling as a tool for optimization and migration of nutrients (vitamins and minerals) and contaminants (mycotoxins and chemical agents). Covering such diverse information, including both positive and negative results, allows a global understanding of the nature of the process and the product. Therefore, this literature review aims to provide broad knowledge, for laypeople, entrepreneurs, and researchers alike.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balbinoti TCV, Jorge LM de M, Jorge RMM (2018a) Modeling the hydration step of the rice (Oryza sativa) parboiling process. J Food Eng 216:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2017.07.020
Heinemann RJB, Fagundes PL, Pinto EA, Penteado MVC, Lanfer-Marquez UM (2005) Comparative study of nutrient composition of commercial brown, parboiled and milled rice from Brazil. J Food Compos Anal 18:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2004.07.005
Vanier NL, Paraginski RT, Berrios JDJ, de Oliveira LC, Elias MC (2015) Thiamine content and technological quality properties of parboiled rice treated with sodium bisulfite: Benefits and food safety risk. J Food Compos Anal 41:98–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2015.02.008
Bhattacharya S (1996) Kinetics on colour changes in rice due to parboiling. J Food Eng 29:99–106
Monks JLF, Vanier NL, Casaril J, Berto RM, de Oliveira M, Gomes CB, de Carvalho MP, Dias ARG, Elias MC (2013) Effects of milling on proximate composition, folic acid, fatty acids and technological properties of rice. J Food Compos Anal 30:73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2013.01.009
Lamberts L, De Bie E, Vandeputte GE, Veraverbeke WS, Derycke V, De Man W, Delcour JA (2007) Effect of milling on colour and nutritional properties of rice. Food Chem 100:1496–1503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.11.042
NasirahmadI A, Emadi B, Abbaspour-Fard MH, Aghagolzade H (2014) Influence of moisture content, variety and parboiling on milling quality of rice grains. Rice Sci 21:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6308(13)60169-9
Paiva FF, Vanier NL, Berrios JDJ, Pinto VZ, Wood D, Williams T, Pan J, Elias MC (2016) Polishing and parboiling effect on the nutritional and technological properties of pigmented rice. Food Chem 191:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.02.047
Doesthale YG, Devara S, Rao S, Belavady B (1979) Effect of milling on mineral and trace element composition of raw and parboiled rice. J Sci Food Agric 30:40–46
Min B, McClung A, Chen M (2014) Effects of hydrothermal processes on antioxidants in brown, purple and red bran whole grain rice (Oryza sativa L.). Food Chem 159:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.164
Newton J, Wang Y-J, Mauromoustakos A (2011) Effects of cultivar and processing condition on physicochemical properties and starch fractions in parboiled Rice. Cereal Chem J 88:414–420. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-01-11-0011
Oli P, Ward R, Adhikari B, Torley P (2014a) Parboiled rice: understanding from a materials science approach. J Food Eng 124:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.09.010
Hu Z, Tang X, Liu J, Zhu Z, Shao Y (2017) Effect of parboiling on phytochemical content , antioxidant activity and physicochemical properties of germinated red rice. Food Chem 214:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.07.097
Patil SB, Khan MK (2011) Germinated brown rice as a value added rice product: a review. J Food Sci Technol 48:661–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0232-4
Buggenhout J, Brijs K, Celus I, Delcour JA (2013) The breakage susceptibility of raw and parboiled rice: A review. J Food Eng 117:304–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.03.009
Sittipod S, Shi Y (2016a) Changes of starch during parboiling of rice kernels. J Cereal Sci 69:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2016.03.015
Thammapat P, Meeso N, Siriamornpun S (2016) Effects of the traditional method and an alternative parboiling process on the fatty acids, vitamin E, γ-oryzanol and phenolic acids of glutinous rice. Food Chem 194:230–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.014
Ali N, Pandya AC (1974) Basic concept of parboiling of paddy. J Agric Eng Res 19:111–115
Swasdisevi T, Sriariyakula W, Tia W, Soponronnarit S (2010) Effect of pre-steaming on production of partially-parboiled rice using hot-air fluidization technique. J Food Eng 96:455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2009.08.026
Buggenhout J, Brijs K, Delcour JA (2014a) Soaking conditions during brown rice parboiling impact the level of breakage-susceptible rice kernels. Cereal Chem J 91:554–559. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-03-14-0038-R
de Pascual CSCI, Massaretto IL, Kawassaki F, Barros RMC, Noldin JA, Marquez UML (2013) Effects of parboiling, storage and cooking on the levels of tocopherols, tocotrienols and γ-oryzanol in brown rice (Oryza sativa L.). Food Res Int 50:676–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2011.07.013
Purohit SR, Rao PS (2017a) Optimization of paddy parboiling process for higher starch crystallinity by response surface methodology. Int J Biol Macromol 104:1091–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.06.089
Dutta H, Mahanta CL (2014) Traditional parboiled rice-based products revisited: current status and future research challenges. Rice Sci 21:187–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-6308(13)60191-2
Kwofie EM, Ngadi M (2017a) A review of rice parboiling systems, energy supply, and consumption. Renew Sust Energ Rev 72:465–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.014
Srichamnong W, Thiyajai P, Charoenkiatkul S (2016) Conventional steaming retains tocols and γ-oryzanol better than boiling and frying in the jasmine rice variety Khao dok mali 105. Food Chem 191:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.027
Balbinoti TCV, Jorge LM de M, Jorge RMM (2018b) Mathematical modeling of paddy (oryza sativa) hydration in different thermal conditions assisted by Raman spectroscopy. J Cereal Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2017.11.019
Buggenhout J, Brijs K, Van Oevelen J, Delcour JA (2014b) Milling breakage susceptibility and mechanical properties of parboiled brown rice kernels. LWT - Food Sci Technol 59:369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.05.001
Islam MR, Shimizu N, Kimura T (2001) Quality evaluation of parboiled rice with physical properties. Food Sci Technol Res 7:57–63
Fracasso AF, Perussello CA, Haminiuk CWI, Jorge LMM, Jorge RMM (2014) Hydration kinetics of soybeans: Transgenic and conventional cultivars. J Cereal Sci 60:584–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2014.07.011
Marques BC, de Matos Jorge LM, Jorge RMM (2016) Chemical properties and water absorption kinetics of transgenic corn grain (2B587 Hx) and its conventional isoline (2B587). J Cereal Sci 71:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2016.08.005
Montanuci FD, Perussello CA, de Matos Jorge LM, Jorge RMM (2014) Experimental analysis and finite element simulation of the hydration process of barley grains. J Food Eng 131:44–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2014.01.011
Omoto ES, Marcos C, Andrade G, Maria R, Jorge M, Coutinho MR, Paraíso PR, Mario L, Jorge DM (2009) Mathematical modeling and analysis of pea grains hydration. Ciência e Tecnol Aliment 29:12–18
Borges CWC, Jorge LM de M, Jorge RMM (2017) Kinetic modeling and thermodynamic properties of soybean cultivar (BRS257) during hydration process. J Food Process Eng 40:e12579. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12579
Pramiu PV, Rizzi RL, do Prado NV, Coelho SRM, Bassinello PZ (2015) Numerical modeling of chickpea (Cicer arietinum) hydration: the effects of temperature and low pressure. J Food Eng 165:112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2015.05.020
Oliveira AL, Colnaghi BG, da Silva EZ, Gouvêa IR, Vieira RL, Augusto PED (2013) Modelling the effect of temperature on the hydration kinetic of adzuki beans (Vigna angularis). J Food Eng 118:417–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.04.034
Botelho FM, Corrêa PC, Luis A, Goneli D, Martins MA, Baptestini FM (2010) Water absorption kinetics in parboiled husk rice. Ciência e Tecnol Aliment 30:713–718
Miah MAK, Haque A, Douglass MP, Clarke B (2002a) Parboiling of rice. Part I: effect of hot soaking time on quality of milled rice. Int J Food Sci Technol 37:527–537
Graham-Acquaah S, Manful JT, Ndindeng SA, Tchatcha DA (2015) Effects of soaking and steaming regimes on the quality of artisanal parboiled rice. J Food Process Preserv 39:2286–2296. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12474
Taghinezhad E, Khoshtaghaza MH, Minaei S, Suzuki T, Brenner T (2016a) Relationship between degree of starch gelatinization and quality attributes of parboiled rice during steaming. Rice Sci 23:339–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2016.06.007
Sridhar BS, Manohar B (2003) Hydration kinetics and energy analysis of parboiling indica paddy. Biosyst Eng 85:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1537-5110(03)00039-4
Ramalingam N, Anthoni Raj S (1996) Studies on the soak water characteristics in various paddy parboiling methods. Bioresour Technol 55:259–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(96)00001-6
Hapsari AH, Kim S-J, Eun J-B (2016) Physical characteristics of parboiled Korean glutinous rice (Olbyeossal) using a modified method. LWT - Food Sci Technol 68:499–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.12.066
Bhattacharya KR, Roa PVS (1966) effect of processing conditions on quality of parboiled rice. J Agric Food Chem 14:476–479. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60147a009
Demont M, Zossou E, Rutsaert P, Ndour M, Van Mele P, Verbeke W (2012) Consumer valuation of improved rice parboiling technologies in Benin. Food Qual Prefer 23:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2011.07.005
Taghinezhad E, Brenner T (2017) Mathematical modeling of starch gelatinization and some quality properties of parboiled rice based on parboiling indicators using RSM. J Food Process Eng 40:e12483. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12483
Taghinezhad E, Khoshtaghaza MH, Suzuki T, Minaei S, Brenner T (2016b) Quantifying the relationship between rice starch gelatinization and moisture-electrical conductivity of paddy during soaking. J Food Process Eng 39:442–452. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12235
Dutta H, Mahanta CL (2012) Effect of hydrothermal treatment varying in time and pressure on the properties of parboiled rices with different amylose content. Food Res Int 49:655–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2012.09.014
Lanning SB, Siebenmorgen TJ (2011) Comparison of milling characteristics of hybrid and pureline rice cultivars. Appl Eng Agric 27:787–795. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.39560
Basutkar NN, Siebenmorgen TJ, Wang Y-J, Patindol JA (2015) Functional properties of commingled rice-cultivar lots. Cereal Chem J 92:114–119. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-04-14-0068-R
Islam MR, ROY P, Shimizu N, Kimura T (2002) Effect of processing conditions on physical properties of parboiled rice. Food Sci Technol Res 8:106–112
Hermansson A-M, Svegmark K (1996) Developments in the understanding of starch functionality. Trends Food Sci Technol 7:345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-2244(96)10036-4
Biliaderis CG, Tonogai JR, Perez CM, Juliano BO (1993) Thermophysical properties of milled rice starch as influenced by variety and parboiling method. Cereal Chem 70:512–516
Derycke V, Vandeputte GE, Vermeylen R, De Man W, Goderis B, Koch MHJ, Delcour JA (2005) Starch gelatinization and amylose–lipid interactions during rice parboiling investigated by temperature resolved wide angle X-ray scattering and differential scanning calorimetry. J Cereal Sci 42:334–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2005.05.002
Corre DL, Bras J, Dufresne A (2010) Starch nanoparticles: a review. Biomacromolecules 11:1139–1153. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm901428y
Dutta H, Mahanta CL, Singh V (2015) Changes in the properties of rice varieties with different amylose content on dry heat parboiling. J Cereal Sci 65:227–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2015.07.016
Ong MH, Blanshard JMV (1995) The significance of starch polymorphism in commercially produced parboiled rice. Starch 47:7–13
Lamberts L, Gomand SV, Derycke V, Delcour JA (2009) Presence of amylose crystallites in parboiled rice. J Agric Food Chem 57:3210–3216. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803385m
Miah MAK, Haque A, Douglass MP, Clarke B (2002b) Parboiling of rice. Part II: effect of hot soaking time on the degree of starch gelatinization. Int J Food Sci Technol 37:539–545
Kasai M, Lewis AR, Ayabe S, Hatae K, Fyfe CA (2007) Quantitative NMR imaging study of the cooking of Japonica and Indica rice. Food Res Int 40:1020–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2007.05.010
Sittipod S, Shi Y (2016b) Changes in physicochemical properties of rice starch during steeping in the parboiling process. J Cereal Sci 69:398–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2016.05.010
Kato H, Ohta T, Tsugita T, Hosaka Y (1983) Effect of parboiling on texture and flavor components of cooked rice. J Agric Food Chem 31:818–823
Damir AA (1985) Comparative studies on the physicochemical properties and microstructure of raw and parboiled rice. Food Chem 16:1–14
Chandrasekhar PR, Chattopadhyay PK (1989) Studies on microstructural changes of parboiled and puffed rice materials and methods. J Food Process Preserv 14:27–37
Kar N, Jain RK, Srivastav PP (1999) Parboiling of dehusked rice. J Food Eng 39:17–22
Larsen HN, Rasmussen OW, Rasmussen PH, Alstrup KK, Biswas SK, Tetens I, Thilsted SH, Hermansen K (2000) Glycaemic index of parboiled rice depends on the severity of processing: study in type 2 diabetic subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr 54:380–385. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600969
Elbert G, Tolaba MP, Suárez C (2001b) Effects of drying conditions on head rice yield and browning index of parboiled rice. J Food Eng 47:37–41
Soponronnarit S, Nathakaranakule A, Jirajindalert A, Taechapairoj C (2006) Parboiling brown rice using super heated steam fluidization technique. J Food Eng 75:423–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.04.058
Helbig E, Romano CM, Radünz AL, Rutz D, DIAS ÁRG, ELIAS MC (2007) Efeitos da Amilose e do Processamento na Formação e Estabilidade do Amido Resistente em Arroz. Braz J Food Technol 10:296–301
Lamberts L, Rombouts I, Brijs K, Gebruers K, Delcour JA (2008) Impact of parboiling conditions on Maillard precursors and indicators in long-grain rice cultivars. Food Chem 110:916–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.080
Oli P, Ward R, Adhikari B, Torley P (2014b) The diffusion of moisture in paddy during hydration and dehydration processes. Dry Technol 32:1423–1434. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2014.899249
Ahiduzzaman M, Islam AKMS (2009) Energy utilization and environmental aspects of rice processing industries in Bangladesh. Energies 2:134–149. https://doi.org/10.3390/en20100134
Roy P, Shimizu N, Shiina T, Kimura T (2006) Energy consumption and cost analysis of local parboiling processes. J Food Eng 76:646–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.06.034
Kwofie EM, Ngadi M, Mainoo A (2016) Local rice parboiling and its energy dynamics in Ghana. Energy Sustain Dev 34:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esd.2016.06.007
Kwofie EM, Ngadi M (2016) Sustainable energy supply for local rice parboiling in West Africa: the potential of rice husk. Renew Sust Energ Rev 56:1409–1418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.030
Kwofie EM, Ngadi M, Sotocinal S (2017) Energy efficiency and emission assessment of a continuous rice husk stove for rice parboiling. Energy 122:340–349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2016.12.104
Roy P, Ijiri T, Okadome H, Nei D, Orikasa T, Nakamura N, Shiina T (2008) Effect of processing conditions on overall energy consumption and quality of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Food Eng 89:343–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2008.05.015
Balasubramanian V, Sie M, Hijmans RJ, Otsuka K (2007) Increasing rice production in sub-Saharan Africa: challenges and opportunities. In: Advances in agronomy. pp 55–133
ROY P, SHIMIZU N, KIMURA T (2004) Energy conservation in cooking of milled raw and parboiled rice. Food Sci Technol Res 10:121–126. https://doi.org/10.3136/fstr.10.121
Kwofie EM, Ngadi M (2017b) A comparative lifecycle assessment of rural parboiling system and an integrated steaming and drying system fired with rice husk. J Clean Prod 140:622–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.008
Issah MH, Appiah F, Ninfaa AD (2015) Effect of parboiling on the quality of processed degan rice (Oryza spp). Int J Sci Basic Appl Res 24:153–163
Ndindeng SA, Manful J, Futakuchi K, Mapiemfu-Lamare D, Akoa-Etoa JM, Tang EN, Bigoga J, Graham-Acquaah S, Moreira J (2015) Upgrading the quality of Africa’s rice: a novel artisanal parboiling technology for rice processors in sub-Saharan Africa. Food Sci Nutr 3:557–568. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.242
Igathinathane C, Chattopadhyay PK, Pordesimo LO (2005) Combination soaking procedure for rough rice parboiling. Am Soc Agric Eng 48:665–671
Vellupillai L, Verma LR (1982) Parboiled rice quality as affected by the level and distribution of moisture after the soaking process. Trans ASAE 25:1450–1456
Sarangapani C, Devi Y, Thirundas R, Annapure US, Deshmukh RR (2015) Effect of low-pressure plasma on physico-chemical properties of parboiled rice. LWT - Food Sci Technol 63:452–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.03.026
Han A, Jinn J-R, Mauromoustakos A, Wang Y-J (2016) Effect of parboiling on milling, physicochemical, and textural properties of medium- and long-grain germinated brown rice. Cereal Chem J 93:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1094/CCHEM-01-15-0013-R
Paraginski RT, Ziegler V, Talhamento A, Elias MC, de OM (2014) Propriedades tecnológicas e de cocção em grãos de arroz condicionados em diferentes temperaturas antes da parboilização. Braz J Food Technol 17:146–153
Warning A, Verboven P, Nicolaï B, van Dalen G, Datta AK (2014) Computation of mass transport properties of apple and rice from X-ray microtomography images. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 24:14–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2013.12.017
Das I, Das SK, Bal S (2004) Specific energy and quality aspects of infrared (IR) dried parboiled rice. J Food Eng 62:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0260-8774(03)00164-X
Courtois F, Faessel M, Bonazzi C (2010) Assessing breakage and cracks of parboiled rice kernels by image analysis techniques. Food Control 21:567–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2009.08.006
Dors GC, da Bierhals VS, Badiale-Furlong E (2011) Parboiled rice: chemical composition and the occurrence of mycotoxins. Ciência e Tecnol Aliment 31:172–177
De Assis LM, da Zavareze ER, Radünz AL, Dias ÁRG, Gutkoski LC, Elias MC (2009) Propriedades nutricionais, tecnológicas e sensoriais de biscoitos com substituição de farinha de trigo por farinha de aveia ou farinha de arroz parboilizado. Alim Nutr 20:15–24
Islam M, Shimizu N, Kimura T (2004) Energy requirement in parboiling and its relationship to some important quality indicators. J Food Eng 63:433–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2003.09.002
Bello M, Baeza R, Tolaba MP (2006) Quality characteristics of milled and cooked rice affected by hydrothermal treatment. J Food Eng 72:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2004.11.026
Patindol J, Newton J, Wang Y-J (2008) Functional properties as affected by laboratory-scale parboiling of rough rice and brown rice. J Food Sci 73:E370–E377. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2008.00926.x
Kam K, Murray JM, Arcot J, Ward R (2012c) Fortification of parboiled rice with folic acid: Consumer acceptance and sensory evaluation. Food Res Int 49:354–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2012.07.064
Oli P, Ward R, Adhikari B, Torley P (2016b) Colour change in rice during hydration: effect of hull and bran layers. J Food Eng 173:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2015.10.036
Parnsakhorn S, Noomhorm A (2008) Changes in physicochemical properties of parboiled brown rice during heat treatment. Agric Eng Int X:1–20
Mir SA, Bosco SJD (2013) Effect of soaking temperature on physical and functional properties of parboiled rice cultivars grown in temperate region of India. Food Nutr Sci 4:282–288. https://doi.org/10.4236/fns.2013.43038
Lamberts L, De Bie E, Derycke V, Veraverbeke WS, De Man W, Delcour JA (2006a) Effect of processing conditions on color change of brown and milled parboiled rice. Cereal Chem J 83:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1094/CC-83-0080
Lamberts L, Brijs K, Mohamed R, Verhelst N, Delcour JA (2006b) Impact of browning reactions and bran pigments on color of parboiled rice. J Agric Food Chem 54:9924–9929. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf062140j
Sareepuang K, Siriamornpun S, Wiset L, Meeso N (2008) Effect of soaking temperature on physical, chemical and cooking properties of parboiled fragrant rice. World J Agric Sci 4:409–415
Thiyajai P, Saetang P, Kettawan A, Charoenkiatkul S, Srichamnong W (2016) Promising industrial fl our processing and household applications of parboiled germinated brown rice ( Khao dok mali 105 ). LWT - Food Sci Technol 73:406–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.06.044
Casiraghi MC, Brighenti F, Pellegrini N, Leopardi E, Testolin G (1993) Effect of processing on rice starch digestibility evaluated by in vivo and in vitro methods. J Cereal Sci 17:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcrs.1993.1015
Wolever TMS, Jenkins DJA, Kalmusky J, Jenkins A, Giordano C, Giudici S, Josse RG, Wong GS (1986) Comparison of regular and parboiled rices: explanation of discrepancies between reported glycemic responses to rice. Nutr RESEARC 6:349–357
Sujatha SJ, Ahmad R, Rama Bhat P (2004) Physicochemical properties and cooking qualities of two varieties of raw and parboiled rice cultivated in the coastal region of Dakshina Kannada, India. Food Chem 86:211–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.08.018
Dors GC, Pinto RH, Badiale-furlong E (2009) Influence of the conditions of the parboiling process in the chemical composition of rice. Ciência e Tecnol Aliment 29:219–224
Storck CR, da Silva LP, Fagundes CAA (2005) Categorizing rice cultivars based on differences in chemical composition. J Food Compos Anal 18:333–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2004.09.005
Denardin CC, da Silva LP, Storck CR, Nörnberg JL (2004) Composição mineral de cultivares de arroz ntegral, parboilizado e branco. Alim Nutr 15:125–130
Lamberts L, Delcour JA (2008) Carotenoids in raw and parboiled brown and milled rice. J Agric Food Chem 56:11914–11919. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf802613c
Scaglioni PT, de Souza TD, Schmidt CG, Badiale-Furlong E (2014) Availability of free and bound phenolic compounds in rice after hydrothermal treatment. J Cereal Sci 60:526–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2014.08.005
Santa María C, Revilla E, Rodríguez-Morgado B, Castaño A, Carbonero P, Gordillo B, Cert R, Parrado J (2016) Effect of rice parboiling on the functional properties of an enzymatic extract from rice bran. J Cereal Sci 72:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2016.09.010
Wunjuntuk K, Kettawan A, Rungruang T, Charoenkiatkul S (2016) Anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects of parboiled germinated brown rice ( Oryza sativa “KDML 105”) in rats with induced liver fibrosis. J Funct Foods 26:363–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2016.08.009
Helbig E, Dias ÁRG, Tavares RA, Schirmer MA, Elias MC (2008) Arroz parboilizado efeito na glicemia de ratos Wistar. Organo Of la Soc Latinoam Nutr 58:149–155
Lu L, Venn B, Lu J, Monro J, Rush E (2017) Effect of cold storage and reheating of parboiled rice on postprandial glycaemic response, satiety, palatability and chewed particle size distribution. Nutrients 9:475. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9050475
Chang UJ, Hong YH, Suh HJ, Jung EY (2010) Lowering the energy density of parboiled rice by adding water-rich vegetables can decrease total energy intake in a parboiled rice-based diet without reducing satiety on healthy women. Appetite 55:338–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2010.07.007
Gul K, Yousuf B, Singh AK, Singh P, Wani AA (2015) Rice bran: nutritional values and its emerging potential for development of functional food—a review. Bioact Carbohydrates Diet Fibre 6:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcdf.2015.06.002
Tomlins KI, Manful JT, Larwer P, Hammond L (2005) Urban consumer preferences and sensory evaluation of locally produced and imported rice in West Africa. Food Qual Prefer 16:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodqual.2004.02.002
Heinemann RJB, Behrens JH, Lanfer-Marquez UM (2006) A study on the acceptability and consumer attitude towards parboiled rice. Int J Food Sci Technol 41:627–634. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2005.01118.x
Behrens JH, Heinemann RJ, Lanfer-Marquez UM (2007) Parboiled rice: a study about attitude, consumer liking and consumption in São Paulo, Brazil. J Sci Food Agric 87:992–999. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2794
de Pinheiro ACA, Lisboa MT, Ribeiro AS, Nunes AM, Yamasaki A (2014) AVALIAÇÃO DA MINERALIZAÇÃO DE ARROZ EM SISTEMA DE REFLUXO PARA A DETERMINAÇÃO DE Cu, Fe, Mn E Zn POR FAAS. Quim Nov 37:6–9
Oli P, Ward R, Adhikari B, Mawson AJ, Adhikari R, Wess T, Pallas L, Spiers K, Paterson D, Torley P (2016a) Synchrotron X-ray fluorescence microscopy study of the diffusion of iron, manganese, potassium and zinc in parboiled rice kernels. LWT - Food Sci Technol 71:138–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.03.034
Prom-u-thai C, Fukai S, Godwin ID, Rerkasem B, Huang L (2008) Iron-fortified parboiled rice—a novel solution to high iron density in rice-based diets. Food Chem 110:390–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.043
Prom-u-thai C, Rerkasem B, Cakmak I, Huang L (2010a) Zinc fortification of whole rice grain through parboiling process. Food Chem 120:858–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.11.027
Kam K, Arcot J, Ward R (2012b) Fortification of rice with folic acid using parboiling technique: Effect of parboiling conditions on nutrient uptake and physical characteristics of milled rice. J Cereal Sci 56:587–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcs.2012.08.010
Tulyathan V, Laokuldilok T, Jongkaewwattana S (2007) Retention of iodine in fortified parboiled rice and its pasting characteristics during storage. J Food Biochem 31:217–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4514.2007.00109.x
Kam K, Arcot J, Adesina AA (2012a) Folic acid fortification of parboiled rice: multifactorial analysis and kinetic investigation. J Food Eng 108:238–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.07.032
Prom-u-thai C, Glahn RP, Cheng Z, Fukai S, Rerkasem B, Huang L (2009) The bioavailability of iron fortified in whole grain parboiled rice. Food Chem 112:982–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.07.020
Prom-u-thai C, Rerkasem B, Fukai S, Huang L (2010b) Key factors affecting Fe density in Fe-fortified-parboiled rice: parboiling conditions, storage duration, external Fe-loading rate and genotypic differences. Food Chem 123:628–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.04.081
Hotz C, Kabir KA, Dipti SS, Arsenault JE, Bipul M (2015a) Rice fortification with zinc during parboiling may improve the adequacy of zinc intakes in Bangladesh. J Sci Food Agric 95:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.6730
Hotz C, Kabir K, Dipti S, Arsenault J, Bipul M (2015b) Addition of zinc to soaking water during parboiling increases the zinc content of Bangladeshi rice. Eur J Nutr Food Saf 5:475–476. https://doi.org/10.9734/EJNFS/2015/20919
Nunes IL, Magagnin G, Bertolin TE, Furlong EB (2003) Arroz comercializado na região sul do Brasil: aspectos micotoxicológicos e microscópicos. Ciência e Tecnol Aliment 23:190–194. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612003000200015
Coelho CSP, Furlong EB, Almeida TL (1999) Migração de Micotoxinas Durante a Parboilização do Arroz. Braz. J Food Technol 2:39–44
de Guimarães ÍCO, Souza ARM, de Cornélio VMO, Pereira J, Villela VA (2010) Identificação de Aspergillus spp. toxigênico em arroz. Ciência e Tecnol Aliment 30:60–62
Heidtmann-Bemvenuti R, dos Hackbart HCS, de Souza MM, Badiale-Furlong E, Dors GC, Fagundes CA (2012) Determinação de deoxinivalenol e zearalenona em arroz natural e parboilizado e suas frações utilizando QuEChERS e HPLC/UV-FL. Quim Nov 35:1244–1249
Purohit SR, Rao PS (2017b) Water absorption and gelatinization kinetics of non-issuable rice and its characterization. J Food Meas Charact 11:2110–2118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9595-1
Sivasinthujah P, Srikaran R, Thavaranjit AC, Velauthamurty K, Tharmila CJ (2014) Contents of nitrate, nitrite and the occurrence of bacteria in fermented cooked parboiled rice and their potential ingestion in the diet. J Microbiol Biotechnol Res 4:56–61
Bakalis S, Kyritsi A, Karathanos VT, Yanniotis S (2009) Modeling of rice hydration using finite elements. J Food Eng 94:321–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2009.03.023
Thakur AK, Gupta AK (2006) Water absorption characteristics of paddy, brown rice and husk during soaking. J Food Eng 75:252–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.04.014
Bello MO, Tolaba MP, Suarez C (2007) Water absorption and starch gelatinization in whole rice grain during soaking. LWT - Food Sci Technol 40:313–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2005.09.017
Bello M, Tolaba MP, Aguerre RJ, Suarez C (2010) Modeling water uptake in a cereal grain during soaking. J Food Eng 97:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2009.09.020
Perez JH, Tanaka F, Uchino T (2012) Modeling of mass transfer and initiation of hygroscopically induced cracks in rice grains in a thermally controlled soaking condition: with dependency of diffusion coefficient to moisture content and temperature—a 3D finite element approach. J Food Eng 111:519–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.02.029
Igathinathane C, Chattopadhyay PK, Pordesimo LO (2008) Moisture diffusion modeling of parboiled paddy accelerated tempering process with extended application to multi-pass drying simulation. J Food Eng 88:239–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2008.02.014
Rao PS, Bal S, Goswami TK (2007) Modelling and optimization of drying variables in thin layer drying of parboiled paddy. J Food Eng 78:480–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.10.019
Shittu TA, Olaniyi MB, Oyekanmi AA, Okeleye KA (2012) Physical and water absorption characteristics of some improved rice varieties. Food Bioprocess Technol 5:298–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-009-0288-6
Nicolin DJ, Marques BC, Balbinoti TCV, Jorge RMM, Jorge LM de M (2017) Modeling rice and corn hydration kinetic by Nicolin-Jorge model. J Food Process Eng 40:e12588. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12588
Becker HA (1960) On the absorption of liquid water by the wheat kernel. Cereal Chem 37:309–323
Crank J (1975) The mathematics of diffusion, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Bristol
Crank J (1984) Free and moving boundary problems, 1st edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Danbaba N, Nkama I, Ukwungwu MN, Maji AT, Abo ME, Hauwawu H, Fati KI, Oko AO (2014) Optimization of rice parboiling process for optimum head rice yield: a response surface methodology (RSM) approach. Int J Agric For 4:154–165. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.ijaf.20140403.02
Elbert G, Tolaba MP, Suárez C (2001a) Model application: hydration and gelatinization during rice parboiling. Dry Technol 19:571–581
Bakshi AS, Singh RP (1980) Kinetics of water diffusion and starch gelatinization during rice parboilings. J Food Sci 45:1387–1392
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the support provided by the Federal University of Paraná, Araucaria Foundation, CAPES and CNPq (The National Council for Scientific and Technological Development).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balbinoti, T.C.V., Nicolin, D.J., de Matos Jorge, L.M. et al. Parboiled Rice and Parboiling Process. Food Eng Rev 10, 165–185 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-018-9177-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12393-018-9177-y