Abstract
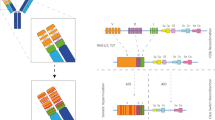
Despite the significant advances of antibodies as therapeutic agents, there is still much room for improvement concerning the discovery of these macromolecules. Here, we present a new synthetic cell-based strategy that takes advantage of eukaryotic cell biology to produce highly diverse antibody libraries and, simultaneously, link them to a high-throughput selection mechanism, replicating B cell diversification mechanisms. The interference of site-specific recognition by CRISPR/Cas9 with error-prone DNA repair mechanisms was explored for the generation of diversity, in a cell population containing a gene for a light chain antibody fragment. We achieved up to 93% of cells containing a mutated antibody gene after diversification mechanisms, specifically inside one of the antigen-binding sites. This targeted variability strategy was then integrated into an intracellular selection mechanism. By fusing the antibody with a KDEL retention signal, the interaction of antibodies and native membrane antigens occurs inside the endoplasmic reticulum during the process of protein secretion, enabling the detection of high-quality leads for expression and affinity by flow cytometry. We successfully obtained antibody lead candidates against CD3 as proof of concept. In summary, we developed a novel antibody discovery platform against native antigens by endoplasmic synthetic library generation using CRISPR/Cas9, which will contribute to a faster discovery of new biotherapeutic molecules, reducing the time-to-market.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amendola M, Venneri MA, Biffi A, Vigna E, Naldini L (2005) Coordinate dual-gene transgenesis by lentiviral vectors carrying synthetic bidirectional promoters. Nat Biotechnol 23:108–116
Baeuerle PA, Kufer P, Bargou R (2009) BiTE: teaching antibodies to engage T-cells for cancer therapy. Curr Opin Mol Ther 11:22–30
Bai X, Chen JD, Yang AG, Torti F, Chen SY (1998) Genetic co-inactivation of macrophage- and T-tropic HIV-1 chemokine coreceptors CCR-5 and CXCR-4 by intrakines. Gene Ther 5:984–994
Barbas CF, Kang AS, Lerner RA, Benkovic SJ (1991) Assembly of combinatorial antibody libraries on phage surfaces: the gene III site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:7978–7982
Batey MA, Zhao Y, Kyle S, Richardson C, Slade A, Martin NMB (2013) Preclinical evaluation of a novel ATM inhibitor, KU59403, in vitro and in vivo in p53 functional and dysfunctional models of human cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 12:959–967
Beerli RR, Bauer M, Buser RB, Gwerder M, Muntwiler S, Maurer P, Saudan P, Bachmann MF (2008) Isolation of human monoclonal antibodies by mammalian cell display. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:14336–14341
Berdougo E, Mattia K, Doranz BJ (2013) Isolating membrane protein antibodies. Genet Eng Biotechnol News 33
Bétermier M, Bertrand P, Lopez BS (2014) Is non-homologous end-joining really an inherently error-prone process? PLoS Genet 10:e1004086
Boder ET, Raeeszadeh-Sarmazdeh M, Price JV (2012) Engineering antibodies by yeast display. Arch Biochem Biophys 526:99–106
Böldicke T (2007) Blocking translocation of cell surface molecules from the ER to the cell surface by intracellular antibodies targeted to the ER. J Cell Mol Med 11:54–70
Briney BS, Willis JR, Crowe JE (2013) Location and length distribution of somatic hypermutation-associated DNA insertions and deletions reveals regions of antibody structural plasticity. Genes Immun 13:523–529
Cadwell RC, Joyce GF (1994) Mutagenic PCR. PCR Methods Appl 3:S136–S140
Capitani M, Sallese M (2009) The KDEL receptor: new functions for an old protein. FEBS Lett 583:3863–3871
Chan CEZ, Lim APC, MacAry PA, Hanson BJ (2014) The role of phage display in therapeutic antibody discovery. Int Immunol 26:649–657
Chandhasin C, Ducu RI, Berkovich E, Kastan MB, Marriott SJ (2008) Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax attenuates the ATM-mediated cellular DNA damage response. J Virol 82:6952–6961
Chen JD, Bai X, Yang AG, Cong Y, Chen SY (1997) Inactivation of HIV-1 chemokine co-receptor CXCR-4 by a novel intrakine strategy. Nat Med 3:1110–1116
Chun HH, Gatti RA (2004) Ataxia-telangiectasia, an evolving phenotype. DNA Repair 3:1187–1196
Coia G, Hudson PJ, Irving RA (2001) Protein affinity maturation in vivo using E. coli mutator cells. J Immunol Methods 251:187–193
Coleman JE, Huentelman MJ, Kasparov S, Metcalfe BL, Paton JFR, Katovich MJ, Semple-Rowland SL, Raizada MK (2003) Efficient large-scale production and concentration of HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors for use in vivo. Physiol Genomics 12:221–228
Coloma MJ, Hastings A, Wims LA, Morrison SL (1992) Novel vectors for the expression of antibody molecules using variable regions generated by polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol Methods 152:89–104
Devilder MC, Moyon M, Gautreau-Rolland L, Navet B, Perroteau J, Delbos F, Gesnel MC, Breathnach R, Saulquin X (2019) Ex vivo evolution of human antibodies by CRISPR-X: from a naïve B cell repertoire to affinity matured antibodies. BMC Biotechnol 19:14
Gaj T, Sirk SJ, Shui S, Liu J (2016) Genome-editing technologies: principles and applications. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 8:a023754
Gonçalves J, Aires-da-Silva F, Côrte-Real S, Oliveira SS (2013) Cell-based methods for coupling protein interactions and binding molecule selection and diversification WO2014133405
Goodman MF, Scharff MD, Romesberg FE (2007) AID-initiated purposeful mutations in immunoglobulin genes. Adv Immunol 94:127–155
Gray SA, Weigel KM, Miller KD, Ndung’U J, Büscher P, Tran T, Baird C, Cangelosi GA (2010) Flow cytometry-based methods for assessing soluble scFv activities and detecting antigens in solution. Biotechnol Bioeng 105:973–981
Helmink BA, Sleckman BP (2012) The response to and repair of RAG-mediated DNA double stranded breaks. Annu Rev Immunol 30:175–202
Ho M, Pastan I (2009) Mammalian cell display for antibody engineering. Methods Mol Biol 525:337–352
Hsu PD, Scott DA, Weinstein JA, Ran A, Konermann S, Agarwala V, Li Y, Fine EJ, Wu X, Shalem O, Cradick TJ, Marraffini LA, Bao G, Zhang F (2013) DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 31:827–832
Jiang W, Bikard D, Cox D, Zhang F, Marraffini LA (2013) RNA-guided editing of bacterial genomes using CRISPR-Cas systems. Nat Biotechnol 31:233–239
Jinek M, Chylinski C, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337:816–822
Jo M, Jung ST (2016) Engineering therapeutic antibodies targeting G-protein-coupled receptors. Exp Mol Med 48:e207
Jones ML, Alfaleh MA, Kumble S, Zhang S, Osborne GW, Yeh M, Arora N, Hou JJ, Howard CB, Chin DY, Mahler SM (2016) Targeting membrane proteins for antibody discovery using phage display. Sci Rep 6:26240
Jóźwik A, Soroczyńska M, Witkowski JM, Bryl E (2004) CD3 receptor modulation in Jurkat leukemic cell line. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 42:41–43
Jung D, Giallourakis C, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW (2006) Mechanism and control of V(D)J recombination at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. Annu Rev Immunol 24:541–570
Kim H, Kim JS (2014) A guide to genome engineering with programmable nucleases. Nat Rev Genet 15:321–334
Kitamura T, Onishi M, Kinoshita S, Shibuya A, Miyajima A, Nolan GP (1995) Efficient screening of retroviral cDNA expression libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:9146–9150
Köhler G, Milstein C (1975) Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 256:495–497
Kuhn C, Weiner HL (2016) Therapeutic anti-CD3 monoclonal antibodies: from bench to bedside. Immunotherapy 8:889–906
Liu LD, Huang M, Dai P, Liu T, Fan S, Cheng X, Zhao Y, Yeap LS, Meng FL (2018) Intrinsic nucleotide preference of diversifying base editors guides antibody ex vivo affinity maturation. Cell Rep 25:884–892
Lluis MW, Godfroy JI, Yin H (2013) Protein engineering methods applied to membrane protein targets. Protein Eng Des Sel 26:91–100
Loc’h J, Rosario S, Delarue M (2016) Structural basis for a new templated activity by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase: implications for V(D)J recombination. Structure 24:1452–1463
Lois C, Hong EJ, Pease S, Brown EJ, Baltimore D (2002) Germline transmission and tissue-specific expression of transgenes delivered by lentiviral vectors. Science 295:868–872
Ma N, Pang H, Shen W, Zhang F, Cui Z, Wang J, Wang J, Liu L, Zhang H (2014) Downregulation of CXCR4 by SDF-KDEL in SBC-5 cells inhibits their migration in vitro and organ metastasis in vivo. Int J Mol Med 35:425–432
Majoul I, Straub M, Hell SW, Duden R, Söling HD (2001) KDEL-cargo regulates interactions between proteins involved in COPI vesicle traffic: measurements in living cells using FRET. Dev Cell 1:139–153
Malu S, Malshetty V, Francis D, Cortes P (2012) Role of non-homologous end joining in V(D)J recombination. Immunol Res 54:233–246
Marriott SJ, Semmes OJ (2005) Impact of HTLV-I Tax on cell cycle progression and the cellular DNA damage repair response. Oncogene 24:5986–5995
Marschall AL, Dübel S, Böldicke T (2015) Specific in vivo knockdown of protein function by intrabodies. MAbs 7:1010–1035
Mason DM, Weber CR, Parola C, Meng SM, Greiff V, Kelton WJ, Reddy ST (2018) High-throughput antibody engineering in mammalian cells by CRISPR/Cas9-mediated homology-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res 46:7436–7449
Matuck JG, Fann JC, Schulz C, Roy NA, Bruton DF, Mcintire J, Valley C, Chang YD, Seewoester T (2016) Methods of producing adalimumab US928437161
McCafferty J, Griffiths AD, Winter G, Chiswell DJ (1990) Phage antibodies: filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nature 348:552–554
Miyake H, Suzuki T, Hirai H, Yoshida M (1999) Trans-activator Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 enhances mutation frequency of the cellular genome. Virology 253:155–161
Motea EA, Berdis AJ (2010) Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase: the story of a misguided DNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1804:1151–1166
Munro S, Pelham HRB (1987) A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell 48:899–907
Nagorsen D, Bargou R, Rüttinger D, Kufer P, Baeuerle PA, Zugmaier G (2009) Immunotherapy of lymphoma and leukemia with T-cell engaging BiTE antibody blinatumomab. Leuk Lymphoma 50:886–891
O’Geen H, Yu AS, Segal DJ (2015) How specific is CRISPR/Cas9 really? Curr Opin Chem Biol 29:72–78
Reaper PM, Griffiths MR, Long JM, Charrier JD, MacCormick S, Charlton PA, Golec JMC, Pollard JR (2011) Selective killing of ATM- or p53-deficient cancer cells through inhibition of ATR. Nat Chem Biol 7:428–430
Repasky JAE, Corbett E, Boboila C, Schatz DG (2004) Mutational analysis of terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated N-nucleotide addition in V(D)J recombination. J Immunol 172:5478–5488
Rodgers K, Mcvey M (2016) Error-prone repair of DNA double-strand breaks. J Cell Physiol 231:15–24
Schmid-Burgk JL (2017) Disruptive non-disruptive applications of CRISPR/Cas9. Curr Opin Biotechnol 48:203–209
Shalem O, Sanjana NE, Hartenian E, Shi X, Scott DA, Heckl D, Ebert BL, Root DE, Doench JG (2014) Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in human cells. Science 343:84–87
Smith SA, Crowe JE (2015) Use of human hybridoma technology to isolate human monoclonal antibodies. Microbiol Spectr 3:AID-0027-2014
Stornaiuolo M, Lotti LV, Borgese N, Torrisi MR, Mottola G, Martire G, Bonatti S (2003) KDEL and KKXX retrieval signals appended to the same reporter protein determine different trafficking between endoplasmic reticulum, intermediate compartment, and golgi complex. Mol Biol Cell 14:889–902
Tate CG (2001) Overexpression of mammalian integral membrane proteins for structural studies. FEBS Lett 504:94–98
Thie H, Voedisch B, Dübel S, Hust M, Schirrmann T (2009) Affinity maturation by phage display. Methods Mol Biol 525:309–322
Van Anken E, Braakman I (2005) Versatility of the endoplasmic reticulum protein folding factory. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 40:191–228
Waldmeier L, Hellmann I, Gutknecht CK, Wolter FI, Cook SC, Reddy ST, Grawunder U, Beerli RR (2016) Transpo-mAb display: transposition-mediated B cell display and functional screening of full lenght IgG antibody libraries. Mabs 8:726–740
Wang T, Birsoy K, Hughes NW, Krupczak M, Post Y, Wei JJ, Lander ES, Sabatini DM (2015) Identification and characterization of essential genes in the human genome. Science 350:1096–1101
Xiao X, Douthwaite JA, Chen Y, Kemp B, Kidd S, Percival-Alwyn J, Smith A, Goode K, Swerdlow B, Lowe D, Wu H, Dall’Acqua WF, Chowdhury PS (2017) A high-throughput platform for population reformatting and mammalian expression of phage display libraries to enable functional screening as full-length IgG. Mabs 9:996–1006
Yamtich J, Sweasy JB (2010) DNA polymerase family X: function, structure, and cellular roles. Biochim Biophys Acta 1804:1136–1150
Zhou C, Jacobsen FW, Cai L, Chen Q, Shen WD (2010) Development of a novel mammalian cell surface antibody display platform. MAbs 2:508–518
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Portuguese Funding Agency, Fundacão para a Ciência e a Tecnologia, FCT IP, for financial support: PTDC/QEQ-MED/4412/2014 to J.G, IF/01010/2013 to FAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This study was supported by TechnoPhage SA. The authors would like to disclose that TechnoPhage SA have a pending patent application related to the development of CellectAb (patent number 9487773). JM, SO, JO, and SCR at the time of the work were employees of TechnoPhage SA and therefore have a theoretical conflict of interest through being employed by the organization that both funded the work and has potential commercial interest in the findings. JG, FAS, and MC have no financial interests in TechnoPhage.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 424 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ministro, J.H., Oliveira, S.S., Oliveira, J.G. et al. Synthetic antibody discovery against native antigens by CRISPR/Cas9-library generation and endoplasmic reticulum screening. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 2501–2512 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10423-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10423-3