Abstract
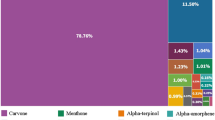
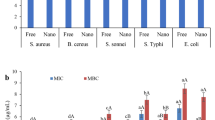
Thyme oil in water nanomulsion was prepared under subcritical water conditions using water and saponin, as solvent and emulsifier, respectively. Gas chromatography revealed that there were 44 bioactive components in the extracted thyme essential oil which, thymol and carvacrol were two mains of them. Experiments were designed based on central composite design and effects of amounts of saponin and thyme essential oil were evaluated on particle size, polydispersity index (PDI) and zeta potential of the prepared nanoemulsions using response surface methodology. Obtained results revealed that more desirable thyme oil nanoemulsions with minimum particle size (184.51 nm) and PDI (0.514), and maximum zeta potential (− 22.51 mV) were prepared using 0.94 g of saponin and 0.28 mL of thyme essential oil. Furthermore, results indicated that prepared nanoemulsion using obtained optimum production conditions had relatively high antioxidant activity (24%) and high antibacterial and antifungal activities against Staphylococcus aureus and Penicillium digitatum.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi O, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H, Jodeiri N. Eco-friendly microwave-enhanced green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Aloe vera leaf extract and their physico-chemical and antibacterial studies. Green Process. Synth. 7: 231-240 (2018)
Ahmadi O, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H, Jodeiri N. Optimization of processing parameters for hydrothermal silver nanoparticles synthesis using Aloe vera leaf extract and estimation of their physico-chemical and antifungal properties. Z. Phys. Chem. 233: 651-667 (2019)
Anarjan N, Fahimdanesh M, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H. β-Carotene nanodispersions synthesis by three-component stabilizer system using mixture design. J. Food Sci. Technol. 54: 3731-3736 (2017)
Anarjan N, Jaberi N, Yeganeh-Zare S, Banafshehchin E, Rahimirad A, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H. Optimization of mixing parameters for α-tocopherol nanodispersions prepared using solvent displacement method. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 91: 1397-1405 (2014a)
Anarjan N, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H, Ling TC, Tan CP. Effects of pH, ions, and thermal treatments on physical stability of astaxanthin nanodispersions. Int. J. Food Prop. 17: 937-947 (2014b)
Anarjan N, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H, Nehdi IA, Sbihi HM, Al-Resayes SI, Tan CP. Effects of homogenization process parameters on physicochemical properties of astaxanthin nanodispersions prepared using a solvent-diffusion technique. Int. J. Nanomed. 10: 1109-1118 (2015)
Bai L, Huan S, Gu J, McClements DJ. Fabrication of oil-in-water nanoemulsions by dual-channel microfluidization using natural emulsifiers: Saponins, phospholipids, proteins, and polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 61: 703-711 (2016)
Chang Y, McLandsborough L, McClements DJ. Physical properties and antimicrobial efficacy of thyme oil nanoemulsions: Influence of ripening inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 60: 12056-12063 (2012)
Chang Y, McLandsborough L, McClements DJ. Fabrication, stability and efficacy of dual-component antimicrobial nanoemulsions: Essential oil (thyme oil) and cationic surfactant (lauric arginate). Food Chem. 172: 298-304 (2015)
Chen Z, Shu G, Taarji N, Barrow CJ, Nakajima M, Khalid N, Neves MA. Gypenosides as natural emulsifiers for oil-in-water nanoemulsions loaded with astaxanthin: Insights of formulation, stability and release properties. Food Chem. 261: 322-328 (2018)
Chung C, Sher A, Rousset P, Decker EA, McClements DJ. Formulation of food emulsions using natural emulsifiers: Utilization of quillaja saponin and soy lecithin to fabricate liquid coffee whiteners. J. Food Eng. 209: 1-11 (2017a)
Chung C, Sher A, Rousset P, McClements DJ. Influence of homogenization on physical properties of model coffee creamers stabilized by quillaja saponin. Food Res. Int. 99: 770-777 (2017b)
Chung C, Sher A, Rousset P, McClements DJ. Use of natural emulsifiers in model coffee creamers: Physical properties of quillaja saponin-stabilized emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 67: 111-119 (2017c)
Gupta A, Eral HB, Hatton TA, Doyle PS. Nanoemulsions: Formation, properties and applications. Soft Matter. 12: 2826-2841 (2016)
Kaur K, Kumar R, Mehta SK. Formulation of saponin stabilized nanoemulsion by ultrasonic method and its role to protect the degradation of quercitin from UV light. Ultrason. Sonochem. 31: 29-38 (2016)
Krstonošić V, Dokić L, Nikolić I, Milanović M. Influence of xanthan gum on oil-in-water emulsion characteristics stabilized by OSA starch. Food Hydrocoll. 45: 9-17 (2015)
McClements DJ. Edible nanoemulsions: Fabrication, properties, and functional performance. Soft Matter. 7: 2297-2316 (2011)
McClements DJ, Rao J. Food-grade nanoemulsions: Formulation, fabrication, properties, performance, biological fate, and potential toxicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 51: 285-330 (2011)
Mohammadlou M, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H, Maghsoudi H. Hydrothermal green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Pelargonium/Geranium leaf extract and evaluation of their antifungal activity. Green Process. Synth. 6: 31-42 (2017)
Ozturk B, Argin S, Ozilgen M, McClements DJ. Formation and stabilization of nanoemulsion-based vitamin E delivery systems using natural surfactants: Quillaja saponin and lecithin. J. Food Eng.142: 57-63 (2014)
Pavela R, Žabka M, Vrchotová N, Tříska J. Effect of foliar nutrition on the essential oil yield of Thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.). Ind. Crop. Prod. 112: 762-765 (2018)
Ryu V, McClements DJ, Corradini MG, McLandsborough L. Effect of ripening inhibitor type on formation, stability, and antimicrobial activity of thyme oil nanoemulsion. Food Chem. 245: 104-111 (2018)
Ryu V, McClements DJ, Corradini MG, Yang JS, McLandsborough L. Natural antimicrobial delivery systems: Formulation, antimicrobial activity, and mechanism of action of quillaja saponin-stabilized carvacrol nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 82: 442-450 (2018)
Sayyar Z, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H. Temperature effects on thermodynamic parameters and solubility of curcumin O/W nanodispersions using different thermodynamic models. Int. J. Food Eng. 15(1-2): 1-14 (2019a)
Sayyar Z, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H. Preparation, Characterization and evaluation of curcumin nanodispersions using three different methods: Novel subcritical water conditions, spontaneous emulsification and solvent displacement. Z. Phys. Chem. 233: 1485-1502 (2019b)
Sayyar Z, Jafarizadeh-Malmiri H. Photocatalytic and antibacterial activities study of prepared self-cleaning nanostructure surfaces using synthesized and coated ZnO nanoparticles with Curcumin nanodispersion. Z. Kristallogr. Cryst. Mater. 234: 307-328 (2019c)
Shu G, Khalid N, Chen Z, Neves MA, Barrow CJ, Nakajima M. Formulation and characterization of astaxanthin-enriched nanoemulsions stabilized using ginseng saponins as natural emulsifiers. Food Chem. 255: 67-74 (2018)
Taarji N, Rabelo da Silva CA, Khalid N, Gadhi C, Hafidi A, Kobayashi I, Neves MA, Isoda H, Nakajima M. Formulation and stabilization of oil-in-water nanoemulsions using a saponins-rich extract from argan oil press-cake. Food Chem. 246: 457-463 (2018)
Tan Y, Deng X, Liu T, Yang B, Zhao M, Zhao Q. Influence of NaCl on the oil/water interfacial and emulsifying properties of walnut protein-xanthan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 72: 73-80 (2017)
Uluata S, McClements DJ, Decker EA. Physical stability, autoxidation, and photosensitized oxidation of ω-3 oils in nanoemulsions prepared with natural and synthetic surfactants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 63: 9333-9340 (2015)
Yang Y, Leser ME, Sher AA, McClements DJ. Formation and stability of emulsions using a natural small molecule surfactant: Quillaja saponin (Q-Naturale®). Food Hydrocoll. 30: 589-596 (2013)
Zhang J, Bing L, Reineccius GA. Comparison of modified starch and Quillaja saponins in the formation and stabilization of flavor nanoemulsions. Food Chem. 192: 53-59 (2015a)
Zhang J, Bing L, Reineccius GA. Formation, optical property and stability of orange oil nanoemulsions stabilized by Quallija saponins. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 64: 1063-1070 (2015b)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Sahand University of Technology for funding the development of an innovative methodology for safety assessment of industrial nanomaterials (Grant No. 30.5592).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadi, O., Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Green approach in food nanotechnology based on subcritical water: effects of thyme oil and saponin on characteristics of the prepared oil in water nanoemulsions. Food Sci Biotechnol 29, 783–792 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00727-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-019-00727-0