Abstract
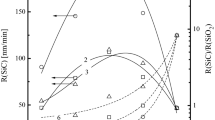
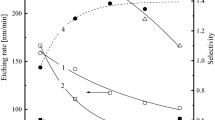
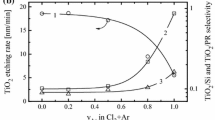
The investigation of etching kinetics and surface conditions for KNbxOy thin films in CF4 + Ar and Cl2 + Ar inductively coupled plasmas was carried out. The variable processing parameters were Ar content in a feed gas (0–75% Ar), gas pressure (4–10 mTorr) and input power (400–700 W) at constant bias power of 100 W. The combination of plasma diagnostics by Langmuir probes and plasma modeling provided the data on internal plasma parameters, gas-phase chemistry and steady-state densities of plasma active species. The compositional changes of the etched surfaces were investigated using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). It was found that the fluorine-based etching chemistry provides the much lower halogen atom flux together with the much higher KNbxOy etching rate under the condition of quite close ion momentum fluxes in both gas systems. The correlations between measured etching rates and model-predicted fluxes of active species suggested the neutral-flux-limited etching regime with the much lower effective reaction probability between KNbxOy and Cl atoms. The last effect may be related to lower volatility of NbClx compared with NbFx (that is confirmed by XPS data) as well as to the higher energy threshold for KNbxOy + Cl reaction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zheng Q, Zhang H, Shi B, Xue X, Liu Z, Jin Y, Ma T, Zou Y, Wang X, An Z, Tang W, Zhang W, Yang F, Liu Y, Lang X, Xu Z, Li Z, Wnag ZL (2016) In vivo self-powered wireless cardiac monitoring via implantable triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 10:6510
Priya S (2010) Criterion for material selection in design of bulk piezoelectric energy harvesters. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 57:2610
Niu X, Jia W, Qian S, Zhu J, Zhang J, Hou X, Mu J, Mu J, Geng W, Cho J, He J, Chou X (2019) High-performance PZT-based stretchable piezoelectric nanogenerator. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:979
Xu S, Yeh Y-W, Poirier G, McAlpine MC, Register RA, Yao N (2013) Flexible piezoelectric PMN-PT nanowire-based nanocomposite and device. Nano Lett 13:2393
Kim BY, Seo IT, Lee YS, Kim JS, Nahm S, Kang C-Y, Yoon S-J, Paik J-H, Jeong Y-H (2015) High-performance (Na0.5K0.5)NbO3 thin film piezoelectric energy harvester. J Am Ceram Soc 98:119
Zhang B, Wu J, Cheng X, Wang X, Xiao D, Zhu J, Wang X, Lou X (2013) Lead-free piezoelectrics based on potassium-sodium niobate with giant d33. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:7718
Saito Y, Takao H, Tani T, Nonoyama T, Takatori K, Homma T, Nagaya T, Nakamura M (2004) High performance lead-free piezoelectric material. Nature 432:84
Birol H, Damjanovic D, Setter N (2005) Preparation and characterization of KNbO3 ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 88:1754
Wang G, Selbach SM, Yu Y, Zhang X, Hrande T, Einarsrud M-A (2009) Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of KNbO3 nanorods. CrystEngComm 11:1958
Kim D-H, Joung M-R, Seo I-T, Hur J, Kim J-H, Kim B-Y, Lee H-J, Nahm S (2014) Influence of sintering conditions on piezoelectric properties of KNbO3 ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 34:4193
Son J, Efremov A, Yun SJ, Yeom GY, Kwon K-H (2014) Etching characteristics and mechanism of SiNx films for nano-devices in CH2F2/O2/Ar inductively coupled plasma: effect of O2 mixing ratio. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 14:9534
Efremov A, Lee J, Kwon K-H (2017) A comparative study of CF4, Cl2 and HBr + Ar inductively coupled plasmas for dry etching applications. Thin Solid Films 629:39
Sugavara M (1998) Plasma etching: fundamentals and applications. Oxford University Press, New York
Efremov A, Min N-K, Choi B-G, Baek K-H, Kwon K-H (2008) Model-based analysis of plasma parameters and active species kinetics in Cl2/X (X = Ar, He, N2) inductively coupled plasmas. J Electrochem Soc 155:D777
Lim N, Efremov A, Kwon K-H (2019) Gas-phase chemistry and etching mechanism of SiNx thin films in C4F8 + Ar inductively coupled plasma. Thin Solid Films 685:97
Chun I, Efremov A, Yeom GY, Kwon K-H (2015) A comparative study of CF4/O2/Ar and C4F8/O2/Ar plasmas for dry etching applications. Thin Solid Films 579:136
Efremov AM, Murin DB, Kwon KH (2018) Parameters of plasma and kinetics of active particles in CF4(CHF3) + Ar mixtures of a variable initial composition. Russ Microlectron 47:371
Efremov AM, Kim D-P, Kim C-I (2004) Effect of gas mixing ratio on gas-phase composition and etch rate in an inductively coupled CF4/Ar plasma. Vacuum 75:133
Efremov AM, Kim G-H, Kim J-G, Bogomolov AV, Kim C-I (2007) Applicability of self-consistent global model for characterization of inductively coupled Cl2 plasma. Vacuum 81:669
Hsu C-C, Nierode MA, Coburn JW, Graves DB (2006) Comparison of model and experiment for Ar, Ar/O2 and Ar/O2/Cl2 inductively coupled plasmas. J Phys D Appl Phys 39:3272
Gray DC, Tepermeister I, Sawin HH (1993) Phenomenological modeling of ion enhanced surface kinetics in fluorine-based plasma etching. J Vac Sci Technol B 11:1243
Lee C, Graves DB, Lieberman MA (1996) Role of etch products in polysilicon etching in a high-density chlorine discharge. Plasma Chem Plasma Proc 16:99
Chistophorou LG, Olthoff JK (2004) Fundamental electron interactions with plasma processing gases. Springer, New York
Jin W, Vitale SA, Sawin HH (2002) Plasma–surface kinetics and simulation of feature profile evolution in Cl2 + HBr etching of polysilicon. J Vac Sci Technol A 20:2106
Lieberman MA, Lichtenberg AJ (1994) Principles of plasma discharges and materials processing. Wiley, New York
Efremov AM, Kim D-P, Kim C-I (2003) On mechanisms of argon addition influence on etching rate in chlorine plasma. Thin Solid Films 435:232
Efremov AM, Kim DP, Kim CI (2004) Simple model for ion-assisted etching using Cl2/Ar inductively coupled plasma. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 32:1344
DR Lide (1998–1999) Handbook of chemistry and physics. CRC Press, New York
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a Korea University Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, N., Efremov, A., Hwang, HG. et al. Etching Kinetics and Surface Conditions for KNbxOy Thin Films with Fluorine- and Chlorine-Based Plasma Chemistries. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 40, 625–640 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-020-10064-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-020-10064-4