Abstract
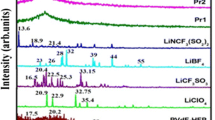
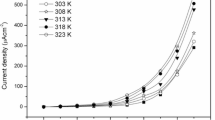
In the present study, a magnesium ion conducting polymer electrolyte membrane system based on polyethylene oxide (PEO) containing magnesium triflate Mg(CF3SO3)2 salt and 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (EMIM-BF4) ionic liquid is prepared using standard solution casting technique. X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetry studies reveal change in crystalline character with variation in Mg(CF3SO3)2 concentration within PEMs. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy technique reflects ion-polymer interactions within the prepared polymer electrolyte system. Dielectric and modulus properties of prepared electrolyte membranes show significant changes in dielectric constant and relaxation behavior respectively on varying Mg(CF3SO3)2 concentration. The optimized polymer electrolyte membrane with 6 wt% of magnesium triflate salt shows maximum ionic conductivity of ~ 9.4 × 10−5 S cm−1 at room temperature. The ionic conductivity variation with temperature shows Arrhenius behavior for PEMs. The Mg2+ conduction within the PEMs is established using CV study and electrochemical stability window of ~ 4.0 V is determined using linear sweep voltammetry. The PEMs are dominantly ionic conducting with Mg2+ transport number ~ 0.22 for the optimized PEM.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deng D (2015) Li-ion batteries: basics, progress, and challenges. Energy Sci & Eng 3:385–418
Huang B, Pan Z, Su X, An L (2018) Recycling of lithium-ion batteries: recent advances and perspectives. J Power Sources 399:274–286
Zubi G, López RD, Carvalho M, Pasaoglu G (2018) The lithium-ion battery: state of the art and future perspectives. Renew Sust Energ Rev 89:292–308
Vignarooban K, Kushagra R, Elango A, Badani P, Mellander BE, Xu X, Tucker TG, Nam C, Kannan AM (2016) Current trends and future challenges of electrolytes for sodium-ion batteries. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:2829–2846
Kumar D, Rajouria SK, Kuhar SB, Kanchan DK (2017) Progress and prospects of sodium-sulfur batteries: a review. Solid State Ionics 312:8–16
Deivanayagam R, Ingram BJ, Yassar RS (2019) Progress in development of electrolytes for magnesium batteries. Energy Storage Mater 21:136–153
Li H, Ma L, Han C, Wang Z, Liu Z, Tang Z, Zhi C (2019) Advanced rechargeable zinc-based batteries: recent progress and future perspectives. Nano Energy 62:550–587
Niu X, Li L, Qiu J, Yang J, Huang J, Wu Z, Zou J, Jiang C, Gao J, Wang L (2019) Salt-concentrated electrolytes for graphite anode in potassium ion battery. Solid State Ionics 341:115050
Zafar ZA, Imtiaz S, Li R, Zhang J, Razaq R, Xin Y, Li Q, Zhang Z, Huang Y (2018) A super-long life rechargeable aluminum battery. Solid State Ionics 320:70–75
Kong L, Yan C, Huang JQ, Zhao MQ, Titirici MM, Xiang R, Zhang Q (2018) A review of advanced energy materials for magnesium–sulfur batteries. Energy Environ Mater 1:100–112
Saha P, Datta MK, Velikokhatnyi OI, Manivannan A, Alman D, Kumta PN (2014) Rechargeable magnesium battery: current status and key challenges for the future. Prog Mater Sci 66:1–86
Angell CA (2017) Polymer electrolytes—some principles, cautions, and new practices. Electrochim Acta 250:368–375
Wang Y, Sokolov AP (2015) Design of superionic polymer electrolytes. Current Opin Chem Eng 7:113–119
Lu D, Liu H, Huang T, Xu Z, Ma L, Yang P, Qiang P, Zhang F, Wu D (2018) Magnesium ion based organic secondary batteries. J Mater Chem A 6:17297–17302
Mohanta J, Padhi DK, Si S (2018) Li-ion conductivity in PEO-graphene oxide nanocomposite polymer electrolytes: a study on effect of the counter anion. J Appl Polym Sci 135:46336
Ma Z, MacFarlane DR, Kar M (2019) Mg cathode materials and electrolytes for rechargeable Mg batteries: a review. Batteries Supercaps 2:115–127
Zardalidis G, Ioannou E, Pispas S, Floudas G (2013) Relating structure, viscoelasticity, and local mobility to conductivity in PEO/LiTf electrolytes. Macromolecules 46:2705–2714
Shobukawa H, Tokuda H, Susan MABH, Watanbe M (2005) Ion transport properties of lithium ionic liquids and their ion gels. Electrochim Acta 50:3872–3387
Ueki T, Watanabe M (2008) Macromolecules in ionic liquids: progress, challenges, and opportunities. Macromolecules 41:3739–3749
Tang J, Muchakayala R, Song S, Wang M, Kumar KN (2016) Effect of EMIMBF4 ionic liquid addition on the structure and ionic conductivity of LiBF4-complexed PVdF-HFP polymer electrolyte films. Polym Test 50:247–254
Aziz SB, Woo TJ, Kadir MFZ, Ahmed HM (2018) A conceptual review on polymer electrolytes and ion transport models. J Sci: Adv Mater Devices 3:1–17
Chaurasia SK, Singh RK, Chandra S (2011) Dielectric relaxation and conductivity studies on (PEO:LiClO4) polymer electrolyte with added ionic liquid [BMIM][PF6]: evidence of ion–ion interaction. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 49:291–300
Chaurasia SK, Singh RK, Chandra S (2011) Ion–polymer and ion–ion interaction in PEO-based polymer electrolytes having complexing salt LiClO4 and/or ionic liquid, [BMIM][PF6]. J Raman Spectrosc 42:2168–2172
Ren C, Liu M, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Zhan X, Chen F (2018) Solid-state single-ion conducting comb-like siloxane copolymer electrolyte with improved conductivity and electrochemical window for lithium batteries. J Appl Polym Sci 135:45848
Liebenow C (1998) A novel type of magnesium ion conducting polymer electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 43:1253–1256
Pandey GP, Agarwal RC, Hashmi SA (2011) Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with fumed silica for rechargeable magnesium battery application. J Solid State Electrochem 15:2253–2264
Morita M, Yoshimoto N, Yakushiji S, Ishikawa M (2001) Rechargeable magnesium batteries using a novel polymeric solid electrolyte. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 4:177–179
Kumar GG, Munichandraiah N (2000) A gel polymer electrolyte of magnesium triflate. Solid State Ionics 128:203–210
Reddy MJ, Chu PP (2002) Ion pair formation and its effect in PEO:Mg solid polymer electrolyte system. J Power Sources 109:340–346
Sarangika HNM, Dissanayake MAKL, Senadeera GKR, Rathnayake RRDV, Pitawala HMJC (2016) Polyethylene oxide and ionic liquid-based solid polymer electrolyte for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Ionics 23(10):2829–2835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1870-3
Saroj AL, Singh RK, Chandra S (2014) Thermal, vibrational, and dielectric studies on PVP/LiBF4 + ionic liquid [EMIM][BF4]-based polymer electrolyte films. J Phys Chem Solids 75:849–857
Sharma J, Hashmi SA (2019) Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolyte nanocomposites: effect of active and passive nanofillers. Polym Compos 40:1295–1306
Wilkes JS, Zaworotko MJ (1992) Air and water stable I-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium based ionic liquids. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 965-967
Cooper EI, O’Sullivan EJM (1992) Proceedings of 8th international symposium on ionic liquids (Eds. R. J. Gale, G. Blomgren, and H. Kojima). The Electrochemical Society, Pennington, NJ, p 386
Maurya KK, Srivastava N, Hashmi SA, Chandra S (1992) Proton conducting polymer electrolyte: II poly ethylene oxide + NH4l system. J Mater Sci 27:6357–6364
Chaurasia SK, Saroj AL, Shalu SVK, Tripathi AK, Gupta AK, Verma YL, Singh RK (2015) Studies on structural, thermal and AC conductivity scaling of PEO-LiPF6 polymer electrolyte with added ionic liquid [BMIMPF6]. AIP Adv 5:077178
Maruthupandy M, Anand M, Maduraiveran G, Suresh S, Beevi ASH, Priya RJ (2016) Adv Nat Sci Nanosci Nanotechnol 7:045011 (9pp)
Parthiban V, Akula S, Peera SG, Islam N, Sahu AK (2016) Proton conducting Nafion-sulfonated graphene hybrid membranes for direct methanol fuel cells with reduced methanol crossover. Energy Fuel 30:725–734
Chaurasia SK, Singh RK, Chandra S (2011) Structural and transport studies on polymeric membranes of PEO containing ionic liquid, EMIM-TY: evidence of complexation. Solid State Ionics 183:32–39
Pasaribu MH, Arcana IM, Wahyuningrum D (2015) Molecular structure, vibrational spectra, and hydrogen bonding of the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methyl-1H-imidazolium tetrafluoroborate. AIP Conf Proc 1677:070014
Skin JH, Kim KW, Ahn HJ, Ahn JH (2002) Electrochemical properties and interfacial stability of (PEO)10LiCF3SO3–TinO2n−1 composite polymer electrolytes for lithium/sulfur battery. J Mater Sci Eng B 95:148–156
Mishra K, Hashmi SA, Rai DK (2014) Protic ionic liquid-based gel polymer electrolyte: structural and ion transport studies and its application in proton battery. J Solid State Electrochem 18:2255–2266
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Ion transport and ion–filler-polymer interaction in poly(methyl methacrylate)-based, sodium ion conducting, gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with silica nanoparticles. J Power Sources 195:5101–5108
Ramesh S, Lu S (2011) Effect of lithium salt concentration on crystallinity of poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)-based solid polymer electrolytes. J Mol Struct 994:403–409
Pradhan DK, Choudhary RNP, Samantary BK (2008) Studies of dielectric relaxation and AC conductivity behavior of plasticized polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. Int J Electrochem Sci 3:597–608
Ramya CS, Pandian SS, Savitha T, Hirankumar G, Angelo PC (2007) Vibrational and impedance spectroscopic study on PVP–NH4SCN based polymer electrolytes. Phys B Condens Matter 393:11–17
Osman Z, Ghazali M, Othman L, Isa K (2012) AC ionic conductivity and DC polarization method of lithium ion transport in PMMA–LiBF4 gel polymer electrolytes. Result Phy 2:1–4
Kumar D, Kanchan DK (2019) Dielectric and electrochemical studies on carbonate free Na-ion conducting electrolytes for sodium-sulfur batteries. J Energy Storage 22:44–49
Gohel K, Kanchan DK (2018) Ionic conductivity and relaxation studies in PVDF-HFP:PMMA-based gel polymer blend electrolyte with LiClO4 salt. J Adv Dielect 8:1850005
Al-Gunaid MQA, Saeed AMN (2018) Effects of the electrolyte content on the electrical permittivity, thermal stability, and optical dispersion of poly(vinyl alcohol)–cesium copper oxide–lithium perchlorate nanocomposite solid-polymer electrolytes. J ApplPolym Sci 135:45852
Woo HJ, Majid SR, Arof AK (2012) Dielectric properties and morphology of polymer electrolyte based on poly (ɛ-caprolactone) and ammonium thiocyanate. Mater Chem Phys 134:755–761
Gohel K, Kanchan DK (2019) Effect of PC: DEC plasticizers on structural and electrical properties of PVDF–HFP: PMMA based gel polymer electrolyte system. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30:12260–12268
Rathika R, Suthanthiraraj SA (2016) Ionic interactions and dielectric relaxation of PEO/PVDF-Mg[(CF3SO2)2N2] blend electrolytes for magnesium ion rechargeable batteries. Macromol Res 24:422–428
Karmakar A, Ghosh A (2012) Dielectric permittivity and electric modulus of polyethylene oxide (PEO)–LiClO4 composite electrolytes. Curr Appl Phys 12:539–543
Hashmi SA, Chandra S (1995) Experimental investigations on a sodium-ion-conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly (ethylene oxide) complexed with NaPF6. J Mater Sci Eng B 34:18–26
Wagner JB Jr, Wagner C (1957) Electrical conductivity measurements on cuprous halides. J Chem Phys 26:1597
Watanabe M, Nagano S, Sanui K, Ogata N (1988) Estimation of Li+ transport number in polymer electrolytes by the combination of complex impedance and potentiostatic polarization measurements. Solid State Ionics 28-30:911–917
Acknowledgments
Deepak Kumar thanks and acknowledges “The M.S. University of Baroda,” Vadodara, Gujarat, India. He also acknowledge encouragement and support received from Electronics and Mechanical Engineering School, Affiliated to Gujarat Technological University, Under Corps of EME, Ministry of Defence, Government of India.
Funding
Kuldeep Mishra acknowledges the funding (File No YSS/2015/001234) from Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maheshwaran, C., Kanchan, D., Gohel, K. et al. Effect of Mg(CF3SO3)2 concentration on structural and electrochemical properties of ionic liquid incorporated polymer electrolyte membranes. J Solid State Electrochem 24, 655–665 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-020-04507-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-020-04507-3