Abstract
Cemented carbides have been widely applied in cutting tools and wear-resistant components due to their ultrahigh hardness and good wear resistance. However, the disadvantages of limited impact toughness and high cost have restricted their further application. Consequently, cemented carbides are usually joining with ductile steels to combine the advantages of both. Among various materials joining technologies, brazing have been an effective method to achieve high quality dissimilar cemented carbide joints. In this paper, the research status of cemented carbide brazing is reviewed. The materials utilized as brazing filler metal in cemented carbide brazing joints are summarized in detail. Researchers have done lots of works utilizing Cu based and Ag based brazing filler metals which are the most commonly used interlayers in brazed joints of cemented carbide and ductile steel. The effects of different filler metal on wettability, microstructure, phase constitution and mechanical properties of brazed cemented carbides joints are analysed. Besides, a series of newly developed brazing filler material such as nickel-based high temperature brazing filler metal, amorphous brazing filler metal and high entropy alloy brazing filler materials are also involved. These newly developed brazing filler metals have shown great potential in fabricating high quality joints. Finally, the current issues of cemented carbide brazing are reviewed and the develop trend is predicted.
Graphic Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Li, K. Chang, A. Yeh, On the microstructure and properties of an advanced cemented carbide system processed by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 782, 440–450 (2019)
D. Xu, X. Yue, Y. Zhang, J. Song, X. Chen, S. Zhong, J. Ma, L. Ba, L. Zhang, S. Du, Enhanced dielectric properties and electrical responses of cobalt-doped CaCu3Ti4O12 thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 773, 853–859 (2019)
D. Xu, X. Yue, J. Song, S. Zhong, J. Ma, L. Bao, L. Zhang, S. Du, Improved dielectric and non-ohmic properties of (Zn + Zr) codoped CaCu3Ti4O12 thin films. Ceram. Int. 45(9), 11421–11427 (2019)
Q. Su, S. Zhu, H. Ding, Y. Bai, P. Di, Comparison of the wear behaviors of advanced and conventional cemented tungsten carbides. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 79, 18–22 (2019)
M. Tarraste, J. Kübarsepp, K. Juhani, A. Mere, M. Kolnes, M. Viljus, B. Maaten, Ferritic chromium steel as binder metal for WC cemented carbides. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 73, 183–191 (2018)
D. Garbiec, P. Siwak, Microstructural evolution and development of mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered WC–Co cemented carbides for machine parts and engineering tools. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 19(1), 215–223 (2019)
G. Liu, Z. Zhou, X. Qian, W. Pang, G. Li, G. Tan, Wear mechanism of cemented carbide tool in high speed milling of stainless steel. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 31(1), 98 (2018)
J. García, V. Collado Ciprés, A. Blomqvist, B. Kaplan, Cemented carbide microstructures: a review. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 80, 40–68 (2019)
D.A. Sandoval, J.J. Roa, O. Ther, E. Tarrés, L. Llanes, Micromechanical properties of WC-(W, Ti, Ta, Nb)C-Co composites. J. Alloys Compd. 777, 593–601 (2019)
I. Konyashin, S. Farag, B. Ries, B. Roebuck, WC–Co–Re cemented carbides: structure, properties and potential applications. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 78, 247–253 (2019)
B. Yu, Y. Li, Q. Lei, Y. Nie, Microstructures and mechanical properties of WC–Co–xCr–Mo cement carbides. J. Alloys Compd. 771, 636–642 (2019)
L.L. Shaw, H. Luo, Y. Zhong, WC–18wt% Co with simultaneous improvements in hardness and toughness derived from nanocrystalline powder. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 537, 39–48 (2012)
G. Chen, X. Shu, J. Liu, B. Zhang, B. Zhang, J. Feng, Investigation on microstructure of electron beam welded WC–Co/40Cr joints. Vacuum 149, 96–100 (2018)
B. Cheniti, D. Miroud, R. Badji, D. Allou, T. Csanádi, M. Fides, P. Hvizdoš, Effect of brazing current on microstructure and mechanical behavior of WC–Co/AISI 1020 steel TIG brazed joint. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 64, 210–218 (2017)
Y. Sechi, T. Tsumura, K. Nakata, Dissimilar laser brazing of boron nitride and tungsten carbide. Mater. Des. 31(4), 2071–2077 (2010)
Y.H. Xiao, P.W. Liu, Z. Wang, Y. Wang, K.Q. Feng, L. Chen, La2O3 addition for improving the brazed joints of WC–Co/1Cr13. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 267, 17–25 (2019)
G.S. Upadhyaya, Materials science of cemented carbides—an overview. Mater. Des. 22(6), 483–489 (2001)
W. Zhu, H. Zhang, C. Guo, Y. Liu, X. Ran, Wetting and brazing characteristic of high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel and 316L austenitic stainless steel by Ag–Cu filler. Vacuum 166, 97–106 (2019)
H. Chen, K. Feng, J. Xiong, Z. Guo, Characterization and stress relaxation of the functionally graded WC–Co/Ni component/stainless steel joint. J. Alloys Compd. 557, 18–22 (2013)
V.L. Silva, C.M. Fernandes, A.M.R. Senos, Copper wettability on tungsten carbide surfaces. Ceram. Int. 42(1), 1191–1196 (2016)
Z. Mirski, T. Piwowarczyk, Wettability of hardmetal surfaces prepared for brazing with various methods. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 11(2), 411–419 (2011)
A.R. Kennedy, J.D. Wood, B.M. Weager, The wetting and spontaneous infiltration of ceramics by molten copper. J. Mater. Sci. 35(12), 2909–2912 (2000)
X.Z. Zhang, G.W. Liu, J.N. Tao, H.C. Shao, H. Fu, T.Z. Pan, G.J. Qiao, Vacuum brazing of WC–8Co cemented carbides to carbon steel using pure Cu and Ag–28Cu as filler metal. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 26(2), 488–494 (2017)
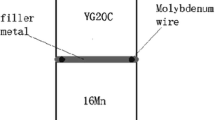
Y. Sui, H. Luo, Y. Lv, F. Wei, J. Qi, Y. He, Q. Meng, Z. Sun, Influence of brazing technology on the microstructure and properties of YG20C cemented carbide and 16Mn steel joints. Weld. World 60(6), 1269–1275 (2016)
M. Amelzadeh, S.E. Mirsalehi, Influence of braze type on microstructure and mechanical behavior of WC–Co/steel dissimilar joints. J. Manuf. Process. 36, 450–458 (2018)
A. Amirnasiri, N. Parvin, M.S. Haghshenas, Dissimilar Diffusion Brazing of WC–Co to AISI 4145 steel using RBCuZn-D interlayer. J. Manuf. Process. 28, 82–93 (2017)
X. Zhang, G. Liu, J. Tao, Y. Guo, J. Wang, G. Qiao, Brazing of WC–8Co cemented carbide to steel using Cu–Ni–Al alloys as filler metal: microstructures and joint mechanical behavior. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34(7), 1180–1188 (2018)
M.I. Barrena, J.M. Gómez De Salazar, L. Matesanz, Interfacial microstructure and mechanical strength of WC–Co/90MnCrV8 cold work tool steel diffusion bonded joint with Cu/Ni electroplated interlayer. Mater. Des. 31(7), 3389–3394 (2010)
W.B. Lee, B.D. Kwon, S.B. Jung, Effect of bonding time on joint properties of vacuum brazed WC–Co hard metal/carbon steel using stacked Cu and Ni alloy as insert metal. Mater. Sci. Technol. 20(11), 1474–1478 (2004)
N. Ray, L. Froyen, K. Vanmeensel, J. Vleugels, Wetting and solidification of silver alloys in the presence of tungsten carbide. Acta Mater. 144, 459–469 (2018)
T. Yamaguchi, K. Harano, K. Yajima, Spreading and reactions of molten metals on and with cemented carbides, in Surfaces and interfaces in ceramic and ceramic—metal systems, ed. by J. Pask, A. Evans (Springer US, Boston, 1981), pp. 503–511
G. Triantafyllou, J.T.S. Irvine, Wetting and interactions of Ag–Cu–Ti and Ag–Cu–Ni alloys with ceramic and steel substrates for use as sealing materials in a DCFC stack. J. Mater. Sci. 51(4), 1766–1778 (2016)
C. Jiang, H. Chen, Q. Wang, Y. Li, Effect of brazing temperature and holding time on joint properties of induction brazed WC–Co/carbon steel using Ag-based alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 229, 562–569 (2016)
S. Yaoita, T. Watanabe, T. Sasaki, Effects of Ni and Co elements in filler metals in Ag-brazing of cemented carbide. Q. J. Jpn. Weld. Soc. 30(4), 298–305 (2012)
K. Kaiwa, S. Yaoita, T. Sasaki, T. Watanabe, Effects of Ni and Co additions to filler metals on Ag-brazed joints of cemented carbide and martensitic stainless steel. Adv. Mater. Res. 922, 322–327 (2014)
C. Jiang, H. Chen, X. Zhao, S. Qiu, D. Han, G. Gou, Microstructure and mechanical properties of brazing bonded WC–15Co/35CrMo joint using AgNi/CuZn/AgNi composite interlayers. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 70, 1–8 (2018)
L. Pan, J. Gu, W. Zou, T. Qiu, H. Zhang, J. Yang, Brazing joining of Ti3AlC2 ceramic and 40Cr steel based on Ag–Cu–Ti filler metal. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 251, 181–187 (2018)
M. Hasanabadi, A. Shamsipur, H.N. Sani, H. Omidvar, S. Sakhaei, Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of tungsten carbide brazed joints using Ag–Cu–Zn + Ni/Mn filler alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27(12), 2638–2646 (2017)
H. Chen, K. Feng, S. Wei, J. Xiong, Z. Guo, H. Wang, Microstructure and properties of WC–Co/3Cr13 joints brazed using Ni electroplated interlayer. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 33, 70–74 (2012)
L. Zhu, L. Luo, J. Luo, Y. Wu, J. Li, Effect of electroless plating Ni–Cu–P layer on brazability of cemented carbide to steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 206(8–9), 2521–2524 (2012)
L. Zhu, L. Luo, J. Luo, J. Li, Y. Wu, Effect of electroless plating Ni–Cu–P layer on the wettability between cemented carbides and soldering tins. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 31, 192–195 (2012)
T. Iamboliev, S. Valkanov, S. Atanasova, Microstructure embrittlement of hard metal–steel joint obtained under induction heating diffusion bonding. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 37, 90–97 (2013)
X. Yu, D. Zhou, D. Yao, F. Lu, P. Xu, Fiber laser welding of WC–Co to carbon steel using Fe–Ni Invar as interlayer. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 56, 76–86 (2016)
G. Chen, B. Zhang, Z. Wu, W. Mao, J. Feng, Electron beam welding–brazing of hard alloy to steel with Ni–Fe intermediate. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 40, 58–63 (2013)
G. Yin, P. Xu, H. Gong, H. Cui, F. Lu, Effect of interlayer thickness on the microstructure and strength of WC–Co/Invar/316L steel joints prepared by fibre laser welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 255, 319–332 (2018)
P.Q. Xu, Dissimilar welding of WC–Co cemented carbide to Ni42Fe50.9C0.6Mn3.5Nb3 invar alloy by laser–tungsten inert gas hybrid welding. Mater. Des. 32, p229–p237 (2011)
B. Binesh, A.J. Gharehbagh, Transient liquid phase bonding of IN738LC/MBF-15/IN738LC: solidification behavior and mechanical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 32, 1137–1151 (2016)
G. Huang, J. Huang, M. Zhang, D. Mu, G. Zhou, X. Xu, Fundamental aspects of ultrasonic assisted induction brazing of diamond onto 1045 steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 260, 123–136 (2018)
M. Singh, R. Asthana, T.P. Shpargel, Brazing of ceramic-matrix composites to Ti and Hastealloy using Ni-base metallic glass interlayers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 498(1–2), 19–30 (2008)
M. Singh, R. Asthana, Joining of zirconium diboride-based ultra high-temperature ceramic composites using metallic glass interlayers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 460–461, 153–162 (2007)
Y. Liu, G. Wang, W. Cao, H. Xu, Z. Huang, D. Zhu, C. Tan, Brazing ZrB2-SiC ceramics to Ti6Al4V alloy with TiCu-based amorphous filler. J. Manuf. Process. 30, 516–522 (2017)
L.X. Zhang, J.M. Shi, H.W. Li, X.Y. Tian, J.C. Feng, Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of ZrB2–SiC-C ceramic and GH99 superalloy joints brazed with a Ti-modified FeCoNiCrCu high-entropy alloy. Mater. Des. 97, 230–238 (2016)
D. Bridges, S. Zhang, S. Lang, M. Gao, Z. Yu, Z. Feng, A. Hu, Laser brazing of a nickel-based superalloy using a Ni–Mn–Fe–Co–Cu high entropy alloy filler metal. Mater. Lett. 215, 11–14 (2018)
A. Rabinkin, Brazing with (NiCoCr)–B–Si amorphous brazing filler metals: alloys, processing, joint structure, properties, applications. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 9(3), 181–199 (2004)
D.B. Miracle, O.N. Senkov, A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 122, 448–511 (2017)
J. Zou, Z. Jiang, Q. Zhao, Z. Chen, Brazing of Si3N4 with amorphous Ti40Zr25Ni15Cu20 filler. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 507, p155–p160 (2009)
Y. Xia, H. Dong, R. Zhang, Y. Wang, X. Hao, P. Li, C. Dong, Interfacial microstructure and shear strength of Ti6Al4V alloy/316L stainless steel joint brazed with Ti33.3Zr16.7Cu50 − xNix amorphous filler metals. Mater. Des. 187, 1083 (2020)
J.B. Wang, Y.Y. Lian, F. Feng, Z. Chen, Y. Tan, S. Yang, X. Liu, J.B. Qiang, T.Z. Liu, M.Y. Wei, Y.M. Wang, Microstructure of the tungsten and reduced activation ferritic-martensitic steel joint brazed with an Fe-based amorphous alloy. Fusion Eng. Des. 138, 164–169 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51375015), Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (1908085QE198), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Provincial Education Department (KJ2019A0061) and the Research Foundation for Young Teachers of Anhui University of Technology (QZ201707).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, X., Ma, Q., Cui, B. et al. Current Review on the Research Status of Cemented Carbide Brazing: Filler Materials and Mechanical Properties. Met. Mater. Int. 27, 571–583 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00608-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00608-w