Abstract
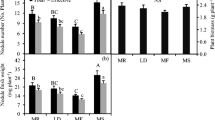
Biochar amendments have been considered to increase the competitive abilities of legumes in mixed cultures. However, little is known about how biochar affects the nutrient and Cd allocation within legume-grass mixtures. Therefore, we conducted a pot experiment to explore the effects of biochar addition rate (0, 1, 2.5, and 5%) on four monocultures, the legume Trifolium repens (Tr), Lolium perenne (Lp), Dactylis glomerata (Dg) and Festuca arundinacea (Fa), and three mixed cultures, i.e., Tr + Lp, Tr + Lp + Dg, and Tr + Lp + Dg + Fa. Regardless of biochar addition, Tr plants showed the lowest aboveground Cd concentration among the monoculture treatments. Compared with non-biochar addition treatment, the 1% biochar addition significantly promoted aboveground biomass accumulation and P, K, Ca, and Mg uptake in the aboveground parts of the Tr monoculture treatments by 39.32, 39.88, 88.27, 69.68, and 51.96%, respectively. Nevertheless, the aboveground biomass and P, K, Ca, and Mg uptake as well as the proportion of these parameters in Tr plants in all plant species mixture treatments decreased after biochar application. Maximum aboveground P and Mg uptake occurred in the four-species mixture treatments without biochar addition, whereas maximum values of these parameters occurred in the three-species mixture treatments with 5% biochar addition. Shoot Cd uptake was not decreased by biochar addition at all plant species treatments. Based on the results, it was suggested that biochar could not reduce Cd uptake by increasing the proportion of legumes in the legume-grass mixtures. The complementarity effects on nutrient uptake in the plant species mixtures depended on the amount of biochar added.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abalos D, De Deyn GB, Kuyper TW, van Groenigen JW (2014) Plant species identity surpasses species richness as a key driver of N2O emissions from grassland. Glob Chang Biol 20:265–275
Abbas T, Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Mahmood A, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Ibrahim M, Arshad M, Qayyum MF (2018) Biochar application increased the growth and yield and reduced cadmium in drought stressed wheat grown in an aged contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:825–833
Ashworth AJ, Weiss SA, Keyser PD, Allen FL, Tyler DD, Taylor A, Beamer KP, West CP, Pote DH (2016) Switchgrass composition and yield response to alternative soil amendments under intensified heat and drought conditions. Agric Ecosyst Environ 233:415–424
Bitarafan Z, Jensen SM, Liu F, Andreasen C (2019) Intercropping fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) and barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) with and without biochar: tests along a competition gradient. J Agron Crop Sci 205:99–107
Bohara H, Dodla S, Wang JJ, Darapuneni M, Acharya BS, Magdi S, Pavuluri K (2019) Influence of poultry litter and biochar on soil water dynamics and nutrient leaching from a very fine sandy loam soil. Soil Tillage Res 189:44–51
Cardinale BJ, Wright JP, Cadotte MW, Carroll IT, Hector A, Srivastava DS, Loreau M, Weis JJ (2007) Impacts of plant diversity on biomass production increase through time because of species complementarity. PNAS 104:18123–18128
Efthymiou A, Jensen B, Jakobsen I (2018) The roles of mycorrhiza and Penicillium inoculants in phosphorus uptake by biochar-amended wheat. Soil Biol Biochem 127:168–177
Egene CE, Van Poucke R, Ok YS, Meers E, Tack FMG (2018) Impact of organic amendments (biochar, compost and peat) on cd and Zn mobility and solubility in contaminated soil of the Campine region after three years. Sci Total Environ 626:195–202
Galende MA, Becerril JM, Barrutia O, Artetxe U, Garbisu C, Hernández A (2014) Field assessment of the effectiveness of organic amendments for aided phytostabilization of a Pb–Zn contaminated mine soil. J Geochem Explor 145:181–189
Gao S, DeLuca TH, Cleveland CC (2019) Biochar additions alter phosphorus and nitrogen availability in agricultural ecosystems: a meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 654:463–472
Guo XF, Li HS, Chen HY (2017) The effects of biochar and intercropping on the Cd, Cr and Zn speciation in soils and plant uptake by Machilus pauhoi. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98:574–581
Høgh-Jensen H (2003) The effect of potassium deficiency on growth and N2-fixation in Trifolium repens. Physiol Plant 119:440–449
Hooper DU, Chapin FS, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setala H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: a consensus of current knowledge. Ecol Monogr 75:3–35
Hu JL, Wu FY, Wu SC, Lam CL, Lin XG, Wong MH (2014) Biochar and Glomus caledonium influence Cd accumulation of upland kangkong (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk.) intercropped with Alfred stonecrop (Sedum alfredii Hance). Sci Rep 4:7
Huang Y, Chen Q, Deng M, Japenga J, Li T, Yang X, He Z (2018) Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of agricultural soils in a typical peri-urban area in Southeast China. J Environ Manag 207:159–168
Khalid S, Shahid M, Niazi NK, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Dumat C (2017) A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. J Geochem Explor 182:247–268
Khan S, Chao C, Waqas M, Arp HPH, Zhu YG (2013) Sewage sludge biochar influence upon rice (Oryza sativa L) yield, metal bioaccumulation and greenhouse gas emissions from acidic paddy soil. Environ Sci Technol 47:8624–8632
Khan MA, Ding X, Khan S, Brusseau ML, Khan A, Nawab J (2018) The influence of various organic amendments on the bioavailability and plant uptake of cadmium present in mine-degraded soil. Sci Total Environ 636:810–817
Lebrun M, Miard F, Nandillon R, Scippa GS, Bourgerie S, Morabito D (2019) Biochar effect associated with compost and iron to promote Pb and as soil stabilization and Salix viminalis L. growth. Chemosphere 222:810–822
Lehmann J, Pereira da Silva J, Steiner C, Nehls T, Zech W, Glaser B (2003) Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological Anthrosol and a Ferralsol of the Central Amazon basin: fertilizer, manure and charcoal amendments. Plant Soil 249:343–357
Li T, Di Z, Yang X, Sparks DL (2011) Effects of dissolved organic matter from the rhizosphere of the hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii on sorption of zinc and cadmium by different soils. J Hazard Mater 192:1616–1622
Lin L, Chen F, Wang J, Liao M, Lv X, Wang Z, Li H, Deng Q, Xia H, Liang D, Tang Y, Wang X, Lai Y, Ren W (2018) Effects of living hyperaccumulator plants and their straws on the growth and cadmium accumulation of Cyphomandra betacea seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 155:109–116
Liu L, Wang YF, Yan XW, Li JW, Jiao NY, Hu SJ (2017a) Biochar amendments increase the yield advantage of legume-based intercropping systems over monoculture. Agric Ecosyst Environ 237:16–23
Liu M, Sun J, Li Y, Xiao Y (2017b) Nitrogen fertilizer enhances growth and nutrient uptake of Medicago sativa inoculated with Glomus tortuosum grown in Cd-contaminated acidic soil. Chemosphere 167:204–211
Lu K, Yang X, Gielen G, Bolan N, Ok YS, Niazi NK, Xu S, Yuan G, Chen X, Zhang X, Liu D, Song Z, Liu X, Wang H (2017) Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the mobility and redistribution of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in contaminated soil. J Environ Manag 186:285–292
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page AL (ed) Methods of soil analysis: part 2 chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 403–430
Oram NJ, van de Voorde TFJ, Ouwehand GJ, Bezemer TM, Mommer L, Jeffery S, Van Groenigen JW (2014) Soil amendment with biochar increases the competitive ability of legumes via increased potassium availability. Agric Ecosyst Environ 191:92–98
Qiao YH, Crowley D, Wang K, Zhang HQ, Li HF (2015) Effects of biochar and Arbuscular mycorrhizae on bioavailability of potentially toxic elements in an aged contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 206:636–643
Rondon MA, Lehmann J, Ramírez J, Hurtado M (2007) Biological nitrogen fixation by common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) increases with bio-char additions. Biol Fertil Soils 43:699–708
Sangakkara UR, Hartwig UA, Nösberger J (1996) Soil moisture and potassium affect the performance of symbiotic nitrogen fixation in faba bean and common bean. Plant Soil 184:123–130
Torssell B, Eckersten H, Kornher A, Nyman P, Boström U (2007) Modelling carbon dynamics in mixed grass–red clover swards. Agric Syst 94:273–280
Wang HF, Zheng H, Jiang ZX, Dai YH, Liu GC, Chen L, Luo XX, Liu MH, Wang ZY (2017) Efficacies of biochar and biochar-based amendment on vegetable yield and nitrogen utilization in four consecutive planting seasons. Sci Total Environ 593:124–133
Xiao Y, Li Y, Che Y, Deng S, Liu M (2018) Effects of biochar and nitrogen addition on nutrient and cd uptake of Cichorium intybus grown in acidic soil. Int J Phytoremediation 20:398–404
Yang Y, Yang J, Zhao T, Huang X, Zhao P (2016) Ecological restoration of highway slope by covering with straw-mat and seeding with grass–legume mixture. Ecol Eng 90:68–76
Zeng L, Lin X, Zhou F, Qin J, Li H (2019) Biochar and crushed straw additions affect cadmium absorption in cassava-peanut intercropping system. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 167:520–530
Zhan FD, Qin L, Guo XH, Tan JB, Liu NN, Zu YQ, Li Y (2016) Cadmium and lead accumulation and low-molecular-weight organic acids secreted by roots in an intercropping of a cadmium accumulator Sonchus asper L. with Vicia faba L. RSC Adv 6:33240–33248
Zhang S, Li T, Zhang X, Yu H, Zheng Z, Wang Y, Hao X, Pu Y (2014) Changes in pH, dissolved organic matter and Cd species in the rhizosphere soils of Cd phytostabilizer Athyrium wardii (Hook.) Makino involved in cd tolerance and accumulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:4605–4613
Zhang F, Liu M, Li Y, Che Y, Xiao Y (2019) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, biochar and cadmium on the yield and element uptake of Medicago sativa. Sci Total Environ 655:1150–1158
Zhou H, Fang H, Zhang Q, Wang Q, Chen C, Mooney SJ, Peng X, Du Z (2019) Biochar enhances soil hydraulic function but not soil aggregation in a sandy loam. Eur J Soil Sci 70:291–300
Funding
This research was supported by the earmarked fund for China Agriculture Research System (CARS-34), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20171378) and the Jiangsu Overseas Visiting Scholar Program for University Prominent Young & Middle-aged Teachers and Presidents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5.71 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Wang, L., Zhao, Z. et al. Biochar shifts biomass and element allocation of legume-grass mixtures in Cd-contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 10835–10845 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07357-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07357-3