Abstract
A method is described for the electrochemical determination of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) antigen, and by testing the effect of 30 nm gold nanoparticles (GNPs). Three comparative studies were performed in the presence and absence of GNPs, and with agglomerated GNPs. The divalent ion Ca(II) was used to induce a strong agglomeration of GNPs, as confirmed by colorimetry and voltammetry. Herein, colorimetry was used to test the best amount of salt needed to aggregate the GNPs. Despite, voltammetry was used to determine the status of biomolecules on the sensor. The topography of the surface of ZnO-coated interdigitated electrodes was analyzed by using 3D-nano profilometry, scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy and high-power microscopy. The interaction between SCC antigen and antibody trigger vibrations on the sensor and cause dipole moment, which was measured using a picoammeter with a linear sweep from 0 to 2 V at 0.01 V step voltage. The sensitivity level was 10 fM by 3σ calculation for the dispersed GNP-conjugated antigen. This indicates a 100-fold enhancement compared to the condition without GNP conjugation. However, the sensitivity level for agglomerated GNPs conjugated antibody was not significant with 100 fM sensitivity. Specificity was tested for other proteins in serum, namely blood clotting factor IX, C-reactive protein, and serum albumin. The SCC antigen was quantified in spiked serum and gave recoveries that ranged between 80 and 90%.

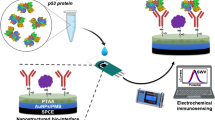
Schematic representation of SCC (squamous cell carcinoma) antigen determination using divalent ion induced agglomerated GNPs. Sensitivity increment depends on the occurrence of more SCC antigen and antibody binding event via GNPs integration. Notably, lower detection limit was achieved at femto molar with proper orientation of biological molecules.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kabir S, Schmults CD, Ruiz ES (2018) A review of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Int J Cancer Manag 11:1–9. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijcm.60846
Qin H De, Liao XY, Chen Y Bin, et al (2016) Genomic characterization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma reveals critical genes underlying tumorigenesis and poor prognosis. Am J Hum Genet 98:709–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.02.021
Voiculescu V, Calenic B, Ghita M et al (2016) From Normal skin to squamous cell carcinoma: a quest for novel biomarkers. Dis Markers 2016:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4517492
Abnet CC, Arnold M, Wei WQ (2018) Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterology 154:360–373. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.08.023
Wang H, Lakshmipriya T, Chen Y, Gopinath SCB (2019) Squamous cell carcinoma biomarker sensing on a strontium oxide-modified Interdigitated electrode surface for the diagnosis of cervical Cancer. Biomed Res Int 2019:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2807123
Wang C, Wu T, Wang X et al (2019) Ultrathin-layered carbon intercalated MoS2 hollow nanospheres integrated with gold nanoparticles for photoelectrochemical immunosensing of squamous cell carcinoma antigen. Sensors actuators B Chem:126716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126716
Qian X, Zhou X, Qu Q et al (2019) Ultrasensitive and robust electrochemical sensing platform for the detection of squamous cell carcinoma antigen using water-soluble pillar [5]arene-Pd/MoS2 nanocomposites. Electrochim Acta 313:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.05.032
Ye X, Li M, Hu Y et al (2018) Sensitive photoelectrochemical immunosensor for squamous cell carcinoma antigen based on MoSe2 nanosheets and hollow gold nanospheres. Sensors Actuators B Chem 275:199–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.08.010
Fan D, Bao C, Liu X, Feng J, Wu D, Ma H, Wang H, Wei Q, du B (2019) Facile fabrication of visible light photoelectrochemical immunosensor for SCCA detection based on BiOBr/bi 2 S 3 heterostructures via self-sacrificial synthesis method. Talanta 198:417–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.02.043
Gopinath SCB, Lakshmipriya T, Md Arshad MK, et al (2019) Nanoelectronics in biosensing applications. Elsevier Inc.
Pundir CS, Narwal V (2018) Biosensing methods for determination of triglycerides: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 100:214–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.09.008
Nikolelis DP, Nikoleli GP (2018) Nanotechnology and biosensors. Nanotechnol Biosens 22:1–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/C2017-0-00358-0
Lakshmipriya T, Fujimaki M, Gopinath SCB, et al (2013) PAPER a high-performance waveguide-mode biosensor for detection of factor IX using PEG-based blocking agents to suppress non-speci fi c binding and improve sensitivity †. 2863–2870. doi: 10.1039/c3an00298e
Kumar A, Boruah BM, Liang X (2011) Gold Nanoparticles: Promising Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis of Cancer and HIV / AIDS:2011. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/202187
Letchumanan I, Gopinath SCB, Arshad MKM, et al (2019) Gold Nano-urchin Integrated Label-free Amperometric Aptasensing Human Blood Clotting Factor IX: A Prognosticative Approach for “Royal Disease.” Biosens Bioelectron https://doi.org/S095656631930106X
Gopinath SCB, Perumal V, Rao BS, Md Arshad MK, Voon CH, Lakshmipriya T, Haarindraprasad R, Vijayakumar T, Chen Y, Hashim U (2017) Voltammetric immunoassay for the human blood clotting factor IX by using nanogapped dielectrode junctions modified with gold nanoparticle-conjugated antibody. Microchim Acta 184:3739–3745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2389-7
Lakshmipriya T, Horiguchi Y, Nagasaki Y (2014) Co-immobilized poly(ethylene glycol)-block-polyamines promote sensitivity and restrict biofouling on gold sensor surface for detecting factor IX in human plasma. Analyst 139:3977–3985. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4an00168k
Anniebell S, Gopinath SCB (2018) Polymer conjugated gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Curr Med Chem 25:1433–1445. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170116123633
Gopinath SCB, Lakshmipriya T, Awazu K (2014) Colorimetric detection of controlled assembly and disassembly of aptamers on unmodified gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 51:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.07.037
Fatin MF, Rahim Ruslinda A, Gopinath SCB et al (2019) Co-ordinated split aptamer assembly and disassembly on gold nanoparticle for functional detection of HIV-1 tat. Process Biochem 79:32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.12.016
Cheen OC, Gopinath SCB, Perumal V, Arshad MKM, Lakshmipriya T, Chen Y, Haarindraprasad R, Rao BS, Hashim U, Pandian K (2017) Aptamer-based impedimetric determination of the human blood clotting factor IX in serum using an interdigitated electrode modified with a ZnO nanolayer. Microchim Acta 184:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2001-6
Gopinath SCB, Perumal V, Kumaresan R, Lakshmipriya T, Rajintraprasad H, Rao BS, Arshad MKM, Chen Y, Kotani N, Hashim U (2016) Nanogapped impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of 16Â kDa heat shock protein against mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microchim Acta 183:2697–2703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1911-7
Letchumanan I, Gopinath SCB, Md Arshad MK, Anbu P, Lakshmipriya T (2019) Gold nano-urchin integrated label-free amperometric aptasensing human blood clotting factor IX: A prognosticative approach for “Royal disease.”. Biosens Bioelectron 131:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.02.006
Lakshmipriya T, Gopinath SCB (2019) An introduction to biosensors and biomolecules. Elsevier Inc.
Perumal V, Hashim U, Gopinath SCB, Haarindraprasad R, Foo KL, Balakrishnan SR, Poopalan P (2015) “Spotted Nanoflowers”: gold-seeded zinc oxide nanohybrid for selective bio-capture. Sci Rep 5:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12231
Sin LL, Arshad MKM, Fathil MFM et al (2016) Zinc oxide interdigitated electrode for biosensor application. AIP Conf Proc 1733:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4948893
Letchumanan I, Md Arshad MK, Balakrishnan SR, Gopinath SCB (2019) Gold-nanorod enhances dielectric voltammetry detection of c-reactive protein: a predictive strategy for cardiac failure. Biosens Bioelectron 130:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.042
Cao L, Kiely J, Piano M, Luxton R (2018) Facile and inexpensive fabrication of zinc oxide based bio-surfaces for C-reactive protein detection. Sci Rep 8:12687. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30793-z
Adam H, Gopinath SCB, Md Arshad MK, Ramanathan S, Ashokkumar T, Azan MIA, Adam T, Hashim U (2019) Fabrication of gold nanorod–zinc oxide nanocomposite on gap-fingered integrated interdigitated aluminum electrodes and their response to electrolytes. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 125:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-3106-7
Lakshmipriya T, Gopinath SCB, Hashim U, Tang TH (2016) Signal enhancement in ELISA: biotin-streptavidin technology against gold nanoparticles. J Taibah Univ Med Sci 11:432–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2016.05.010
Xiao Y (2013) Enzyme-Linked. J Immunol Methods 384:148–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2012.06.009.Enzyme-Linked
Victor dos Santos Junior C, Sader MS, Gonçalves GC et al (2018) Effect of pH on the adsorption and interactions of bovine serum albumin with functionalized silicon nitride surface. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 167:441–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.03.045
Song CK, Oh E, Kang MS, Shin BS, Han SY, Jung M, Lee ES, Yoon SY, Sung MM, Ng WB, Cho NJ, Lee H (2018) Fluorescence-based immunosensor using three-dimensional CNT network structure for sensitive and reproducible detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma biomarker. Anal Chim Acta 1027:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.04.025
Shetti NP, Nayak DS, Malode SJ, Kulkarni RM (2017) An electrochemical sensor for clozapine at ruthenium doped TiO2 nanoparticles modified electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 247:858–867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.03.102
Xu, Xue; Li, Mengzhi; Hu, Jun; Chen, Zheng; Yu, Jinyu; Dong, Yan; Sun, Chengtao; Han J (2018) Somatic mitochondrial DNA D - loop mutations in meningioma discovered : a preliminary data a comprehensive overview of mitochondrial DNA 4977-bp. J Cancer Res Ther 14:1525–1534. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcrt.JCRT
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2550 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Letchumanan, I., Gopinath, S.C.B. & Arshad, M.K.M. Divalent ion-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles for voltammetry Immunosensing: comparison of transducer signals in an assay for the squamous cell carcinoma antigen. Microchim Acta 187, 128 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4115-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4115-0