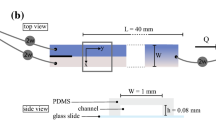
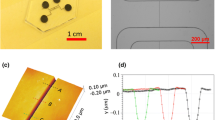
Abstract
The diffusive behavior of nanoparticles inside porous materials is attracting a lot of interest in the context of understanding, modeling, and optimization of many technical processes. A very powerful technique for characterizing the diffusive behavior of particles in free media is dynamic light scattering (DLS). The applicability of the method in porous media is considered, however, to be rather difficult due to the presence of multiple sources of scattering. In contrast to most of the previous approaches, the DLS method was applied without ensuring matching refractive indices of solvent and porous matrix in the present study. To test the capabilities of the method, the diffusion of spherical gold nanoparticles within the interconnected, periodic nanopores of inverse opals was analyzed. Despite the complexity of this system, which involves many interfaces and different refractive indices, a clear signal related to the motion of particles inside the porous media was obtained. As expected, the diffusive process inside the porous sample slowed down compared to the particle diffusion in free media. The obtained effective diffusion coefficients were found to be wave vector-dependent. They increased linearly with increasing spatial extension of the probed particle concentration fluctuations. On average, the slowing-down factor measured in this work agrees within combined uncertainties with literature data.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahadi, A., Giraudet, C., Jawad, H., Croccolo, F., Bataller, H., Saghir, M.Z.: Experimental, theoretical and numerical interpretation of thermodiffusion separation for a non-associating binary mixture in liquid/porous layers. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 80, 108–117 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2014.02.003
Beenakker, C.W.J., Mazur, P.: Diffusion of spheres in a concentrated suspension: resummation of many-body hydrodynamic interactions. Phys. Lett. A 98, 22–24 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-9601(83)90535-2
Berger Bioucas, F.E., Damm, C., Peukert, W., Rausch, M.H., Koller, T.M., Giraudet, C., Fröba, A.P.: Translational and rotational diffusion coefficients of gold nanorods dispersed in mixtures of water and glycerol by polarized dynamic light scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.9b08274
Berne, B.J., Pecora, R.: Dynamic Light Scattering: With Applications to Chemistry, Biology, and Physics. Dover Publications, New York (2000)
Beschieru, V., Rathke, B., Will, S.: Particle diffusion in porous media investigated by dynamic light scattering. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 125, 63–69 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2009.03.042
Bishop, M.T., Langley, K.H., Karasz, F.E.: Dynamic light-scattering studies of polymer diffusion in porous materials: linear polystyrene in porous glass. Macromolecules 22, 1220–1231 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00193a038
Bouchaud, J.-P.: Anomalous relaxation in complex systems: from stretched to compressed exponentials. In: Klages, R., Radons, G., Sokolov, I.M. (eds.) Anomalous Transport, pp. 327–345. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (2008)
Burada, P.S., Marchesoni, F., Hänggi, P., Talkner, P., Schmid, G.: Diffusion in confined geometries. ChemPhysChem 10, 45–54 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.200800526
Cadogan, S.P., Hahn, C.J., Rausch, M.H., Fröba, A.P.: Study on the applicability of dynamic light scattering (DLS) to microemulsions including supercritical carbon dioxide-swollen micelles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 499, 202–208 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.03.111
Cerbino, R., Trappe, V.: Differential dynamic microscopy: probing wave vector dependent dynamics with a microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 1–4 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.188102
Chen, J., Glaus, C., Laforest, R., Zhang, Q., Yang, M., Gidding, M., Welch, M.J., Xia, Y.: Gold nanocages as photothermal transducers for cancer treatment. Small 6, 811–817 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200902216
Cherdhirankorn, T., Retsch, M., Jonas, U., Butt, H.J., Koynov, K.: Tracer diffusion in silica inverse opals. Langmuir 26, 10141–10146 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/la1002572
Farré, M., Gajda-Schrantz, K., Kantiani, L., Barceló, D.: Ecotoxicity and analysis of nanomaterials in the aquatic environment. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 393, 81–95 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2458-1
Feitosa, M.I.M., Mesquita, O.N.: Wall-drag effect on diffusion of colloidal particles near surfaces: a photon correlation study. Phys. Rev. A 44, 6677–6685 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.44.6677
Fröba, A.P.: Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) for the Characterization of Working Fluids in Chemical and Energy Engineering, Habilitation thesis, Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen (2009)
Fröba, A.P., Leipertz, A.: Diffusion measurements in fluids by dynamic light scattering. Diffus. Fundam. 2, 63.1–63.25 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1021/j100245a035
Fukumura, D., Insin, N., Jain, R.K., Stylianopoulos, T., Bawendi, M.G., Poh, M.-Z., Munn, L.L.: Diffusion of particles in the extracellular matrix: the effect of repulsive electrostatic interactions. Biophys. J. 99, 1342–1349 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2010.06.016
Giraudet, C., Croccolo, F., Galliero, G., Pijaudier-Cabot, G., Van Vaerenbergh, S., Ziad Saghir, M., Montel, F., Bataller, H.: Thermodiffusion of the tetrahydronaphthalene and dodecane mixture under high pressure and in porous medium. Comptes Rendus Mécanique. 341, 340–347 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crme.2013.01.007
Haghighi, M., Tahir, M.N., Tremel, W., Butt, H.J., Steffen, W.: Translational and rotational diffusion of gold nanorods near a wall. J. Chem. Phys. 139, 064710 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4817405
Hatton, B., Mishchenko, L., Davis, S., Aizenberg, J., Sandhage, K.H.: Assembly of large-area, highly ordered, crack-free inverse opal films. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107, 10354–10359 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1000954107
He, K., Babaye Khorasani, F., Retterer, S.T., Thomas, D.K., Conrad, J.C., Krishnamoorti, R.: Diffusive dynamics of nanoparticles in arrays of nanoposts. ACS Nano 7, 5122–5130 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn4007303
Kimling, J., Maier, M., Okenve, B., Kotaidis, V., Ballot, H., Plech, A.: Turkevich method for gold nanoparticle synthesis revisited. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 15700–15707 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp061667w
Kluijtmans, S.G.J.M., Dhont, J.K.G., Philipse, A.P.: Dynamics of uncharged colloidal silica spheres confined in bicontinuous porous glass media. Langmuir 13, 4982–4987 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/la9701788
Knoll, M.S.G., Giraudet, C., Hahn, C.J., Rausch, M.H., Fröba, A.P.: Simultaneous study of molecular and micelle diffusion in a technical microemulsion system by dynamic light scattering. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 544, 144–154 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.02.070
Krott, L.B., Gavazzoni, C., Bordin, J.R.: Anomalous diffusion and diffusion anomaly in confined Janus dumbbells. J. Chem. Phys. 145, 244906 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4972578
Lemmon, E.W., Huber, M.L., McLinden, M.O.: REFPROP Reference Fluid Thermodynamic and Transport Properties, Standard Reference Database 23, Version 9.1. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (2013)
Li, Z.: Critical particle size where the Stokes–Einstein relation breaks down. Phys. Rev. E 80, 1–6 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.80.061204
Lu, A.H., Smått, J.H., Lindén, M.: Combined surface and volume templating of highly porous nanocast carbon monoliths. Adv. Funct. Mater. 15, 865–871 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200305183
McHugh, A.J., Brenner, H.: Particle size measurement using chromatography. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 15, 63–117 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408348408542776
Minakuchi, H., Ishizuka, N., Nakanishi, K., Soga, N., Tanaka, N.: Performance of an octadecylsilylated continuous porous silica column in polypeptide separations. J. Chromatogr. A 828, 83–90 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(98)00605-0
Neusius, T., Sokolov, I.M., Smith, J.C.: Subdiffusion in time-averaged, confined random walks. Phys. Rev. E 80, 011109 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.80.011109
Novikov, D.S., Fieremans, E., Jensen, J.H., Helpern, J.A.: Characterizing microstructure of living tissues with time-dependent diffusion. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1316944111
Over, B., Rathke, B., Will, S.: Investigations on particle diffusion in porous glass by angle-dependent dynamic light scattering. J. Mol. Liq. 222, 972–980 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.07.028
Phillips, K.R., England, G.T., Sunny, S., Shirman, E., Shirman, T., Vogel, N., Aizenberg, J.: A colloidoscope of colloid-based porous materials and their uses. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 281–322 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cs00533g
Phillips, K.R., Vogel, N., Hu, Y., Kolle, M., Perry, C.C., Aizenberg, J.: Tunable anisotropy in inverse opals and emerging optical properties. Chem. Mater. 26, 1622–1628 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm403812y
Piszko, M., Wu, W., Will, S., Rausch, M.H., Giraudet, C., Fröba, A.P.: Thermal and mutual diffusivities of fuel-related binary liquid mixtures under pre-combustion conditions. Fuel 242, 562–572 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.01.078
Raccis, R., Nikoubashman, A., Retsch, M., Jonas, U., Koynov, K., Butt, H.J., Likos, C.N., Fytas, G.: Confined diffusion in periodic porous nanostructures. ACS Nano 5, 4607–4616 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn200767x
Reverey, J.F., Jeon, J.-H., Bao, H., Leippe, M., Metzler, R., Selhuber-Unkel, C.: Superdiffusion dominates intracellular particle motion in the supercrowded cytoplasm of pathogenic Acanthamoeba castellanii. Sci. Rep. 5, 11690 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11690
Rička, J.: Dynamic light scattering with single-mode and multimode receivers. Appl. Opt. 32, 2860–2875 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.32.002860
Rička, J.: Brownian dynamics in strongly scattering porous media: DLS with single-mode matching. Macromol. Symp. 79, 45–55 (1994)
Schneider, D., Mehlhorn, D., Zeigermann, P., Kärger, J., Valiullin, R.: Transport properties of hierarchical micro–mesoporous materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 3439–3467 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CS00715A
Schröder, J.M., Wiegand, S.: Experimental suppression of multiple scattering: effect on dynamic and static scattering data. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2, 1493–1495 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1039/a909828c
Shibayama, M.: Universality and specificity of polymer gels viewed by scattering methods. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn 79, 1799–1819 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1246/bcsj.79.1799
Skaug, M.J., Schwartz, D.K.: Tracking nanoparticle diffusion in porous filtration media. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54, 4414–4419 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/ie503895b
Skaug, M.J., Wang, L., Ding, Y., Schwartz, D.K.: Hindered nanoparticle diffusion and void accessibility in a three-dimensional porous medium. ACS Nano 9, 2148–2156 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b00019
Starchev, K., Zhang, J., Buffle, J.: Applications of fluorescence correlation spectroscopy: particle size effect. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 203, 189–196 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcis.1998.5470
Turkevich, J., Stevenson, P.C., Hillier, J.: A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 11, 55–75 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1039/DF9511100055
Turkevich, J., Stevenson, P.C., Hillier, J.: The formation of colloidal gold. J. Phys. Chem. 57, 670–673 (1953). https://doi.org/10.1021/j150508a015
Valfouskaya, A., Adler, P.M., Thovert, J.-F., Fleury, M.: Nuclear-magnetic-resonance diffusion simulations in porous media. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 083510 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1871352
Valfouskaya, A., Adler, P.M., Thovert, J.-F., Fleury, M.: Nuclear magnetic resonance diffusion simulations with surface relaxation in porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 295, 188–201 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.08.021
Viswanathan, G.M., Raposo, E.P., da Luz, M.G.E.: Lévy flights and superdiffusion in the context of biological encounters and random searches. Phys. Life Rev. 5, 133–150 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plrev.2008.03.002
Wang, B., Kuo, J., Granick, S.: Burst of active transport in living cells. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 208102 (2013a). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.208102
Wang, C., Xu, H., Liang, C., Liu, Y., Li, Z., Yang, G., Cheng, L., Li, Y., Liu, Z.: Iron oxide @ polypyrrole nanoparticles as a multifunctional drug carrier for remotely controlled cancer therapy with synergistic antitumor effect. ACS Nano 7, 6782–6795 (2013b). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn4017179
Wang, Z., Volinsky, A.A., Gallant, N.D.: Crosslinking effect on polydimethylsiloxane elastic modulus measured by custom-built compression instrument. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 131, 1–4 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41050
Xi, D., Dong, S., Meng, X., Lu, Q., Meng, L., Yec, J.: Gold nanoparticles as computerized tomography (CT) contrast agents. RSC Adv. 2, 12515–12524 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra21263c
Acknowledgements
This work was supported financially by the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG) by funding the Erlangen Graduate School in Advanced Optical Technologies (SAOT) within the German Excellence Initiative and by funding the Cluster of Excellence Engineering of Advanced Materials (EAM) and the Interdisciplinary Center for Functional Particle Systems (FPS). N. Vogel acknowledges funding from the DFG under Grant Number VO1824/9-1. C. Giraudet and A.P. Fröba thank Michael Eichhorn for providing access to the inverted microscope used in the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giraudet, C., Knoll, M.S.G., Galvan, Y. et al. Diffusion of Gold Nanoparticles in Inverse Opals Probed by Heterodyne Dynamic Light Scattering. Transp Porous Med 131, 723–737 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-019-01364-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-019-01364-1