Abstract
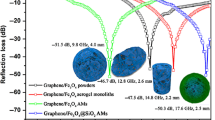
Although graphene aerogels (GA) have been attracted great attention, the easy-operation and large-scale production of GA are still challenges. Further, most GA have a monolith-like appearance, limiting their application-specific needs. Herein, we highlight graphene aerogel spheres with controllable hollow structures (HGAS) that are delicately designed and manufactured via coaxial electrospinning coupled with freeze-drying and calcination. The HGAS exhibit a spherical configuration at the macroscale, while the construction elements of graphene on the microscale showing an interconnected radial microchannel structure. Further, ball-in-ball graphene aerogel spheres (BGAS) are obtained by reference to the triaxial electrospinning technology. The as-prepared spheres possess the controllable integrated conductive networks, leading to the effective dielectric loss and impedance matching, thus bringing on high-performance microwave absorption. The as-obtained HGAS shows a minimum reflection loss of -52.7 dB, and a broad effective absorption bandwidth (fE) of 7.0 GHz with thickness of 2.3 mm. Further, the fE reaches 9.3 GHz for BGAS with thickness of 3.4 mm. Aforementioned superior microwave absorption of HGAS and BGAS confirms combination of multiaxial electrospinning and freeze-drying on the multiscale is an effective strategy for scalable fabrication of advanced microwave absorbing functional graphene aerogel spheres.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balci, O.; Polat, E. O.; Kakenov, N.; Kocabas, C. Graphene-enabled electrically switchable radar-absorbing surfaces. Nat. Commun.2015, 6, 6628.
Wen, B.; Cao, M. S.; Lu, M. M.; Cao, W. Q.; Shi, H. L.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. X.; Jin, H. B.; Fang, X. Y.; Wang, W. Z. et al. Reduced graphene oxides: Light-weight and high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperatures. Adv. Mater.2014, 26, 3484–3489.
Cao, M. S.; Song, W. L.; Hou, Z. L.; Wen, B.; Yuan, J. The effects of temperature and frequency on the dielectric properties, electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave-absorption of short carbon fiber/ silica composites. Carbon2010, 48, 788–796.
Guo, Y. R; Li, J. Y; Meng, F. B.; Wei, W.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. G; Peng, F. X.; Zhou, Z. W. Hybridization-induced polarization of graphene sheets by intercalation-polymerized polyaniline towards high performance of microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2019, 77, 17100–17107.
Chen, Z. P.; Xu, C.; Ma, C. Q.; Ren, W. C; Cheng, H. M. Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater.2013, 25, 1296–1300.
Chen, H. H.; Huang, Z. Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Z.; Qin, B.; Liu, Z. R; Shi, Q.; Xiao, P. S.; Yang, Y. et al. Synergistically assembled MWCNT/graphene foam with highly efficient microwave absorption in both C and X bands. Carbon2017, 124, 506–514.
Meng, F. B.; Wang, H. G; Wei, W.; Chen, Z. J.; Li, T.; Li, C. Y.; Xuan, Y.; Zhou, Z. W. Generation of graphene-based aerogel microspheres for broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption by electrospinning-freeze drying process. Nana Res.2018, 77, 2847–2861.
Nardecchia, S.; Carriazo, D.; Ferrer, M. L.; Gutierrez, M. C.; del Monte, F. Three dimensional macroporous architectures and aerogels built of carbon nanotubes and/or graphene: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev.2013, 42, 794–830.
Zhu, C.; Han, T. Y. J.; Duoss, E. B.; Golobic, A. M.; Kuntz, J. D.; Spadaccini, C. M.; Worsley, M. A. Highly compressible 3D periodic graphene aerogel microlattices. Nat. Commun.2015, 6, 6962.
Jiang, Y. Q.; Xu, Z.; Huang, T. Q.; Liu, Y. J.; Guo, F.; Xi, J. B.; Gao, W. W.; Gao, C. Direct 3D printing of ultralight graphene oxide aerogel microlattices. Adv. Funct. Mater.2018, 28, 1707024.
Wang, C. H; Chen, X.; Wang, B.; Huang, M.; Wang, B.; Jiang, Y; Ruoff, R. S. Freeze-casting produces a graphene oxide aerogel with a radial and centrosymmetric structure. ACS Nana2018, 12, 5816–5825.
Fang, Z. G; Cao, X. M.; Li, C.S.; Zhang, H. T; Zhang, J. S.; Zhang, H. Y. Investigation of carbon foams as microwave absorber: Numerical prediction and experimental validation. Carbon2006, 44, 3368–3370.
Bao, C. L.; Bi, S. G.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. L.; Wang, P. F; Yue, C. Y.; Yang, J. L. Graphene oxide beads for fast clean-up of hazardous chemicals. J. Mater. Chem. A2016, 4, 9437–9446.
Zhang, Q. Q.; Zhang, F.; Xu, X.; Zhou, C.; Lin, D. Three-dimensional printing hollow polymer template-mediated graphene lattices with tailorable architectures and multifunctional properties. ACS Nana2018, 12, 1096–1106.
Zheng, Q. F; Kvit, A.; Cai, Z. Y.; Ma, Z. Q.; Gong, S. Q. A freestanding cellulose nanofibril-reduced graphene oxide-nolybdenum oxynitride aerogel film electrode for all-solid-state supercapacitors with ultrahigh energy density. J. Mater. Chem. A2017, 5, 12528–12541.
Xi, J. B.; Li, Y. L.; Zhou, E. Z.; Liu, Y. J.; Gao, W. W.; Guo, Y.; Ying, J.; Chen, Z. C.; Chen, G. G.; Gao, C. Graphene aerogel films with expansion enhancement effect of high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon2018, 135, 44–51.
Zhao, C. Z.; Fan, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T. Microfluidics-generated graphene oxide microspheres and their application to removal of perfluorooctane sulfonate from polluted water. Nana Res.2016, 9, 866–875.
Bi, H. C.; Yin, K. B.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Y. L.; Wan, N.; Xu, F.; Banhart, F.; Sun, L. T; Ruoff, R. S. Low temperature casting of graphene with high compressive strength. Adv. Mater.2012, 24, 5124–5129.
Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T. F.; Chang, H. C.; Xiao, P. S.; Chen, H. H; Huang, Z. Y.; Chen, Y. S. Broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption of an ultralight and highly compressible graphene foam. Adv. Mater.2015, 27, 2049–2053.
Xu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q. Q.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Z. B.; Li, J. H; Li, J. Y.; Qiao, Y.; Gogotsi, Y. Self-sensing, ultralight, and conductive 3D graphene/iron oxide aerogel elastomer deformable in a magnetic field. ACS Nano2015, 9, 3969–3977.
Du, X. S.; Liu, H. Y.; Mai, Y. W. Ultrafast synthesis of multifunctional N-doped graphene foam in an ethanol flame. ACS Nana2016, 10, 453–462.
Kudin, K. N.; Ozbas, B.; Schniepp, H. C.; Prud’homme, P. K.; Aksay I. A.; Car, R. Raman spectra of graphite oxide and functionalized graphene sheets. Nana Lett.2008, 8, 36–41.
Liao, S. C; Zhai, T. L.; Xia, H. S. Highly adsorptive graphene aerogel microspheres with center-diverging microchannel structures. J. Mater. Chem. A2016, 4, 1068–1077.
Meng, F. B.; Wang, H. G.; Huang F.; Guo, Y. F.; Wang, Z. Y.; Hui, D.; Zhou, Z. W. Graphene-based microwave absorbing composites: Areview and prospective. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 137, 260–277.
Liu, X. R; Nie, X. Y.; Yu, R. H.; Feng, H. B. Design of dual-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption by interface modulation strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 153–161.
Wang, K. R.; Chen, Y. J.; Tian, R.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, H. N.; Liu, H. Z. Porous Co-C core-shell nanocomposites derived from Co-MOF-74 with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2018, 10, 11333–11342.
Wang, H. G; Meng, F. B.; Huang, F.; Jing, C. F.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhou, Z. W. Interface modulating CNTs@PANi hybrids by controlled unzipping of the walls of CNTs to achieve tunable high-performance microwave absorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2019, 11, 12142–12153.
Zhang, W. L.; Jiang, D.; Wang, X. X.; Hao, B. N.; Liu, Y. D.; Liu, J. Q. Growth of polyaniline nanoneedles on MoS2 nanosheets, tunable electroresponse, and electromagnetic wave attenuation analysis. J. Phys. Chem. C2017, 727, 4989–4998.
Meng, F. B.; Liu, X. B. Hyperbranched copper phthalocyanine decorated Fe3O4 microspheres with extraordinary microwave absorption properties. RSC Adv.2015, 5, 7018–7022.
Wei, S.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, B. Q.; Yu, M. X.; Zheng, Y. W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Q. Preparation of hierarchical core-shell C@NiCo204@Fe3O4 composites for enhanced microwave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 477–487.
Zhang, X. J.; Zhu, J. Q.; Yin, P. G; Guo, A. P.; Huang, A. P.; Guo, L.; Wang, G. S. Tunable high-performance microwave absorption of Coi1-xS hollow spheres constructed by nanosheets within ultralow filler loading. Adv. Funt. Mater.2018, 28, 1800761.
Cao, M. S.; Han, C.; Wang, X. X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y. L.; Shu, J. C; Yang, H. J.; Fang, X. Y; Yuan, J. Graphene nanohybrids: Excellent electromagnetic properties for the absorbing and shielding of electromagnetic waves. J. Mater. Chem. C2018, 6, 4586–4602.
Wang, H. C; Meng, F. B.; Li, J. Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Z. J.; Luo, H. B.; Zhou, Z. W. Carbonized design of hierarchical porous carbon/Fe304@Fe derived from loofah sponge to achieve tunable high-performance microwave absorption. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 11801–11810.
Meng, F. B.; Wei, W.; Chen, X. G; Xu, X. L.; Jiang, M.; Lu, J.; Wang Y.; Zhou, Z. W. Design of porous C@Fe304 hybrid nanotubes with excellent microwave absorption. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 2510–2516.
Cao, M. S.; Wang, X. X.; Cao, W. Q.; Fang, X. Y.; Wen, B.; Yuan, J. Thermally driven transport and relaxation switching self-powered electromagnetic energy conversion. Small2018, 14, 1800987.
Cao, W. Q.; Wang, X. X.; Yuan, J.; Wang, W. Z.; Cao, M. S. Temperature dependent microwave absorption of ultrathin graphene composites. J. Mater. Chem. C2015, 3, 10017–10022.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51903213) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Sichuan Province (Nos. 2018GZ0132 and 2018GZ0427).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
12274_2020_2632_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Multiaxial electrospun generation of hollow graphene aerogel spheres for broadband high-performance microwave absorption
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Zhi, D., Chen, Y. et al. Multiaxial electrospun generation of hollow graphene aerogel spheres for broadband high-performance microwave absorption. Nano Res. 13, 477–484 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2632-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2632-0