Abstract
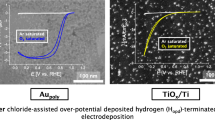
“Approximate” Pt layers hold great promise to be highly active and durable oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalysts. Electrodeposition of such layers on relevant catalyst supports, for example TiOx, requires the application of a “Pt-on-Pt” deposition limiter to keep layers thin and leave no atom behind for catalysis. Classic Pt-on-Pt deposition limiting agents like CO and over-potential deposited hydrogen (Hopd) work reliably on gold but fail on TiOx substrates. Iodide, in contrast, is a new “Pt-on-Pt” deposition limiting agent that shows substantial Pt layer thickness reduction during electrodeposition on gold as well as TiOx substrates.

Limitations are not always a bad thing: The addition of NaI during Pt electrodeposition from Ar-saturated 0.1 mM K2PtCl4 + 0.1 M HClO4 solution limits the Pt deposition amount and leads to a substantial reduction in Pt layer thickness and a concurrent increase in ORR mass activity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.C.K. Vesborg, T.F. Jaramillo, Addressing the terawatt challenge: scalability in the supply of chemical elements for renewable energy. RSC Adv. 2, 7933–7947 (2012)
H.A. Gasteiger, J. Garche, Fuel Cells (Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis, 2008)
Statista. Number of cars sold worldwide from 1990 to 2018 (in million units). 2018.
H.A. Gasteiger, N.M. Marković, Just a dream—or future reality? Science. 324, 48 (2009)
M.K. Debe, Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells. Nature. 486(7401), 43–51 (2012)
M. Shao, Q. Chang, J.-P. Dodelet, R. Chenitz, Recent advances in electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Rev. 116(6), 3594–3657 (2016)
Harkness I, Sharman J. Fibrous Pt Catalysts Created with ALD-Deposited Pt on Oxide, Carbide or Nitride Surface Tie Layers Where the Pt Deposits Extend over the Surface in Large Contiguous Islands or as Continuous Film. Novel Catalyst Structures Employing Pt at Ultra Low and Zero Loadings for Automotive MEAs (CATAPULT); 2014.
Harkness I, Sharman J, Bosund M, Geppert T, El-Sayed H, Gasteiger HA, et al. Demonstration of Pt-Catalysed Non-Carbon Support with Higher Mass Activity than Conventional Pt/C Nanoparticles and in Excess of 0.15 A/Mg Pt. Novel Catalyst Structures Employing Pt at Ultra Low and Zero Loadings for Automotive MEAs (CATAPULT); 2014.
M.K. Debe, Tutorial on the fundamental characteristics and practical properties of nanostructured thin film (NSTF) catalysts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 160, F522–FF34 (2013)
M.K. Debe, Nanostructured thin film electrocatalysts for PEM fuel cells - a tutorial on the fundamental characteristics and practical properties of NSTF catalysts. ECS Trans. 45, 47–68 (2012)
M.K. Debe, R.T. Atanasoski, A.J. Steinbach, Nanostructured thin film electrocatalysts - current status and future potential. ECS Trans. 41, 937–954 (2011)
M. Watanabe, S. Saegusa, P. Stonehart, High platinum electrocatalyst utilizations for direct methanol oxidation. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 271, 213–220 (1989)
M. Watanabe, H. Sei, P. Stonehart, The influence of platinum crystallite size on the electroreduction of oxygen. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 261, 375–387 (1989)
M. Nesselberger, M. Roefzaad, R. Fayçal Hamou, P. Ulrich Biedermann, F.F. Schweinberger, S. Kunz, et al., The effect of particle proximity on the oxygen reduction rate of size-selected platinum clusters. Nat. Mater. 12(10), 919–924 (2013)
J. Speder, L. Altmann, M. Baumer, J.J.K. Kirkensgaard, K. Mortensen, M. Arenz, The particle proximity effect: from model to high surface area fuel cell catalysts. RSC Adv. 4, 14971–14978 (2014)
J. Speder, I. Spanos, A. Zana, J.J.K. Kirkensgaard, K. Mortensen, L. Altmann, et al., From single crystal model catalysts to systematic studies of supported nanoparticles. Surf. Sci. 631, 278–284 (2015)
S. Proch, K. Kodama, M. Inaba, K. Oishi, N. Takahashi, Y. Morimoto, The “Particle Proximity Effect” in three dimensions: a case study on Vulcan XC 72R. Electrocatalysis. 7, 249–261 (2016)
J. Huang, J. Zhang, M.H. Eikerling, Particle proximity effect in nanoparticle electrocatalysis: surface charging and electrostatic interactions. J. Phys. Chem. C 121, 4806–4815 (2017)
S. Proch, S. Yoshino, N. Takahashi, J. Seki, S. Kosaka, K. Kodama, et al., The native oxide on titanium metal as a conductive model substrate for oxygen reduction reaction studies. Electrocatalysis. 9, 608–622 (2018)
S. Proch, S. Yoshino, Y. Kamitaka, N. Takahashi, J. Seki, K. Kodama, Hydrogen treatment as potential protection of electrodeposited Pt, Au, and Pt/Au oxygen reduction catalysts on TiOx. Electrocatalysis. 10, 1–16 (2019)
Proch S, Yoshino S, Kitazumi K, Seki J, Kodama K, Morimoto Y. Over-potential deposited hydrogen (Hopd) as terminating agent for platinum and gold electro(co)deposition. Electrocatalysis. 2019.
R. Borup, J. Meyers, B. Pivovar, Y.S. Kim, R. Mukundan, N. Garland, D. Myers, M. Wilson, F. Garzon, D. Wood, P. Zelenay, K. More, K. Stroh, T. Zawodzinski, J. Boncella, J. McGrath, M. Inaba, K. Miyatake, M. Hori, K. Ota, Z. Ogumi, S. Miyata, A. Nishikata, Z. Siroma, Y. Uchimoto, K. Yasuda, K. Kimijima, N. Iwashita, Scientific aspects of polymer electrolyte fuel cell durability and degradation. Chem. Rev. 107(10), 3904–3951 (2007)
Y. Shao-Horn, W.C. Sheng, S. Chen, P.J. Ferreira, E.F. Holby, D. Morgan, Instability of supported platinum nanoparticles in low-temperature fuel cells. Top. Catal. 46, 285–305 (2007)
N.R. Elezovic, V.R. Radmilovic, N.V. Krstajic, Platinum nanocatalysts on metal oxide based supports for low temperature fuel cell applications. RSC Adv. 6, 6788–6801 (2016)
C.A. Reiser, L. Bregoli, T.W. Patterson, J.S. Yi, J.D. Yang, M.L. Perry, et al., A reverse-current decay mechanism for fuel cells. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 8, A273–A2A6 (2005)
F.N. Buechi, T.J. Schmidt, Polymer electrolyte fuel cell durability (Springer Science + Business Media, LLC., New York, 2009)
A. Michaelis, in Advances in Electrochemical Science and Engineering, ed. by R. C. Alkire, D. M. Kolb, J. Lipkowski, P. N. Ross. Valve metal, Si and ceramic oxides as dielectric films for passive and active electronic devices (WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2008), pp. 1–106
C. Zhang, H. Yu, Y. Li, Y. Gao, Y. Zhao, W. Song, Z. Shao, B. Yi, Supported noble metals on hydrogen-treated TiO2 nanotube arrays as highly ordered electrodes for fuel cells. ChemSusChem. 6(4), 659–666 (2013)
S. Proch, K. Kodama, S. Yoshino, N. Takahashi, N. Kato, Y. Morimoto, CO-terminated platinum electrodeposition on Nb-doped bulk rutile TiO2. Electrocatalysis. 7, 362–375 (2016)
M. Nakada, A. Ishihara, S. Mitsushima, N. Kamiya, Ota K-i. Effect of tin oxides on oxide formation and reduction of platinum particles. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 10, F1–F4 (2007)
B.E. Hayden, Particle size and support effects in electrocatalysis. Acc. Chem. Res. 46(8), 1858–1866 (2013)
B.E. Hayden, D. Pletcher, J.-P. Suchsland, L.J. Williams, The influence of Pt particle size on the surface oxidation of titania supported platinum. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11(10), 1564–1570 (2009)
B.E. Hayden, D. Pletcher, J.-P. Suchsland, L.J. Williams, The influence of support and particle size on the platinum catalysed oxygen reduction reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11(40), 9141–9148 (2009)
D. Schäfer, C. Mardare, A. Savan, M.D. Sanchez, B. Mei, W. Xia, M. Muhler, A. Ludwig, W. Schuhmann, High-throughput characterization of Pt supported on thin film oxide material libraries applied in the oxygen reduction reaction. Anal. Chem. 83(6), 1916–1923 (2011)
A. Ghicov, P. Schmuki, Self-ordering electrochemistry: a review on growth and functionality of TiO2 nanotubes and other self-aligned MOx structures. Chem. Commun. 2019, 2791–2808 (2009)
K. Lee, A. Mazare, P. Schmuki, One-dimensional titanium dioxide nanomaterials: nanotubes. Chem. Rev. 114(19), 9385–9454 (2014)
S. Proch, S. Yoshino, I. Gunjishima, S. Kosaka, N. Takahashi, N. Kato, et al., Acetylene-treated titania nanotube arrays (TNAs) as support for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) platinum thin film catalysts. Electrocatalysis. 8, 351–365 (2017)
S. Proch, S. Yoshino, N. Kato, N. Takahashi, Y. Morimoto, Titania nanotube arrays (TNAs) as support for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) platinum thin film catalysts. Electrocatalysis. 7, 451–465 (2016)
S. Proch, S. Yoshino, N. Takahashi, S. Kosaka, K. Kodama, Y. Morimoto, CO-terminated Pt/Au codeposition on titania nanotube arrays (TNAs). Electrocatalysis. 8, 480–491 (2017)
S. Brimaud, R.J. Behm, Electrodeposition of a Pt monolayer film: using kinetic limitations for atomic layer epitaxy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135(32), 11716–11719 (2013)
Y. Liu, D. Gokcen, U. Bertocci, T.P. Moffat, Self-terminating growth of platinum films by electrochemical deposition. Science. 338(6112), 1327–1330 (2012)
D. Kim, J. Kim, Effect of anionic electrolytes and precursor concentrations on the electrodeposited Pt structures. Electroanalysis. 29, 387–391 (2017)
G. Jerkiewicz, Electrochemical hydrogen adsorption and absorption. Part 1: under-potential deposition of hydrogen. Electrocatalysis. 1, 179–199 (2010)
D. Sazou, K. Saltidou, M. Pagitsas, Understanding the effect of bromides on the stability of titanium oxide films based on a point defect model. Electrochim. Acta 76, 48–61 (2012)
D.C. Johnson, A study of the adsorption and desorption of iodine and iodide at platinum electrodes in 1.0M sulfuric acid. J. Electrochem. Soc. 119, 331–339 (1972)
D. Strmcnik, M. Uchimura, C. Wang, R. Subbaraman, N. Danilovic, van der V, et al. Improving the hydrogen oxidation reaction rate by promotion of hydroxyl adsorption. Nat. Chem. 5(4), 300–306 (2013)
A.J. Bard, L.R. Faulkner, Electrochemical Methods - Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd edn. (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 2001)
M. Nesselberger, S. Ashton, J.C. Meier, I. Katsounaros, K.J.J. Mayrhofer, M. Arenz, The particle size effect on the oxygen reduction reaction activity of Pt catalysts: influence of electrolyte and relation to single crystal models. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133(43), 17428–17433 (2011)
J. Perez, E.R. Gonzalez, H.M. Villullas, Hydrogen evolution reaction on gold single-crystal electrodes in acid solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 10931–10935 (1998)
G. Jerkiewicz, Hydrogen sorption ATIN electrodes. Prog. Surf. Sci. 57, 137–186 (1998)
X.-Q. Gong, A. Selloni, O. Dulub, P. Jacobson, U. Diebold, Small Au and Pt clusters at the anatase TiO2(101) surface: behavior at terraces, steps, and surface oxygen vacancies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(1), 370–381 (2008)
S.M. Alia, B.A. Larsen, S. Pylypenko, D.A. Cullen, D.R. Diercks, K.C. Neyerlin, et al., Platinum-coated nickel nanowires as oxygen-reducing electrocatalysts. ACS Catal. 4, 1114–1119 (2014)
Y. Garsany, O.A. Baturina, K.E. Swider-Lyons, S.S. Kocha, Experimental methods for quantifying the activity of platinum electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Anal. Chem. 82(15), 6321–6328 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Proch, S., Yoshino, S., Seki, J. et al. Iodide as Terminating Agent for Platinum Electrodeposition. Electrocatalysis 11, 14–24 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-019-00562-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12678-019-00562-1