Abstract
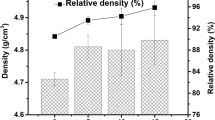
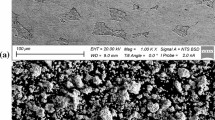
The wear resistance of iron (Fe)-matrix materials could be improved through the in situ formation of vanadium carbide particles (VCp) with high hardness. However, brittleness and low impact toughness limit their application in several industries due to addition of higher carbon content. Carbon-partitioning treatment plays an important role in tuning the microstructure and mechanical properties of in situ VCp-reinforced Fe-matrix composite. In this study, the influences of carbon-partitioning temperatures and times on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and wear resistance of in situ VCp-reinforced Fe-matrix composite were investigated. The experimental results indicated that a certain amount of retained austenite could be stabilized at room temperature through the carbon-partitioning treatment. Microhardness of in situ VCp-reinforced Fematrix composite under carbon-partitioning treatment could be decreased, but impact toughness was improved accordingly when wear resistance was enhanced. In addition, the enhancement of wear resistance could be attributed to transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect, and phase transformation was caused from γ-Fe (face-centered cubic structure, fcc) to α-Fe (body-centered cubic structure, bcc) under a certain load.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.R. Moskalyk and M.A. Alfantazi, Processing of vanadium: a review, Miner. Eng., 16(2003), No. 9, p. 793.
M. Radulovic, M. Fiset, K. Peev, and M. Tomovic, The influence of vanadium on fracture toughness and abrasion resistance in high chromium white cast irons, J. Mater. Sci., 29(1994), No. 19, p. 5085.
L.S. Zhong, M. Hojamberdiev, F.X. Ye, W. Hong, and Y.H. Xu, Fabrication and microstructure of in situ vana-dium carbide ceramic particulates-reinforced iron matrix composites, Ceram. Int., 39(2013), No. 1, p. 731.
L. He, Y. Liu, B.H. Li, H. Cao, and J. Li, Reaction synthesis of in situ vanadium carbide particulates-reinforced iron matrix composites by spark plasma sintering, J. Mater. Sci., 45(2010), No. 9, p. 2538.
L.S. Zhong, F.X. Ye, Y.H. Xu, and J.S. Li, Microstructure and abrasive wear characteristics of in situ vanadium carbide particulate-reinforced iron matrix composites, Mater. Des., 54(2014), p. 564.
Y.S. Wang, Y.C. Ding, J. Wang, F.J. Cheng, and J.G. Shi, In situ production of vanadium carbide particulates rein-forced iron matrix surface composite by cast-sintering, Mater. Des., 28(2007), No. 7, p. 2202.
M. Kawalec and E. Olejnik, Abrasive wear resistance of cast iron with precipitates of spheroidal VC carbides, Arch. Foundry Eng., 12(2012), No. 2, p. 221.
W.M. Zhao, ZX. Liu, Z.L. Ju, B. Liao, and X.G. Chen, Effects of vanadium and rare-earth on carbides and properties of high chromium cast iron, Mater. Sci. Forum, 575–578(2008), p. 1414.
F.X. Ye, M. Hojamberdiev, Y.H. Xu, L.S. Zhong, H.H. Yan, and Z. Chen, (Fe,Cr)7C3-Fe surface gradient composite: Microstructure, microhardness, and wear resistance, Mater. Chem. Phys., 147(2014), No. 3, p. 823.
S.Z. Wei, J.H. Zhu, and L.J. Xu, Research on wear resistance of high speed steel with high vanadium content, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 404(2005), No. 1–2, p. 138.
S.Z. Wei, J.H. Zhu, and L.J. Xu, Effects of vanadium and carbon on microstructures and abrasive wear resistance of high speed steel, Tribol. Int., 39(2006), No. 7, p. 641.
S.Z. Wei, J.H. Zhu, L.J. Xu, and R. Long, Effects of carbon on microstructures and properties of high vanadium high-speed steel, Mater. Des., 27(2006), No. 1, p. 58.
JX. Liu, ZW. Shi, P.J. Ying, S.Z. Guo, W.L. Ji, and R. Long, Effect of carbon on frictional wear behaviours of high vanadium high speed steel under dry sliding condition, Mater. Sci. Forum, 654–656(2010), p. 370.
L.J. Xu, J.D. Xing, S.Z. Wei, Y.Z. Zhang, and R. Long, Study on relative wear resistance and wear stability of highspeed steel with high vanadium content, Wear, 262(2007), No. 3–4, p. 253.
M. Kriiger, High temperature compression strength and oxidation of a V-9Si-13B alloy, Scripta Mater, 121(2016), p. 75.
P.H. Chen, Z.L. Liu, R.Q. Li, and X.Q. Li, The effect of manganese additions on the high temperature oxidation behaviour of the high-vanadium cast iron, J. Alloys Compd., 767(2018), p. 181.
P.H. Chen, R.Q. Li, R.P. Jiang, S.S. Zeng, Y. Zhang, and X.Q. Li, High-temperature oxidation resistance of VCps-re-inforced Fe-matrix composites using an in-situ reaction, AIPAdv., 9(2019), No. 1, p. 015319.
V.F. Zackay, M.D. Bhandarkar, and E.R. Parker, The role of deformation-induced phase transformations in the plasticity of some iron-base alloys, [In] J.J. Burke and V. Weiss, eds., Advances in Deformation Processing, Boston, MA, 1978, p. 351.
L. Skalova, R. Divisova, and D. Jandova, Thermo-mechanical processing of low-alloy TRIP-steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 175(2006), No. 1–3, p. 387.
J. Speer, D.K. Matlock, B.C. de Cooman, and J.G. Schroth, Carbon partitioning into austenite after martensite trans-formation, Acta Mater, 51(2003), No. 9, p. 2611.
J.G. Speer, E. De Moor, K.O. Findley, D.K. Matlock, B.C. de Cooman, and D.V. Edmonds, Analysis of microstruc-ture evolution in quenching and partitioning automotive sheet steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 42(2011), No. 12, p. 3591.
V.F. Zackay and T.H. Hazlett, Some plastic properties of nickel alloys, Acta Metall, 1(1953), No. 6, p. 624.
P.J. Gibbs, E. de Moor, M.J. Merwin, B. Clausen, J.G. Speer, and D.K. Matlock, Austenite stability effects on tensile behavior of manganese-enriched-austenite transformation-induced plasticity steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 42(2011), No. 12, p. 3691.
M. Mansourinejad and M. Ketabchi, Influence of strain state on the kinetics of martensitic transformation induced plasticity (TR.P. in AISI 304 stainless steel, Steel Res. Int., 89(2018), No. 3, p. 1700359.
A.J. Clarke, J.G. Speer, M.K. Mller, RE. Hackenberg, D.V. Edmonds, D.K. Matlock, F.C. Rizzo, K.D. Clarke, and E. De Moor, Carbon partitioning to austenite from martensite or bainite during the quench and partition (Q&P) process: A critical assessment, Acta Mater, 56(2008), No. 1, p. 16.
J.G. Speer, D.V. Edmonds, F.C. Rizzo, and D.K. Matlock, Partitioning of carbon from supersaturated plates of ferrite, with application to steel processing and fundamentals of the bainite transformation, Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 8(2004), No. 3–4, p. 219.
Z.C. Li, H. Ding, R.D.K. Misra, Z.H. Cai, and H.X. Li, M-crostructural evolution and deformation behavior in the Fe-(6, 8.5)Mn-3Al-0.2C.TRI. steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 672(2016), p. 161.
P.H. Chen, Y.B. Li, R.Q. Li, R.P. Jiang, S.S. Zeng, and X.Q. Li, Mcrostructure, mechanical properties, and wear resistance of VCp-reinforced Fe-matrix composites treated by Q&P process, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater, 25(2018), No. 9, p. 1060.
E. De Moor, S. Lacroix, A.J. Clarke, J. Penning, and J.G. Speer, Effect of retained austenite stabilized via quench and partitioning on the strain hardening of martensitic steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 39(2008), p. 2586.
X.C. Xiong, B. Chen, MX. Huang, J.F. Wang, and L. Wang, The effect of morphology on the stability of retained austenite in a quenched and partitioned steel, Scripta Mater, 68(2013), No. 5, p. 321.
L.J. Xu, S.Z. Wei, J.D. Xing, and R. Long, Effects of carbon content and sliding ratio on wear behavior of high-vanadium high-speed steel (HVH.S. under high-stress rolling-sliding contact, Tribol. Int., 70(2014), p. 34.
VG. Efremenko, K. Shimizu, A.P. Cheiliakh, TV. Kozar-evskaya, K. Kusumoto, and K. Yamamoto, Effect of vanadium and chromium on the micro structural features of V-Cr-Mn-Ni spheroidal carbide cast irons, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater, 21(2014), No. 11, p. 1096.
L.J. Xu, J.D. Xing, S.Z. Wei, Y.Z. Zhang, and R. Long, Investigation on wear behaviors of high-vanadium high-speed steel compared with high-chromium cast iron under rolling contact condition, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 434(2006), No. 1–2, p. 63.
L.J. Xu, S.Z. Wei, F.N. Xiao, H. Zhou, G.S. Zhang, and JW. Li, Effects of carbides on abrasive wear properties and failure behaviours of high speed steels with different alloy element content, Wear, 376–377(2017), p. 968.
VG. Efremenko, K. Shimizu, A.P. Cheiliakh, TV. Pastuk-hova, YG. Chabak, and K. Kusumoto, Abrasive resistance of metastable V-Cr-Mn-Ni spheroidal carbide cast irons using the factorial design method, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater, 23(2016), No. 6, p. 645.
VG. Efremenko, K. Shimizu, TV. Pastukhova, YG. Chabak, K. Kusumoto, and A.V. Efremenko, Effect of bulk heat treatment and plasma surface hardening on the micro-structure and erosion wear resistance of complex-alloyed cast irons with spheroidal vanadium carbides, J. Frict. Wear, 38(2017), No. 1, p. 58.
V. Efremenko, K. Shimizu, T. Pastukhova, Y. Chabak, M. Brykov, K. Kusumoto, and A. Efremenko, Three-body ab-rasive wear behaviour of metastable spheroidal carbide cast irons with different chromium contents, Int. J. Mater. Res., 109(2018), No. 2, p. 147.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the China Postdoctoral Foundation (No. 2019M650339), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (No. 2019A1515011858), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (No. 2019JJ50807), the State Key Laboratory of High Performance Complex Manufacturing, China (No. ZZYJKT2017-01), the DGUT Innovation Center of Robotics and Intelligent Equipment of China (No. KCYCXPT2017006), and the Key Laboratory of Robotics and Intelligent Equipment of Guangdong Regular Institutions of Higher Education, China (No. 2017KSYS009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Ph., Zhang, Y., Li, Rq. et al. Influence of carbon-partitioning treatment on the microstructure, mechanical properties and wear resistance of in situ VCp-reinforced Fe-matrix composite. Int J Miner Metall Mater 27, 100–111 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1909-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-019-1909-3