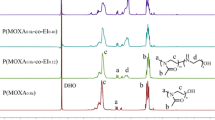
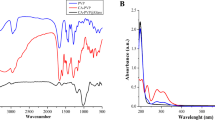
Abstract
Poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) has been widely used in the field of microfluidics, optical systems, and sensors. However, the hydrophobic nature of PDMS leads to low surface wettability and biofouling problems due to the nonspecific proteins–hydrophobic surface interactions and cell/bacterial adhesion. In this work, the PDMS surface was first introduced with amino groups (PDMS-NH2) via KOH-catalyzed reaction with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES). The PDMS-NH2 was then grafted with poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP) based on the self-adhesion reaction between the amino surface and catechol-functionalized PVP (CA-PLL-PVP). CA-PLL-PVP as a comb-polymer was synthesized by conjugating PVP-COOH along with caffeic acid to the ε-polylysine backbone. A significantly enhanced water wettability was observed with contact angles dropped from 116° to 14° after coating with CA-PLL-PVP. The coated surface demonstrated excellent antifouling performance that no appreciable Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation could be observed. This novel facile antifouling coating on PDMS surface may find greater biomedical applications to eliminate the potential adherence problems caused by natural biofouling.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ren, K., Chen, Y., & Wu, H. (2014). New materials for microfluidics in biology. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 25, 78–85.
Schneider, F., Fellner, T., Wilde, J., & Wallrabe, U. (2008). Mechanical properties of silicones for MEMS. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 18(6), 065008.
Shih, T.-K., Chen, C.-F., Ho, J.-R., & Chuang, F.-T. (2006). Fabrication of PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) microlens and diffuser using replica molding. Microelectronic Engineering, 83(11–12), 2499–2503.
Zhang, H., & Chiao, M. (2015). Anti-fouling coatings of poly (dimethylsiloxane) devices for biological and biomedical applications. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 35(2), 143–155.
Sui, G., Wang, J., Lee, C.-C., Lu, W., Lee, S. P., Leyton, J. V., Wu, A. M., & Tseng, H.-R. (2006). Solution-phase surface modification in intact poly (dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic channels. Analytical Chemistry, 78(15), 5543–5551.
Hoek, I., Tho, F., & Arnold, W. M. (2010). Sodium hydroxide treatment of PDMS based microfluidic devices. Lab on a Chip, 10(17), 2283–2285.
Zhang, J., Chen, Y., & Brook, M. A. (2013). Facile functionalization of PDMS elastomer surfaces using thiol–ene click chemistry. Langmuir, 29(40), 12432–12442.
Brook, M. A., Zhao, S., Liu, L., & Chen, Y. (2011). Surface etching of silicone elastomers by depolymerization. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 90(1), 153–160.
Chen, H., Zhang, Z., Chen, Y., Brook, M. A., & Sheardown, H. (2005). Protein repellant silicone surfaces by covalent immobilization of poly (ethylene oxide). Biomaterials, 26(15), 2391–2399.
Guo, D.-J., Han, H.-M., Xiao, S.-J., & Dai, Z.-D. (2007). Surface-hydrophilic and protein-resistant silicone elastomers prepared by hydrosilylation of vinyl poly (ethylene glycol) on hydrosilanes-poly (dimethylsiloxane) surfaces. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 308(1–3), 129–135.
Wang, A.-J., Feng, J.-J., & Fan, J. (2008). Covalent modified hydrophilic polymer brushes onto poly (dimethylsiloxane) microchannel surface for electrophoresis separation of amino acids. Journal of Chromatography A, 1192(1), 173–179.
Yeh, P. Y., Zhang, Z., Lin, M., & Cao, X. (2012). Nonfouling hydrophilic poly (ethylene glycol) engraftment strategy for PDMS/SU-8 heterogeneous microfluidic devices. Langmuir, 28(46), 16227–16236.
Seo, J.-H., Shibayama, T., Takai, M., & Ishihara, K. (2011). Quick and simple modification of a poly (dimethylsiloxane) surface by optimized molecular design of the anti-biofouling phospholipid copolymer. Soft Matter, 7(6), 2968–2976.
Kuo, W.-H., Wang, M.-J., Chien, H.-W., Wei, T.-C., Lee, C., & Tsai, W.-B. (2011). Surface modification with poly (sulfobetaine methacrylate-co-acrylic acid) to reduce fibrinogen adsorption, platelet adhesion, and plasma coagulation. Biomacromolecules, 12(12), 4348–4356.
Keefe, A. J., Brault, N. D., & Jiang, S. (2012). Suppressing surface reconstruction of superhydrophobic PDMS using a superhydrophilic zwitterionic polymer. Biomacromolecules, 13(5), 1683–1687.
Wu, Z., Tong, W., Jiang, W., Liu, X., Wang, Y., & Chen, H. (2012). Poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone)-modified poly (dimethylsiloxane) elastomers as anti-biofouling materials. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 96, 37–43.
Liu, X., Tong, W., Wu, Z., & Jiang, W. (2013). Poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone)-grafted poly (dimethylsiloxane) surfaces with tunable microtopography and anti-biofouling properties. RSC Advances, 3(14), 4716–4722.
Liu, X., Xu, Y., Wu, Z., & Chen, H. (2013). Poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone)-modified surfaces for biomedical applications. Macromolecular Bioscience, 13(2), 147–154.
Lee, H., Dellatore, S. M., Miller, W. M., & Messersmith, P. B. (2007). Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science, 318(5849), 426–430.
Kang, S. M., Hwang, N. S., Yeom, J., Park, S. Y., Messersmith, P. B., Choi, I. S., Langer, R., Anderson, D. G., & Lee, H. (2012). One-step multipurpose surface functionalization by adhesive catecholamine. Advanced Functional Materials, 22(14), 2949–2955.
Li, A., Mu, Y., Jiang, W., & Wan, X. (2015). A mussel-inspired adhesive with stronger bonding strength under underwater conditions than under dry conditions. Chemical Communications, 51(44), 9117–9120.
Mosaiab, T., Jeong, C. J., Shin, G. J., Choi, K. H., Lee, S. K., Lee, I., In, I., & Park, S. Y. (2013). Recyclable and stable silver deposited magnetic nanoparticles with poly (vinyl pyrrolidone)-catechol coated iron oxide for antimicrobial activity. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 33(7), 3786–3794.
Au-Duong, A.-N., & Lee, C.-K. (2018). Facile protein-resistant and anti-biofilm surface coating based on catechol-conjugated poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone). Colloid and Polymer Science, 296(7), 1173–1182.
Le, T.-N., Au-Duong, A.-N., & Lee, C.-K. (2019). Facile coating on microporous polypropylene membrane for antifouling microfiltration using comb-shaped poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone) with multivalent catechol. Journal of Membrane Science, 574, 164–173.
Aroua, S., Tiu, E. G. V., Ayer, M., Ishikawa, T., & Yamakoshi, Y. (2015). RAFT synthesis of poly (vinylpyrrolidone) amine and preparation of a water-soluble C 60-PVP conjugate. Polymer Chemistry, 6(14), 2616–2619.
Torchilin, V., Levchenko, T., Whiteman, K., Yaroslavov, A., Tsatsakis, A., Rizos, A., Michailova, E., & Shtilman, M. (2001). Amphiphilic poly-N-vinylpyrrolidones:: synthesis, properties and liposome surface modification. Biomaterials, 22(22), 3035–3044.
Weng, L., Rostamzadeh, P., Nooryshokry, N., Le, H. C., & Golzarian, J. (2013). In vitro and in vivo evaluation of biodegradable embolic microspheres with tunable anticancer drug release. Acta Biomaterialia, 9(6), 6823–6833.
Le, T. N., Au-Duong, A. N., & Lee, C. K. (2019). Facile coating on microporous polypropylene membrane for antifouling microfiltration using comb-shaped poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone) with multivalent catechol. Journal of Membrane Science, 574, 164–173.
Kim, J., Chaudhury, M. K., Owen, M. J., & Orbeck, T. (2001). The mechanisms of hydrophobic recovery of polydimethylsiloxane elastomers exposed to partial electrical discharges. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 244(1), 200–207.
Mack, D., Becker, P., Chatterjee, I., Dobinsky, S., Knobloch, J. K. M., Peters, G., Rohde, H., & Herrmann, M. (2004). Mechanisms of biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus: functional molecules, regulatory circuits, and adaptive responses. International Journal of Medical Microbiology, 294(2–3), 203–212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The presenting author of this manuscript in ACB2019 is Trong-Nghia Le
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2616 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, TN., Lee, CK. Surface Functionalization of Poly(N-Vinylpyrrolidone) onto Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) for Anti-Biofilm Application. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 191, 29–44 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03238-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03238-5