Abstract
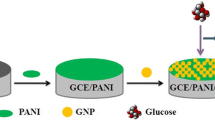
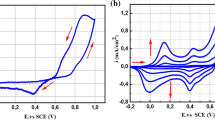
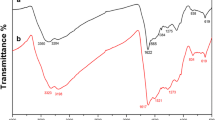
This study aims the amperometric enzyme-free glucose sensing of interlayered Polyaniline nanosheets @reduced grapheme oxide (PANINS@rGO). Conductive PANINS were synthesized using in situ chemical oxidative polymerization method. The PANINS@rGO nanocomposite was prepared by the solution mixing method and as-synthesized material was fully examined using various spectroscopy and microscopy techniques. PANINS@rGO composite coated on screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) was studied for electrochemical behaviour for the detection of non-enzymatic glucose. The fabricated sensor matrix was tested towards detection of glucose efficacy using cyclic voltammetry (CV) and Chronoamperometry (CA) techniques in the presence of 0.1 M NaOH electrolyte in a range of 1–10 mM at an optimum working potential of 60 mV s−1. PANINS@rGO/SPCE absorbed with high sensitivity (3448.27 μA mM−1 cm−2) and excellent low detection limit (LOD) 30 nM, (S/N = 3). Furthermore, the obtained results of the proposed PANINS@rGO/SPCE fabricated a finite sensor for non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Thus this report proves the practical opportunities for the development of environmentally benign, cost effective and chemically stable electrode materials for sensors, which may be beneficial for the expansion of economically viable enzyme free electrochemical glucose sensor devices.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.J. Zhai, J.H. Li, X.Y. Chu, M.Z. Xu, F.J. Jin, X. Li, X. Fang, Z.P. Wei, X.H. Wang, MoS2 microflowers based electrochemical sensing platform for non-enzymatic glucose detection. J. Alloys Compd. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.02.130
A.D. Association, Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 37, S81–S90 (2014)
D.W. Hwang, S. Lee, M. Seo, T.D. Chung, Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors—a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 1033, 1–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.05.051
S.A. Zaidi, J.H. Shin, Recent developments in nanostructure based electrochemical glucose sensors. Talanta 140, 30–42 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.11.033
L. Liu, W. Qi, X. Gao, C. Wang, G. Wang, Synergistic effect of metal ion additives on graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet-templated electrodeposition of Cu@CuO for enzymefree glucose detection. J. Alloys Compd. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.02.19
R. Rebelo, A.I. Barbosa, D. Caballero, I.K. Kwon, J.M. Oliveira, S.C. Kundu, R.L. Reis, V.M. Correlo, 3D biosensors in advanced medical diagnostics of high mortality diseases. Biosens. Bioelectron. 130, 20–39 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.12.057
M.S. Steiner, A. Duerkop, O.S. Wolfbeis, Optical methods for sensing glucose. Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 4805–4839 (2011)
P.W. Barone, R.S. Parker, M.S. Strano, In Vivo fluorescence detection of glucose using a single-walled carbon nanotube optical sensor: design, fluorophore properties, advantages, and disadvantages. Anal. Chem. 77, 7556–7562 (2005)
J. Luo, P. Luo, M. Xie, K. Du, B. Zhao, F. Pan, P. Fan, F. Zeng, D. Zhang, Z. Zheng, G. Liang, A new type of glucose biosensor based on surface acoustic wave resonator using Mn-doped ZnO multilayer structure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 49, 512–518 (2013)
J. Tian, S. Liu, Y. Luo, X. Sun, Fe(III)-based coordination polymer nanoparticles: peroxidase-like catalytic activity and their application to hydrogen peroxide and glucose detection. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2, 432–436 (2012)
G. Wang, X. He, L. Wang, A. Gu, Y. Huang, B. Fang, B. Geng, X. Zhang, Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of glucose. Microchim. Acta 180, 161–186 (2013)
D. Zhai, B. Liu, Y. Shi, L. Pan, Y. Wang, W. Li, R. Zhang, G. Yu, Highly sensitive Glucose sensor based on Pt nanoparticle/polyaniline hydrogel heterostructures. ACS Nano 7, 3540–3546 (2013)
X. Kang, J. Wang, H. Wu, I.A. Aksay, J. Liu, Y. Lin, Glucose oxidase-graphene Chitosan modified electrode for direct electrochemistry and glucose sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 25, 901–905 (2009)
S. Liu, J. Tian, L. Wang, Y. Luo, W. Lu, X. Sun, Self-assembled graphene platelet Glucose oxidase nanostructures for glucose biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26, 4491–4496 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0923-1
W.-C. Lee, K.-B. Kim, N.G. Gurudatt, K.K. Hussain, C.S. Choi, D.-S. Park, Y.-B. Shim, Comparison of enzymatic and non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on hierarchical Au-Ni alloy with a conductive polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.028
N. Karikalan, M. Velmurugan, S.M. Chen, C. Karuppiah, Modern approach to the synthesis of Ni (OH) 2 decorated sulfur doped carbon nanoparticles for the nonenzymatic glucose sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 22545–22553 (2016)
S. Radhakrishnan, J. Mathiyarasu, Graphene–carbon nanotubes modified electrochemical sensors, in Graphene-based electrochemical sensors for biomolecules, ed. by A. Pandikumar, P. Rameshkumar (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019), pp. 187–205
A. Mahmoud, M. Echabaane, K. Omri, L. El Mir, R.B. Chaabane, Development of an impedimetric non-enzymatic sensor based on ZnO and Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles for the detection of glucose. J. Alloys Compd. 786, 960–968 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.060
L. Sinha, S. Pakhira, P. Bhojane, S. Mali, C.K. Hong, P.M. Shirage, Hybridization of Co3O4 and α-MnO2 nanostructures for high-performance nonenzymatic glucose sensing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 6(10), 13248–13261 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b02835
Y. Xie, Y. Song, Y. Zhang, L. Xu, L. Miao, C. Peng, L. Wang, Cu metalorganic framework-derived Cu Nanospheres@Porous carbon/macroporous carbon for electrochemical sensing glucose. J. Alloys Compd. 235, 97–102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.064
H. Dai, P. Cao, D. Chen, Y. Li, N. Wang, H. Ma, M. Lin, Ni-Co-S/PPy core-shell nanohybrid on nickel foam as a non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor. Synth. Met. 235, 97–102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2017.12.004
S. Komathi, A.I. Gopalan, N. Muthuchamy, K.P. Lee, Polyaniline nanoflowers grafted onto nanodiamonds via a soft template-guided secondary nucleation process for high-performance glucose sensing. RSC Adv. 7(25), 15342–15351 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra24760a
K. Justice Babu, S. Sheet, Y.S. Lee, G. Gnana Kumar, Three-dimensional dendrite Cu−Co/reduced graphene oxide architectures on a disposable pencil graphite electrode as an electrochemical sensor for nonenzymatic glucose detection. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03314
G.G. Wallace, P.R. Teasdale, G.M. Spinks, L.A. Kane-Maguire, Conductive electroactive polymers: intelligent materials systems (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2002)
R. Arukula, M. Vinothkannan, A.R. Kim, D.J. Yoo, Cumulative effect of bimetallic alloy, conductive polymer and graphene toward electrooxidation of methanol: an efficient anode catalyst for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Alloys Compd. 771, 477–488 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.08.303
M. Jaymand, Recent progress in chemical modification of polyaniline. Progr. Polym. Sci. 38(9), 1287–1306 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2013.05.015
C. Xiong, T. Li, Y. Zhu, T. Zhao, A. Dang, H. Li, X. Ji, Y. Shang, M. Khan, Two-step approach of fabrication of interconnected nanoporous 3D reduced graphene oxide-carbon nanotube-polyaniline hybrid as a binder-free supercapacitor electrode. J. Alloys Compd. 695, 1248–1259 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.10.253
H. Wang, L. Ma, M. Gan, T. Zhou, "Design and fabrication of macroporous polyaniline nanorods@ graphene-like MoS2 nanocomposite with the high electrochemical performance for supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 699, 176–182 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.344
J. Wang, Z. Wu, K. Hu, X. Chen, H. Yin, High conductivity graphene-like MoS2/polyaniline nanocomposites and its application in a supercapacitor. J. Alloys Compd. 619, 38–43 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.09.008
Z. Zhou, S. Gu, Y. Zhang, F. Wu, N. Zhou, Lithium storage performance improvement of NaTi2 (PO4) 3 with nitrogen-doped carbon derived from Polyaniline,". J. Alloys Compd. 767, 745–752 (2018)
N. Chen, Y. Ren, P. Kong, L. Tan, H. Feng, Y. Luo, In situ one-pot preparation of reduced graphene oxide/polyaniline composite for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 392, 71–79 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.07.168
M. Mitra, C. Kulsi, K. Chatterjee, K. Kargupta, S. Ganguly, D. Banerjee, S. Goswami, Reduced graphene oxide-polyaniline composites—synthesis, characterization and optimization for thermoelectric applications. RSC Adv. 5(39), 31039–31048 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra01794g
A. Bhattacharya, A. De, Conducting polymers in solution—progress toward processibility. J. Macromol. Sci. C 39, 17–56 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1081/MC-100101416
K. Krukiewicz, A. Katunin, The effect of the reaction medium on the conductivity and morphology of polyaniline doped with camphorsulfonic acid. A Synth. Met. 214, 45–49 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2016.01.017
K. Tzou, R.V. Gregory, A method to prepare soluble polyaniline salt solutions—in situ doping of PANI base with organic dopants in polar solvents. Synth. Met. 53(3), 365–377 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0379-6779(93)91106-C
A. Esmaeeli, A. Ghaffarinejad, A. Zahedi, O. Vahidi, Copper oxide-polyaniline nanofiber modified fluorine doped tin oxide (FTO) electrode as a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Sens. Actuators B 266, 294–301 (2018)
Q. Xu, S.-X. Gu, L. Jin, Y.-E. Zhou, Z. Yang, W. Wang, X. Hu, Graphene/polyaniline/gold nanoparticles nanocomposite for the direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase and glucose biosensing. Sens. Actuators B 190, 562–569 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.09.049
S. Bilal, W. Ullah, Polyaniline@ CuNi nanocomposite: a highly selective, stable and efficient electrode material for binder free non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Electrochim. Acta 284, 382–391 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.07.165
Y. Kong, Y. Sha, Y. Tao, Y. Qin, H. Xue, M. Lu, Non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on nickel hexacyanoferrate/polyaniline hybrids on graphene prepared by a one-step process. J. Electrochem. Soc. 161(12), B269–B274 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0961412jes
Y. Wang, J. Zhong, F. Ding, Q. Zhao, Z. Zhang, X. Liu, Y. Liu, H. Rao, P. Zou, X. Wang, A bifunctional NiCo2S4/reduced graphene oxide@ polyaniline nanocomposite as a highly-efficient electrode for glucose and rutin detection. New J. Chem. 42(12), 9398–9409 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NJ00663F
K. Ghanbari, F. Ahmadi, NiO hedgehog-like nanostructures/Au/polyaniline nanofibers/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite with electrocatalytic activity for non-enzymatic detection of glucose. Anal. Biochem. 518, 143–153 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.11.020
M. Xu, Y. Song, Y. Ye, C. Gong, Y. Shen, L. Wang, L. Wang, A novel flexible electrochemical glucose sensor based on gold nanoparticles/polyaniline arrays/carbon cloth electrode. Sens. Actuators B 252, 1187–1193 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.147
S. Kailasa, B. Geeta, N. Jayrambabu, R. Kiran Kumar Reddy, S. Sharma, K. Venkateswara Rao, Conductive polyaniline nanosheets (CPANINS) for a non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Mater. Lett. 245, 118–121 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.02.103
H. Wu, J. Fan, E. Liu, X. Hu, Y. Ma, X. Fan, Y. Li, C. Tang, Facile hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2 nanospindles-reduced graphene oxide composite with enhanced photocatalytic activity. J. Alloys Compd. 623, 298–303 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.10.153
M. Ghorbani, H. Abdizadeh, M.R. Golobostanfard, Reduction of graphene oxide via modified hummers method. Procedia Mater. Sci. 11, 326–330 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2015.11.104
W. Zheng, L. Hu, L.Y. Lee, K.Y. Wong, Copper nanoparticles/polyaniline/graphene composite as a highly sensitive electrochemical glucose sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 781, 155–160 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.08.004
A. Viswanathan, A.N. Shetty, Single-step synthesis of rGO, copper oxide and polyaniline nanocomposites for high energy supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 289, 204–217 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.09.033
Y. Wang, Z. Hua, L. Jia, H. Li, T. Li, C. Kai, Y. Gu, Optimizing the polymerization conditions of soluble polyaniline doped with itaconic acid. J. Macromol. Sci. A 51(7), 577–581 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2014.916179
S. Kailasa et al., Twisted polyaniline nanobelts@ rGO for room temperature NO2 sensing. Mater. Lett. 257, 126687 (2019)
H. Zeghioud, S. Lamouri, Z. Safidine, M. Belbachir, Chemical synthesis and characterization of highly soluble conducting polyaniline in mixtures of common solvents. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 80(7), 917–931 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC140719003Z
A. Chiolerio, S. Bocchini, F. Scaravaggi, S. Porro, D. Perrone, D. Beretta, C.F. Pirri, Synthesis of polyaniline-based inks for inkjet printed devices: electrical characterization highlighting the effect of primary and secondary doping. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 30(10), 104001 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0268-1242/30/10/104001
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Centre for Nanoscience and Technology, Institute of Science Technology, JNTU Hyderabad.
Funding
The authors did not receive any research fund or grant from any organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kailasa, S., Reddy, R.K.K., Reddy, M.S.B. et al. High sensitive polyaniline nanosheets (PANINS) @rGO as non-enzymatic glucose sensor. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31, 2926–2937 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02837-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02837-1