Abstract
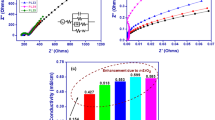
The paper reports effect of dispersion of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanofiller on the sodium ion conducting nanocomposite polymer electrolyte membranes consisting of TiO2 dispersed membranes of poly(vinylidenedifluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (PVdF-HFP) soaked in a liquid electrolyte of sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF6) in ethylene carbonate (EC) and propylene carbonate (PC). The TiO2 dispersed membranes have been prepared by phase inversion technique. The structural and morphological properties of the polymer electrolyte membranes have been investigated using x-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscopy. The membranes have been found to be highly porous with maximum porosity ~ 72% and liquid electrolyte uptake ~ 270%. Ionic conductivity of the electrolyte membranes containing different concentrations of TiO2 has been measured by complex impedance spectroscopy. The maximum room temperature ionic conductivity has been found to be ~ 1.3 × 10−3 S cm−1. The ionic conductivity measured with temperature has been found to follow VTF behavior. The ion transport numbers of the membranes have been studied using dc polarization, complex impedance, and cyclic voltammetry. The membranes have been found to be predominantly ionically conducting with Na+ transport number ~ 0.31. The electrochemical stability window of the membranes has also been measured using cyclic voltammetry and found to be 3.5 V.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwang JY, Myung ST, Sun YK (2017) Sodium-ion batteries: present and future. Chem Soc Rev 4(12):3529–3614
Nayak PK, Yang L, Brehm W, Adelhelm P (2018) From lithium-ion to sodium-ion batteries: advantages, challenges, and surprises. Angew Chem Int Ed 57(1):102–120
Adelhelm P, Hartmann P, Bender CL, Busche M, Eufinger C, Janek J (2015) From lithium to sodium: cell chemistry of room temperature sodium-air and sodium-sulfur batteries. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 6(1):1016–1055
Ye YS, Rick J, Hwang BJ (2013) Ionic liquid polymer electrolytes. J Mater Chem A 1:2719
Wang Y, Song S, Xu C, Hu N, Molenda J, Lu L (2019) Development of solid-state electrolytes for sodium-ion battery – a short review. Nano Mater Sci 1(2):91–100
Goodenough JB, Singh P (2015) Review—solid electrolytes in rechargeable electrochemical cells. J Electrochem Soc 162(14):A2387–A2392
Agrawal RC, Pandey GP (2008) Solid polymer electrolytes: materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(223001):18
Prater KB (1994) Polymer electrolyte fuel cells: a review of recent developments. J Power Sources 51(1–2):129–144
Ngai KS, Ramesh S, Ramesh K, Juan JC (2016) A review of polymer electrolytes: fundamental, approaches and applications. Ionics 22(8):1259–1279
Mishra K (2013) Preparation, characterization and battery applications of proton conducting polymer electrolytes. Doctoral dissertation, Jaypee Institute of Information Technology
Cheng X, Pan J, Zhao Y, Liao M, Peng H (2018) Gel polymer electrolytes for electrochemical energy storage. Adv Energy Mater 8(7):1–16
Stephan AM (2006) Review on gel polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Eur Polym J 42(1):21–42
Feuillade G, Perche P (1975) Ion-conductive macromolecular gels and membranes for solid lithium cells. J Appl Electrochem 5(1):63–69
Harshlata, Mishra K, Rai DK (2018) Electro-chemical studies on sodium ion conducting gel polymer electrolyte of PVdF-HFP+NaPF6. AIP Conf Proc 2009(1):020041
Sharma J, Hashmi SA (2013) Magnesium ion transport in poly(ethylene oxide)-based polymer electrolyte containing plastic-crystalline succinonitrile. J Solid State Electrochem 17(8):2283–2291
Mishra K, Hashmi SA, Rai DK (2014) Studies on a proton battery using gel polymer electrolyte. High Perform Polym 26(6):672–676
Tarascon JM, Gozdz AS, Schmutz C, Shokoohi F, Warren PC (1996) Performance of Bellcore’s plastic rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ionics 86–88(PART 1):49–54
Huang X (2012) A lithium-ion battery separator prepared using a phase inversion process. J Power Sources 216:216–221
Pu W, He X, Wang L, Tian Z, Jiang C, Wan C (2006) Preparation of P (AN – MMA) microporous membrane for Li-ion batteries by phase inversion. J Membr Sci 280:6–9
Miao R, Liu B, Zhu Z, Liu Y, Li J, Wang X, Li Q (2008) PVDF-HFP-based porous polymer electrolyte membranes for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 184:420–426
Asghar MR, Zhang Y, Wu A, Yan X, Shen S, Ke C (2018) Preparation of microporous cellulose / poly (vinylidene fluoride- hexa fl uoropropylene) membrane for lithium ion batteries by phase inversion method. J Power Sources 379(July 2017):197–205
Shalu S, Singh VK, Singh RK (2015) Development of ion conducting polymer gel electrolyte membranes based on polymer PVdF-HFP, BMIMTFSI ionic liquid and the Li-salt with improved electrical, thermal and structural properties. J Mater Chem C 3(28):7305–7318
Saito Y, Stephan AM, Kataoka H (2003) Ionic conduction mechanisms of lithium gel polymer electrolytes investigated by the conductivity and diffusion coefficient. Solid State Ionics 160(1–2):149–153
Yadav N, Mishra K, Hashmi SA (2017) Optimization of porous polymer electrolyte for quasi-solid-state electrical double layer supercapacitor. Electrochim Acta 235:570–582
Liang B, Jiang Q, Tang S, Li S, Chen X (2016) Porous polymer electrolytes with high ionic conductivity and good mechanical property for rechargeable batteries. J Power Sources 307:320–328
Ahn J, Wang GX, Liu HK, Dou SX (2003) Nanoparticle-dispersed PEO polymer electrolytes for Li batteries. J Power Sources 121:422–426
Liu W, Liu N, Sun J, Hsu PC, Li Y, Lee HW, Cui Y (2015) Ionic conductivity enhancement of polymer electrolytes with ceramic nanowire fillers. Nano Lett 15(4):2740–2745
Croce F, Appetecchi GB, Persi L, Scrosati B (1998) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nature 394(6692):456–458
Yadav N, Mishra K, Hashmi SA (2018) Nanofiller-incorporated porous polymer electrolyte for electrochemical energy storage devices. High Perform Polym 30(8):957–970
Harshlata, Mishra K, Rai DK (2018) Sodium ion conducting polymer electrolyte membrane prepared by phase inversion technique. AIP Conf Proc 1942(1):140050
Deka M, Kumar A (2009) Ionic transport in P (VdF – HFP)–PEO based novel microporous polymer electrolytes. Bull Mater Sci 32(6):627–632
Idris NH, Wang J (2012) Microporous gel polymer electrolytes for lithium rechargeable battery application. J Power Sources 201(March):294–300
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Ionic liquid based sodium ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 181(8–10):416–423
Watanabe M, Nagano S, Sanui K, Ogata N (1988) Estimation of Li+ transport number in polymer electrolytes by the combination of complex impedance and potentiostatic polarization measurements. Solid State Ionics 28–30(PART 2):911–917
Martins P, Lopes AC, Lanceros-mendez S (2014) Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): determination, processing and applications. Prog Polym Sci 39(4):683–706
Kumar D, Suleman M, Hashmi SA (2011) Studies on poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexa fluoropropylene) based gel electrolyte nanocomposite for sodium – sulfur batteries. Solid State Ionics 202(1):45–53
Sim LN, Majid SR, Arof AK (2012) FTIR studies of PEMA / PVdF-HFP blend polymer electrolyte system incorporated with LiCF3SO3 salt. Vib Spectrosc 58:57–66
Leon A, Reuquen P, Garín C, Segura R, Vargas P, Zapata P, Orihuela PA (2017) FTIR and Raman characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles coated with polyethylene glycol as carrier for 2-methoxyestradiol. Appl Sci 7(49):1–9
Bhatt C, Swaroop R, Arya A, Sharma AL (2015) Effect of nano-filler on the properties of polymer nanocomposite films of PEO/PAN complexed with NaPF6. J Mat Science and Engg B 5(11–12):418–434
Sim LN, Majid SR, Arof AK (2014) Effects of 1–butyl–3–methyl imidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate ionic liquid in poly(ethyl methacrylate)/poly (vinylidenefluoride–co–hexafluoropropylene) blend based polymer electrolyte system. Electrochim Acta 123:190–197
Sharma S, Pathak D, Dhiman N, Kumar R, Kumar M (2019) FTIR, thermal and ionic conductivity studies of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Surf Innov 7(1):51–58
Mishra K, Hashmi SA, Rai DK (2013) Nanocomposite blend gel polymer electrolyte for proton battery application. J Solid State Electrochem 17(3):785–793
Pandey GP, Agrawal RC, Hashmi SA (2011) Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with fumed silica for rechargeable magnesium battery application. J Solid State Electrochem 15:2253–2264
Kumar D, Suleman M, Hashmi SA (2011) Studies on poly (vinylidene fl uoride-co-hexa fl uoropropylene) based gel electrolyte nanocomposite for sodium – sulfur batteries. Solid State Ionics 202(1):45–53
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Ion transport and ion – filler-polymer interaction in poly (methyl methacrylate)-based , sodium ion conducting , gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with silica nanoparticles. J Power Sources 195(15):5101–5108
Pandey GP, Agrawal RC, Hashmi SA (2009) Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with nanosized magnesium oxide. J Power Sources 190:563–572
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support received from Science and Engineering Research Board, a statutory body of Department of Science and Technology, Government of India (File No: YSS/2015/001234) and research facilities provided by JIIT, Noida. One of us (Harshlata) is also thankful to JIIT, Noida, for providing research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, H., Mishra, K. & Rai, D.K. Sodium ion conducting nanocomposite polymer electrolyte membrane for sodium ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 24, 521–532 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04490-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04490-4