Abstract
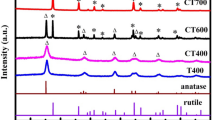
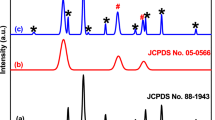
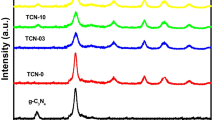
In order to produce a photocatalyst with increased visible photocatalytic ability, MIL-125 and melamine were selected as raw materials to prepare Z-scheme g-C3N4/TiO2 heterojunction photocatalyst using a simple calcination method. TEM, HRTEM, XRD, FTIR, EDS, and UV–vis absorption spectra were employed to investigate the prepared specimens. The visible-light catalytic property was examined via the degradation of methylene blue (MB). The recombination and separation activity of electrons and holes (h+/e−) were explored by the transient photocurrent response (TPR) and PL spectra. In contrast with plain TiO2 and g-C3N4, the g-C3N4/TiO2 photocatalyst exhibited increased photocatalytic activities when exposed to visible-light irradiation. With the addition of g-C3N4 at 8 wt%, the Z-scheme g-C3N4/TiO2 heterojunction performed best in the photocatalytic test toward MB dye at a degradation rate of 97.7%. Under visible-light irradiation, the Z-scheme heterojunction between g-C3N4 and TiO2 enables the high-efficient segregation of photogenic electrons and holes (h+/e−), leading to the increased photocatalytic ability. Meanwhile, the large specific surface area of the composite photocatalyst is conducive to the adsorption of the contaminant on the catalyst surface, which has an important effect on the catalytic reaction.

The direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/TiO2 was obtained by an in-situ heat treatment process with MIL-125 (Ti) and melamine as raw materials. The g-C3N4/TiO2 photocatalyst with 8 wt% g-C3N4 exhibited the optimal degradation efficiency, which was due to the high separation efficiency of photogenic electrons and holes (h+/e−) of the Z-scheme heterojunction.
Highlights
-
MOF-derived direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/TiO2 heterojunction photocatalyst was prepared.
-
The g-C3N4/TiO2 heterojunction photocatalyst with an amount of 8 wt% g-C3N4 has the best degradation efficiency.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang W, Yu J, Xiang Q (2012) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of hierarchical macro/mesoporous TiO2-graphene composites for photodegradation of acetone in air. Appl Catal B 109:119–120
Gong Y, Zhao X, Zhang H, Yang B, Xiao K, Guo T, Zhang J, Shao H, Wang Y, Yu G (2018) MOF-derived nitrogen doped carbon modified g-C3N4 heterostructure composite with enhanced photocatalytic activity for bisphenol A degradation with peroxymonosulfate under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B 233:35–45
Sun L, Wang G, Hao R, Han D, Cao S (2015) Solvothermal fabrication and enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of Cu2O-reduced graphene oxide composite microspheres for photodegradation of Rhodamine. B. Appl Surf Sci 358:91–99
G Wang, L Xu, J Zhang, T Yin, D Han (2012) A review on nanotube film photocatalysts prepared by liquid-phase deposition. Int J Photoenergy 2012:4651–4661
Fujishima A, Honda K (1972) Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 238:37–38
Liu L, Chen X (2014) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: self-structural modifications. Chem Rev 114:9890–9918
Fujishima A, Zhang X, Tryk DA (2008) TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf Sci Rep 63:515–582
Zhang L, Liu Q, Aoki T, Crozier P (2015) Structural evolution during photocorrosion of Ni/NiO core/shell cocatalyst on TiO2. J Phys Chem C 119:7207–7214
Zhang T, Tang X, Zhang J, Zhou T, Wang H, Wu C, Xia X, Xie C, Zeng D (2018) Metal-organic framework-assisted construction of TiO2/Co3O4 highly ordered necklace-like heterostructures for enhanced ethanol vapor sensing performance. Langmuir 34:14577–14585
Low J, Cheng B, Yu J (2017) Surface modification and enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction performance of TiO2: a review. Appl Surf Sci 392:658–686
Das SK, Bhunia MK, Bhaumik A (2010) Self-assembled TiO2 nanoparticles: mesoporosity, optical and catalytic properties. Dalton Trans 39:4382–4390
Hao R, Wang G, Tang H, Sun L, Xu C, Han D (2016) Template-free preparation of macro/mesoporous g-C3N4/TiO2 heterojunction photocatalysts with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B 187:47–58
Zhang L, Jing D, She X, Liu H, Yang D, Lu Y, Li J, Zheng Z, Guo L (2014) Heterojunctions in g-C3N4/TiO2(B) nanofibres with exposed (001) plane and enhanced visible-light photoactivity. J Mater Chem A 2:2071–2078
Liu Z, Sun D, Guo P, Leckie JO (2007) An efficient bicomponent TiO2/SnO2 nanofiber photocatalyst fabricated by electrospinning with a side-by-side dual spinneret method. Nano Lett 7:1081–1085
Cao T, Li Y, Wang C, Shao C, Liu Y (2011) A facile in situ hydrothermal method to SrTiO3/TiO2 nanofiber heterostructures with high photocatalytic activity. Langmiur 27:2946–2952
Ghassemi H, Harlow W, Mashtalir O, Beidaghi M, Lukatskaya M, Gogotsi Y, Taheri M (2014) In situ environmental transmission electron microscopy study of oxidation of two-dimensional Ti3C2 and formation of carbon-supported TiO2. J Mater Chem A 2:14339–14343
Wang X, Maeda K, Thomas A, Takanabe K, Xin G, Carlsson JM, Domen K, Antonietti M (2009) A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light. Nat Mater 8:76–80
Jiang L, Yuan X, Zeng G, Liang J, Wu Z, Wang H, Zhang J, Xiong T, Li H (2018) A facile band alignment of polymeric carbon nitride isotype heterojunctions for enhanced photocatalytic tetracycline degradation. Environ Sci: Nano 5:2604–2617
Shi Y, Jiang S, Zhou K, Bao C, Yu B, Qian X, Wang B, Hong N, Wen P, Gui Z (2013) Influence of g-C3N4 nanosheets on thermal stability and mechanical properties of biopolymer electrolyte nanocomposite films: a novel investigation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:429–437
Xia KX, Chen ZG, Yi JJ, Xu H, Yu YH, She XJ, Mo Z, Chen HX, Xu YG, Li HM (2018) Highly efficient visible-light-driven schottky catalyst MoN/2D g-C3N4 for hydrogen production and organic pollutants degradation. Ind Eng Chem Res 5727:8863–8870
Shiraishi Y, Kanazawa S, Sugano Y, Tsukamoto D, Sakamoto H, Ichikawa S, Hirai T (2016) Highly selective production of hydrogen peroxide on graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) photocatalyst activated by visible light. ACS Catal 4:774–780
Yu J, Wang S, Low J, Xiao W (2013) Enhanced photocatalytic performance of direct Z-scheme g-C3N4-TiO2 photocatalysts for the decomposition of formaldehyde in air. Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:16883–16890
Hao J, Zhang S, Ren F, Wang Z, Lei J, Wang X, Cheng T, Li L (2017) Synthesis of TiO2@g-C3N4 core-shell nanorod arrays with Z-scheme enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light. J Colloid Interface Sci 508:419–425
Wei Z, Liang F, Liu Y, Luo W, Wang J, Yao W, Zhu Y (2017) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of phenol-containing wastewater by TiO2/g-C3N4 hybrid heterostructure thin film. Appl Catal B 201:600–606
Wang S, Lin J, Wang X (2014) Semiconductor-redox catalysis promoted by metal-organic frameworks for CO2 reduction. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:14656–14660
Wang S, Yao W, Lin J, Ding Z, Wang X (2014) Cobalt imidazolate metal-organic frameworks photosplit CO2 under mild reaction conditions. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:1034–1038
Wang SB, Wang XC (2016) Imidazolium ionic liquids, imidazolylidene heterocyclic carbenes, and zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for CO2 capture and photochemical reduction. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:2308–2320
Fu Y, Sun D, Chen Y, Huang R, Ding Z, Fu X, Li Z (2012) An amine-functionalized titanium metal-organic framework photocatalyst with visible-light-induced activity for CO2 reduction. Angew Chem 51:3364–3367
Liu Q, Ai L, Jiang J (2018) MXene-derived TiO2@C/g-C3N4 heterojunctions for highly efficient nitrogen photofixation. J Mater Chem A 6:4102–4110
Ye L, Wang D, Chen S (2016) Fabrication and enhanced photoelectrochemical performance of MoS2/S-doped g-C3N4 heterojunction film. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8:5280–5289
Wen J, Xie J, Chen X, Li X (2017) A review on g-C3N4-based photocatalysts. Appl Surf Sci 391:72–123
Tong Z, Yang D, Xiao T, Tian V, Jiang Z (2015) Biomimetic fabrication of g-C3N4/TiO2 nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activity toward organic pollutant degradation. Chem Eng J 260:117–125
Ye C, Li J, Li Z, Li X, Fan X, Zhang L, Chen B, Tung C, Wu L (2015) Enhanced driving force and charge separation efficiency of protonated g-C3N4 for photocatalytic O2 evolution. ACS Catal 5:6973–6979
Wu Z, Gong C, Yu J, Sun L, Xiao W, Lin C (2017) Enhanced visible light photoelectrocatalytic activity over CuxZn1–xIn2S4@TiO2 nanotube array hetero-structures. J Mater Chem A 5:1292–1299
Xu Z, Yu J (2011) Visible-light-induced photoelectrochemical behaviors of Fe-modified TiO2 nanotube arrays. Nanoscale 3:3138–3144
Acknowledgements
The research is supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. ZR2018BEM019, ZR2017LEM006), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51802117), Youth Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant No. BS2011CL028) and the Shandong Jiaotong University “Climbing” Research Innovation Team Program. We acknowledge TopEdit LLC for linguistic editing and proofreading during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, J., Wang, Y., Xu, M. et al. MOF-derived the direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/TiO2 with enhanced visible photocatalytic activity. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 93, 123–130 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05172-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05172-3