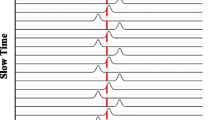
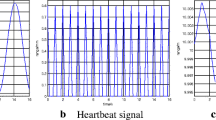
Abstract
Contactless detection of human beings via extracting vital sign features (VSF) is a perfect technology by employing an ultra-wideband radar. Only using Fourier transform, it is a challenging task to extract VSF in a complex environment, which can cause a lower signal to noise ratio (SNR) and significant errors due to the harmonics. This paper proposes an improved signal processing algorithm for VSF extraction via analyzing the skewness and standard deviation of the collected impulses. The discrete windowed Fourier transform technique is used to estimate the time of arrival of the pulses. The frequency of human breathing movements is obtained using an accumulation scheme in frequency domain, which can better cancel out the harmonics. The capabilities of removing clutters and improving SNR are validated compared with several well-known methods experimentally.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, B. (1977). Short term spectral analysis, synthesis, and modification by discrete fourier transform. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 25(3), 235–238.
Ascione, M., et al. (2013). A new measurement method based on music algorithm for through-the-wall detection of life signs. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 62(1), 13–26.
Baldi, M., et al. (2015). Non-invasive UWB sensing of astronauts’ breathing activity. Sensors, 15(1), 565–591.
Conte, E., Filippi, A., & Tomasin, S. (2010). ML period estimation with application to vital sign monitoring. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 17(11), 905–908.
Gennarelli, G., Ludeno, G., & Soldovieri, F. (2016). Real-time through-wall situation awareness using a microwave doppler radar sensor. Remote Sensing, 8(8), 621.
Gu, C., & Li, C. (2015). Assessment of human respiration patterns via noncontact sensing using doppler multi-radar system. Sensors, 15(3), 6383–6398.
Hu, X., & Jin, T. (2016). Short-range vital signs sensing based on EEMD and CWT using IR-UWB radar. Sensors, 16(12), 2025.
Hu, W., et al. (2014). Noncontact accurate measurement of cardiopulmonary activity using a compact quadrature Doppler radar sensor. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 61(3), 725–735.
Huang, Q., Qu, L., & Fang, G. (2010). UWB through-tall imaging based on compressive sensing. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 48(3), 1408–1415.
Huang, M. C., et al. (2016). A self-calibrating radar sensor system for measuring vital signs. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 10(2), 352–363.
JalaliBidgoli, F., Moghadami, S., & Ardalan, S. (2016). A compact portable microwave life-detection device for finding survivors. IEEE Embedded Systems Letters, 8(1), 10–13.
Koo, Y. S., et al. (2013). UWB MicroDoppler radar for human gait analysis, tracking more than one person, and vital sign detection of moving persons. In IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest, Seattle, WA, USA (pp. 1–4).
Lazaro, A., Girbau, D., & Villarino, R. (2014). Techniques for clutter suppression in the presence of body movements during the detection of respiratory activity through UWB radars. Sensors, 14(2), 2595–2618.
Le, C., et al. (2009). Ultra-wideband radar imaging of building interior: Measurements and predictions. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 47(5), 1409–1420.
Li, W. Z. (2013). A new method for non-line-of-sight vital sign monitoring based on developed adaptive line enhancer using low centre frequency UWB radar. Progress in Electromagnetics Research, 133(34), 535–554.
Li, C., & Lin, J. (2008). Random body movement cancellation in Doppler radar vital sign detection. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 56(12), 3143–3152.
Li, Z., et al. (2013). A novel method for respiration-like clutter cancellation in life detection by dual-frequency IR-UWB radar. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 61(5), 2086–2092.
Li, J., et al. (2014). Advanced signal processing for vital sign extraction with applications in UWB radar detection of trapped victims in complex environments. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 7(3), 783–791.
Liang, S. D. (2016). Sense-through-wall human detection based on UWB radar sensors. Signal Process, 126, 117–124.
Liang, X., et al. (2017). Energy detector based TOA estimation for MMW systems using machine learning. Telecommunication Systems, 64(2), 417–427.
Liang, X., et al. (2018a). Experimental study of wireless monitoring of human respiratory movements using UWB impulse radar systems. Sensors, 18(9), 3065.
Liang, X., et al. (2018b). Ultra-wideband impulse radar through-wall detection of vital signs. Scientific Reports, 8, 13367.
Liang, X., et al. (2018c). An improved algorithm for through-wall target detection using ultra-wideband impulse radar. IEEE Access, 5(99), 22101–22118.
Liang, X., et al. (2018d). Improved denoising method for through-wall vital sign detection using UWB impulse radar. Digital Signal Processing, 74, 72–93.
Liang, X., et al. (2018e). Ultra-wide band impulse radar for life detection using wavelet packet decomposition. Physical Communication, 4(4), 1–20.
Liang, X., et al. (2018f). Through-wall human being detection using UWB impulse radar. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2018(46), 1–17.
Liu, L., Liu, Z., & Barrowes, B. (2011). Through-wall bio-radiolocation with UWB impulse radar—Observation, simulation and signal extraction. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 4(4), 791–798.
Liu, L., et al. (2014). Numerical simulation of UWB impulse radar vital sign detection at an earthquake disaster site. Ad Hoc Networks, 13(1), 34–41.
Lv, H., et al. (2016). Improved detection of human respiration using data fusion based on a multistatic UWB radar. Remote Sensing, 8(9), 773.
Mak, J. C. C., Bois, A., & Poon, J. K. S. (2016). Programmable multiring butterworth filters with automated resonance and coupling tuning. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 22(6), 1–9.
Marple, L. (1999). Computing the discrete-time “analytic” signal via FFT. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 47(9), 2600–2603.
Mercuri, M., et al. (2013). Optimized SFCW radar sensor aiming at fall detection in a real room environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE biomedical wireless technologies, networks, and sensing systems, Austin, TX, USA (pp. 4–6).
Mercuri, M., et al. (2013). Analysis of an indoor biomedical radar-based system for health monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 61(5), 2061–2068.
Naishadham, K., & Piou, J. E. (2008). A robust state space model for the characterization of extended returns in radar target signatures. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 56(6), 1742–1751.
Nezirovíc, A., Yarovoy, A., & Ligthart, L. (2010). Signal processing for improved detection of trapped victims using UWB radar. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 48(4), 2005–2014.
Nijsure, Y., et al. (2013). An impulse radio ultrawideband system for contactless noninvasive respiratory monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 60(6), 1509–1517.
Park, B. K., Boric-Lubecke, O., & Lubecke, V. M. (2007). Arctangent demodulation with DC offset compensation in quadrature Doppler radar receiver systems. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 55(5), 1073–1079.
Ren, L. (2015). Noncontact multiple heartbeats detection and subject localization using UWB impulse doppler radar. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 25(10), 690–692.
Ren, L., et al. (2016). Phase-based methods for heart rate detection using UWB impulse Doppler radar. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 64(10), 3319–3331.
Singh, A., et al. (2013). Data-based quadrature imbalance compensation for a CW Doppler radar system. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 61(4), 1718–1724.
Vu, V. T., et al. (2010). Detection of moving targets by focusing in UWB SAR theory and experimental results. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 48(10), 3799–3815.
Wang, S., et al. (2015). A novel ultra-wideband 80 GHz FMCW radar system for contactless monitoring of vital signs. In Proceedings of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, Milan, Italy (pp. 4978–4981).
Wang, Y., Liu, Q., & Fathy, A. E. (2012). Simultaneous localization and respiration detection of multiple people using low cost UWB biometric pulse Doppler radar sensor. In IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium digest, Montreal, QC, Canada (pp. 1–3).
Wang, Y., Liu, Q., & Fathy, A. E. (2013). CW and pulse-Doppler radar processing based on FPGA for human sensing applications. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 51(5), 3097–3107.
Wang, J., et al. (2014a). Noncontact distance and amplitude-independent vibration measurement based on an extended DACM algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 63(1), 145–153.
Wang, G., et al. (2014b). A hybrid FMCW-interferometry radar for indoor precise positioning and versatile life activity monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 62(11), 2812–2822.
Wang, Z., et al. (2018a). Cooperative RSS-based localization in wireless sensor networks using relative error estimation and semidefinite programming. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2018.2880991.
Wang, Z., et al. (2018b). A grid-based localization algorithm for wireless sensor networks using connectivity and RSS rank. IEEE Access, 6(1), 8426–8439.
Wójcicki, K., et al. (2008). Exploiting conjugate symmetry of the short-time Fourier spectrum for speech enhancement. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 15, 461–464.
Wu, S., et al. (2016). Improved human respiration detection method via ultra-wideband radar in through-wall or other similar conditions. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 10(3), 468–476.
Zhang, Z. (2013). Human-target detection and surrounding structure estimation under a simulated rubble via UWB radar. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 10(2), 328–331.
Zhuge, X., & Yarovoy, A. (2011). A sparse aperture MIMO-SAR based UWB imaging system for concealed weapon detection. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 49(1), 509–518.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Science and Technology on Electronic Test and Measurement Laboratory (614200102010617, 614200103010117, 614200105010217), and China Electronics Technology Group Corporation Innovation Fund (KJ1701008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, X., Zhang, H., Lu, T. et al. An improved signal processing algorithm for VSF extraction. Multidim Syst Sign Process 30, 1811–1827 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-019-00629-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-019-00629-8